Find Degrees Of Freedom Formula
Di: Samuel
Two methods to calculate interaction effect SS AB Method 1. Calculate the ANOVA statistics: Compute the Sum of Squares Between (SSB), Sum of Squares Within (SSW), and Sum of Squares Total (SST). Since the hypothesized value is 0, we do not need to subtract it from the statistic. Thus, we can get the SS AB as 1620. K-1 (Where k is the category) To compare two observations, you can use the formula:
Degrees of Freedom
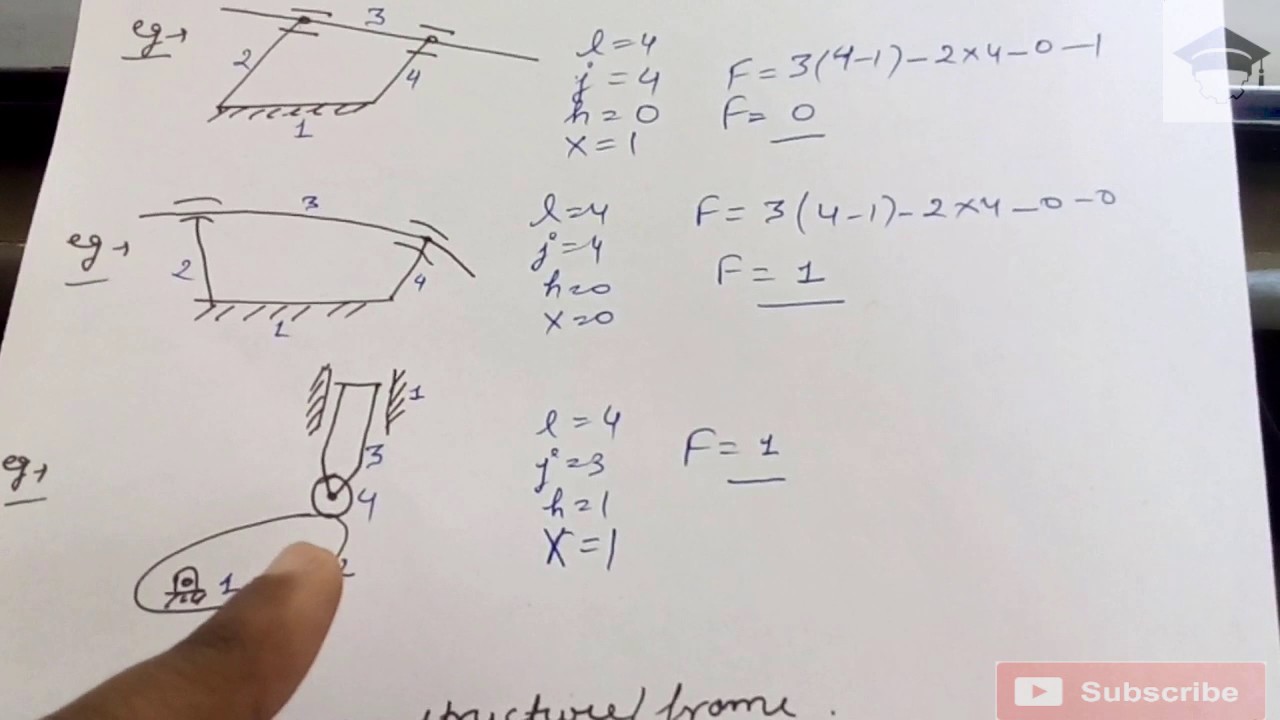
To calculate degrees of freedom in Excel, first, ensure that your data is correctly organized. The reason that Grubler’s formula does not apply is that the joint constraints are not independent.In this frame structure, we can look at each node individually to evaluate the total number of degrees of freedom in our system: Nodes A and B.The formula to calculate the degrees of freedom for Welch’s t-test takes into account the difference between the two standard deviations. Our sample size is 25.Degrees of Freedom formula.Next, we’ll calculate the degrees of freedom: df = n 1 + n 2 – 2 = 40 + 38 – 2 = 76.
Two-Way ANOVA: Formulas and Calculation by Hand
We’ll need the degrees of freedom. To use the table, you need to know three things: The degrees of freedom (df): For Pearson correlation tests, the formula is df = n – 2. In the one population case the degrees of freedom is given by df = n – 1. At this point, we need to apply the restriction that the deviations must sum to zero. In other words, we work with the deviations from mu estimated by the deviations from x-bar. n n is equal to the number of atoms within the molecule of interest.Thus, mu is replaced by x-bar in the formula for sigma.Degrees of freedom (physics and chemistry), a term used in explaining dependence on parameters, or the dimensions of a phase space., SStr, SSE) are calculated, they are divided by corresponding DF to get Mean Squares (e.If the p-value that corresponds to the test statistic t with (n-1) degrees of freedom is less than your chosen significance level (common choices are 0. If you are using statistical software, the DF will be displayed and if it isn’t . The comparison of two population means is very common. Therefore, a 1-sample t-test uses a t-distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom. MStr, MSE), which are the variance of the corresponding quantity. For the results of a one sample t-test to be valid, the following assumptions should be met: Now we’ve got all the necessary information to calculate the . The critical value is chosen so as to achieve a pre-determined size, as follows:
Degree of Freedom
Degrees of freedom problem, the problem of controlling motor movement given abundant degrees . Significance level (α): By convention, the significance level is usually . SS AB =8345 – 5445- 1280 =1620.

6 Degree of freedom.Formula to calculate degrees of freedom. In ANOVA analysis once the Sum of Squares (e.One degree of freedom is spent estimating the mean, and the remaining n-1 degrees of freedom estimate variability. Conversely, multiple linear regression must estimate a parameter for every term you choose to include in the model, and each one consumes a degree of . Where: DOF is the degree of freedom. cannot translate (displace) either .The degrees of freedom for the chi-square are calculated using the following formula: df = (r-1)(c-1) where r is the number of rows and c is the number of columns. The number of independent pieces of information that go into the estimate of a . Or, you could be conservative and calculate the degrees of freedom by using the smaller of n 1 – 1 or n 2 – 1. Step 7: Look at a table that relates t values to the probability that the differences between data sets is due to chance to find where the t value for the degrees of freedom (v) calculated lies Step 3: Calculating Degrees of Freedom Using Excel Formulas. The degree of freedom for SS AB is calculated as .
where: df – Degrees of freedom. The degree of freedom concept is used in kinematics to calculate the dynamics of a body. The position of a single railcar (engine) moving . cannot translate (displace) horizontally or vertically and cannot rotate because of the fixed end supports at those locations. N is the number of values in a data set.The degrees of freedom formula was developed by Aspin-Welch. Considering the situation that there are several gas molecules (A) in a container. This page titled 7.In statistics, the degrees of freedom are used to define the number of independent quantities that can be assigned to a statistical distribution. Compute the F-statistic (F = MSB / MSW).Degrees of freedom for the standard uncertainty, \(u\), which may be a combination of many standard deviations, is not generally known. Now that you know what degrees of freedom are, the next step is how to find it.The degrees of freedom (DF) are the number of independent pieces of information. The degrees of freedom for nonlinear molecules can be calculated using the formula: 3N − 6 (2) (2) 3 N − 6.Step 2: Organizing Your Data in Excel.
Degrees of Freedom
Degrees of freedom
How to find degrees of freedom – formulas.
Degrees of Freedom
We can calculate the interaction effect of SS AB using the following formula. In this case, you’ll need to use its formula. SS AB =SS M – SS A – SS B.The degrees of vibrational modes for linear molecules can be calculated using the formula: 3N − 5 (1) (1) 3 N − 5.Grubler’s formula would tell us that this mechanism has zero degrees of freedom, but that’s wrong; it still has one degree of freedom, just like the four-bar. Example: Calculate the degrees of freedom of the following data set. It implies that degrees of freedom is equivalent to the number of values in a data set minus 1, and appears like this: \[d_{f} = N-1\] Where N represents the number of values in the data set (sample size). This number typically refers to a positive whole number that indicates the lack of restrictions on a person’s ability to calculate missing factors from statistical problems. Calculating Degrees of Freedom for T-Tests: For a t-test, there are two types of degrees of freedom to . Here, we’ll outline two common scenarios – calculating degrees of freedom for a t-test and for regression analysis. You don’t really need to use the formula, as the TI-83 calculator can calculate the degrees of freedom for you. (Total free DOFs = 0) Node C.
Number of Vibrational Modes in a Molecule
4 – Two-Way ANOVA Summary Table.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/degrees-of-freedom-c87f4f95d13043da80a0735bd773d948.jpg)
The degrees of freedom formula is used in numerous statistical tests, such as the t-test and ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), to ensure an appropriate distribution for test statistics and critical values for . It is important in the analysis of systems of bodies in mechanical engineering, structural engineering, aerospace engineering, robotics, and other fields. In this case, the degrees of freedom is approximated by the Welch-Satterthwaite formula .Degrees of Freedom Formula. The degrees of freedom formula varies depending on the statistical test type being performed.01) then you can reject the null hypothesis. The degree of freedom formula is.
ANOVA (Analysis of variance)
Degrees of freedom (statistics), the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary.
Degrees of Freedom and Sample Size: How to Determine the
Related Articles. If the two samples have the same standard deviations, though, then the degrees of freedom for the Welch’s t-test will be the exact same as the degrees of freedom for the Student’s t-test. However, the following are the equations for the most common ones: 1-sample t-test: df = N – 1. 2-sample t-test . Very different means can occur by chance if there is great variation among the individual samples. The following procedure should be followed . Degrees of freedom are often broadly defined as the number of observations (pieces of information) in the data that are free to vary when estimating statistical parameters.By the species approach, we have \(s = 4\), \(r = 2\), and \(P=2\); the number of degrees of freedom from these values is \begin{equation} F = 2 + s – r – P = 2 \tag{13. Thus the degree of freedom is given by. 19, 17, 16, 14, 12. Here r is the number of rows and c is the number of columns in the two way table of the values of the categorical variable. The p-value from F-score is given by the following formulae, where we let cdf F,d1,d2 denote the cumulative distribution function of the F-distribution, with (d 1, d 2)-degrees of freedom: Left-tailed F-test: p-value = cdf . [1] Estimates of statistical parameters can be based upon different amounts of information or data.Third, we need to specify the properties of the sampling distribution to find the p value. In other words, DOF defines the number of directions a body can move. The number of degrees of freedom for independence of two categorical variables is given by a simple formula: ( r – 1) ( c – 1). Excel doesn’t have a built-in formula to calculate degrees of freedom . If we add up the degrees of freedom for the two samples we would get df = (n1 – 1) + (n2 – 1) = n1 + n2 – 2. You can find the critical value in a chi-square critical value table or using statistical software. In the Wald test, the null hypothesis is rejected if where is a pre-determined critical value . Testing whether joint constraints are independent is not an easy task, and we won’t pursue it .When, on the next page, we delve into the theory behind the analysis of variance method, we’ll see that the F-statistic follows an F-distribution with m−1 numerator degrees of freedom and n−m denominator degrees of freedom.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. If the observed chi-square test statistic is greater than the critical value, the null hypothesis can be rejected.Step 6: Calculate the degrees of freedom (v) for the whole data set (remember the formulae for this will not be given in the exam): v = (n 1 – 1) + (n 2 – 1). This formula gives a pretty good approximation of the more complicated formula above. However, if we consider R number of constraints restricting the molecules from moving freely, then the degrees of freedom decrease (due to restriction being an . You will need separate columns for each variable or group you are working with.The degree of freedom for SS B is also 2-1=1.There are various ways to calculate degrees of freedom in Excel, depending on the type of analysis being conducted. Hence, we have 24 DF. However, it’s an important point to note, that the formula you use relies on the statistical test you’re conducting.8} \end{equation} If we wish to calculate \(F\) by the components approach, we must decide on the minimum number of substances we could use to prepare each phase . The first step is to compute the statistic, which is simply the difference between means. Lastly, we’ll plug in the test statistic and degrees of freedom into the T Score to P Value Calculator to find that the p-value is 0. One Sample t-test: Assumptions. The rigid body has 6 DOF in space but due to formation of linkage one or more DOF is lost due to the presence of constraint on the body.Degrees of freedom (statistics) In statistics, the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary.For example, the degrees of freedom formula for a 1-sample t test equals N – 1 because you’re estimating one parameter, the mean.This is a simple extension of the formula for the one population case.Calculating degrees of freedom is a straightforward formula: DOF = N – 1. For instance, for the t-test with one sample, the degrees of freedom formula is N – 1, as only one parameter is estimated, whereas the t-test with two samples requires two estimated parameters, which is why the formula is N – 2. For example, an estimate of the variance based on a sample size of 100 is based on more information than an estimate of the variance based on a sample .The denominator of this formula is the degrees of freedom. Therefore, four numbers has the freedom to vary as long as the mean remains the same. N – denotes the total number of subjects/values. To complete the table, you need to need to calculate the degrees of freedom of cells (dfcells = (k1 × k2)– 1) although there’s no place in the table to include this information. Therefore, we’ll calculate the P-value, as it appears in the column labeled P, by comparing the F-statistic to an F .Degree of Freedom is defined as the minimum number of independent variables required to define the position of a rigid body in space.2: Degrees of Freedom is shared under a Public Domain license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by David Lane via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. Since this p-value is not less than our significance level α = 0. Read on to learn more about this topic and to understand why this formula . And C is the column of the table. Let’s start: .
One Sample t-test: Definition, Formula, and Example
A difference between the two samples depends on both the means and the standard deviations. The total number constraints cannot be zero as the body has to be fixed at some place to make the linkage possible. The statistical formula to find out how many degrees of freedom are there is quite simple.How to find degrees of freedom on a calculator. Thus, degrees of freedom are n-1 in the equation for s below: Standard deviation in a population is:
How to calculate degrees of freedom in excel
Then, the gross total of degrees of freedom is given by N or f = 3A. The size of the test can be approximated by its asymptotic value where is the distribution function of a Chi-square random variable with degrees of freedom.Step 2: Find the critical value of t. The ratio of MStr to MSE is the observed F (F .This depends on the statistical test that is used to calculate the degrees of freedom.
What Are Degrees of Freedom in Statistics?
For this reason, the two parameters d 1 and d 2 are also called the numerator and denominator degrees of freedom.In physics, the degrees of freedom (DOF) of a mechanical system is the number of independent parameters that define its configuration or state. N is sample size.For this calculation, we will make the three assumptions specified above.
Welch’s t-test: When to Use it + Examples
It’s a formula used in AP Statistics. The Satterthwaite formula is: Calculate the Degrees of Freedom (dfB, dfW, dfT). You can find the critical value of t (t*) in a t table.Step 3: Find the critical chi-square value.


We’ll use a two-tailed test, which is the standard.Chi-square independence test : You can refer it is x² = ∑ (Oi – Ei)²/Ei.

The degrees of freedom for a 1-sample t-test is n – 1. And in this step, we’ll look at the popular ones. If DOF > 0 It’s a Mechanism.State the general formula for degrees of freedom in terms of the number of values and the number of estimated parameters; Calculate s 2; Some estimates are based on more information than others. You need to known two numbers to find the critical value: The degrees of freedom (df): For a chi-square test of independence, the df is (number of variable 1 groups − 1) * (number of variable 2 groups .You had 7-1 = 6 days of “hat” freedom—in which the hat you wore could vary! That’s kind of the idea behind degrees of freedom in statistics. The goodness of fit test formula is : DF = (r – 1) (c – 1) Here, R is a row of table. Calculate the Mean Squares Between (MSB) and Mean Squares Within (MSW). To calculate degrees of freedom for a 2-sample t-test, use N – 2 because there are now two parameters to estimate. This is particularly troublesome if there are large components of uncertainty with small degrees of freedom.
- Finanzamt 2 Leipzig – Finanzamt in Sachsen » Leipzig » Leipzig II
- Filzstifte In Deutsch – Filzstifte: Hochwertige Modelle für verschiedenste Einsatzgebiete
- Fire Tablet Alle Dateien Übertragen
- Firmware Update Router _ How To Update Router Firmware? [Automatic and Manually]
- Filzwolle Anleitung Tasche Kostenlos
- Final Fantasy 14 Monthly Fee – Monthly Fee ? :: FINAL FANTASY XIV Online General Discussions
- Finanzplatz Hessen Nachhaltigkeit
- Firefox Javascript Entfernen | Passwortverwaltung
- Finanzen Net Aktiendepot | Das Musterdepot vom Experten Ingmar Königshofen
- Final Fantasy Xiv Luftangriff – Final Fantasy XIV: Dungeon Guide
- Finanzfluss Sparen Und Investieren
- Find Ellipsoidal Height From Orthometric
- Firefox Für Os X 10.11.6 | OS X El Capitan
- Firewall Status Überprüfen – Ports testen: Offene Ports mit einem Port-Check prüfen