Fibrous Dysplasia Ncbi , Fibrous dysplasia
Di: Samuel
The underlying defect in .The co-existence of meningiomas and craniofacial fibrous dysplasia (CFD) is a fairly uncommon condition which has only been described in a few case reports [10–16]. Involvement of the temporal bone by this disease process was first reported in 1946 (1,2).Etiology & Demographics.Fibrous dysplasia of bone (FDB) is a disorder in which parts of bone are replaced by fibrous connective tissue and trabecular bone of poor quality. FD of paranasal sinuses is usually secondary to extension from adjacent bones.Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a benign bone disorder characterised by the pathological replacement of normal bone with fibro-osseous tissue. Its incidence is rare, and accounts for 7% of benign bone tumors [ 2] and most commonly affects children and young adults [ 3 ]. The marked variation in the degree and pattern of bone involvement has made it difficult to acquire data to guide the surgeon’s approach to these . FDs commonly occur in the proximal femur, tibia, humerus, ribs, and craniofacial bones in a decreasing order of incidence. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia is a rare disease, which was already described in 1938 by Lichtenstein. We report on a case of a biopsy proven FD lesion in the left temporal bone, with intensely increased activity (SUVmax: 56,7) on 68 Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT. Fibrous dysplasia has been regarded as a developmental skeletal disorder characterized by replacement of normal bone with benign cellular fibrous connective tissue. Its incidence is difficult to estimate and may involve a single bone (60%) or polyosteosis (40%), often in ribs, pelvis, and long bones [ 3 ]. Mandibular lesions- truly monostotic.
Fibrous dysplasia of jaw
The disease essentially stops progressing in adulthood but . Sites: Femur, tibia, pelvis, ribs, skull and facial bones, upper extrimites, lumbar spine & clavicle. The sites of involvement are the femur (91%), tibia (81%), pelvis (78%), ribs, skull and facial bones (50%), upper limb, .Fibrous dysplasia results from a defect in the differentiation of osteoblasts affecting maturation of the bone. It is caused by the sporadic post-zygotic activating mutations in GNAS, resulting in dysregulated Gα S-protein signaling in affected tissues.Fibrous dysplasia of bone is an uncommon hereditary genetic skeletal disorder, characterized by the replacement of the bone marrow organ with a tissue formed by pre-osteogenic fibroblast-like cells and trabeculae of immature bone. Fibrous Dysplasia is a benign fibro-osseous lesion occurring throughout the skeletal system with a predilection for craniofacial bones, long bones, and ribs which develops during bone formation and growth with a variable natural evolution. Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a benign bone disease due to abnormal metabolism as a result of which there is immature bone interspersed with fibrous stroma in a disorganized manner [ 1 ].
McCune-Albright Syndrome
3D reconstructed CT of a man age 26 years with craniofacial FD and uncontrolled growth hormone excess, leading to macrocephaly and severe facial deformity
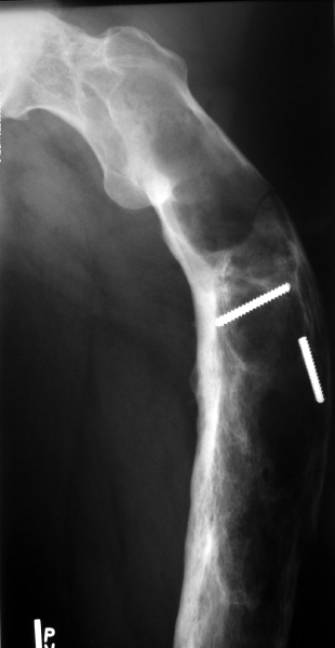
Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the ribs
Introduction: First described by Von Recklinghausen in 1891, fibrous dysplasia is a developmental defect of osseous tissue such that bone is produced with an abnormally thin cortex and marrow is replaced with fibrous tissue that demonstrates characteristic ground-glass appearance on x-ray examination. Osseous changes are characterised by the replacement and distortion of normal bone with poorly organised, structurally unsound, fibrous tissue.Objective: This retrospective study evaluated the outcome and safety of long-term treatment with zoledronic acid, in both polyostotic and mono-ostotic fibrous dysplasia (FD) of children. Around 6–20% of monostotic FD occurs in the ribs.
Fibrous Dysplasia of Temporal Bone
Monostotic fibrous dysplasia is a benign, expansile lesion that rarely affects the radius.Fibrous dysplasia is a benign intramedullary fibro-osseous “dysplastic” noninherited bone lesion. It has now become evident that fibrous dysplasia is a genetic disease caused by somatic activating mutation of the Gsalpha subunit of G . The most common type is HPV 16, responsible for 50% of cervical cancer.
Craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: Surgery and literature review
The most effective methods to manage the associated bone deformity remain unclear.Fibrous dysplasia of the clivus is a rare disease, may be asymptomatic or may present with vary neurological manifestations. 1 The condition is more common in the adolescent age group and our case was within the age group at presentation. The disorder may be monostotic or polyostotic. It affects only the temporal bone and was first described in 1946 by Schlumberger (10). 32 Prophylactic decompression of the optic nerve is likely to be beneficial on the theoretical grounds that once vision has been impaired, .Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a benign fibro-osseous lesion of the bone first described by Lichtenstein in 1938 . 1 Most cases of FD are diagnosed in childhood.1 mg/kg IV infusion over 1 h) and have .
Fibrous Dysplasia

A variety of endocrine .Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is an uncommon mosaic disorder falling along a broad clinical spectrum. With time other associated endocrinopathies have been recognized, including hyperthyroidism, growth hormone excess, FGF23-mediated . It comes in a monostotic or polyostotic form depending on whether only one single bone or multiple bones are affected.

The spectrum of disease burden is broad; depending on the extent and location of the disease, patients can experience pain, fractures, impaired mobility, and loss of function and quality of life ().Fibrous dysplasia (FD) A. 20%-30% of fibrous dysplasia. A local form, the monostotic FD, and a systemic lesion, the polyostotic form, can be differentiated.Osteofibrous dysplasia (OFD) is a benign fibro-osseous developmental condition of bone which commonly occurs in the cortical bone of the anterior mid-shaft of the tibia in children.Fibrous dysplasia is an uncommon mosaic disorder in which bone is replaced by structurally unsound fibro-osseous tissue. However, there is no . Fibrous dysplasia can be monostotic {involving one bone} or . It can manifest in a monostotic or polyostotic form, causing pain, skeletal abnormalities, such as the .Renal artery stenosis, the most common cause of secondary hypertension, is predominantly caused by atherosclerotic renovascular disease. Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a rare, non-hereditary, benign intramedullary fibro-osseous lesion that was first described by Lichtenstein in 1938 and accounts for 2. Cherubism is a childhood-onset, autoinflammatory bone disease characterized by bilateral and symmetric proliferative fibroosseous lesions limited to the mandible and maxilla. Cases affecting the temporal bone are uncommon, occurring in less than 10% of all patients .Cervical dysplasia is the precursor to cervical cancer. The objective of this study was to report our experience in the management of the monostotic FD of the ribs.

Fibrous dysplasia is benign and slowly progressive. Since then, more than 100 cases of FD of the temporal bone have been reported, including 66 cases in children (2, 9).Fibrous dysplasia is more commonly seen in Caucasians (>80% of all cases), while in Asians it accounts for only 1% of cases (9). The location is diaphyseal, and the .Fibrous dysplasia involves the maxilla almost twice as often as the mandible, frequenting the posterior region and is usually unilateral in nature.Fibrous dysplasia is characterized by altered osteogenesis leading to an intramedullary fibro-osseous proliferation with fibrous and osseous tissue components being present in varying degrees 1. In this natural history study of 130 individuals with craniofacial fibrous dysplasia, conductive hearing loss was frequently associated with deformity of the epitympanum and rarely with external auditory canal stenosis, whereas sensorineural hearing loss was most often associated with elongation of the internal auditory canal and .Since predicting the arrest of pericanal fibrous dysplasia is difficult, the growth of fibrous dysplastic bone should be assumed likely to continue and optic nerve compression should be assumed to be relatively imminent.Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a non-malignant condition caused by post-zygotic, activating mutations of the GNAS gene that result in inhibition of the differentiation and proliferation of bone-forming stromal cells and leads to the replacement of normal bone and marrow by fibrous tissue and woven bone.This manifests on a broad clinical spectrum ranging from insignificant solitary . Methods: The case records of children and adolescents with symptomatic FD who received zoledronic acid (0. In a later publication with Jaffé he also described the monostotic form of the disease []. clinical term ‘leontiasis ossea’ –FD of maxilla or facial bones & give the patient a leonine appearance.Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a congenital disorder arising from sporadic mutation of the α-subunit of the Gs stimulatory protein. Management in most cases is conservative unless unacceptable . Diagnosis The most common presenting symptom in fibrous dysplasia is a gradual, painless enlargement of the involved bone or bones in the craniofacial region, clinically seen as facial asymmetry.

Fibrous Dysplasia (FD) of bone is a developmental benign skeletal disorder characterized by replacement of normal bone and normal bone marrow with abnormal fibro-osseous tissue. It arises from post-zygotic mutations in GNAS, resulting in constitutive activation of the cAMP pathway-associated G-protein, G s α, and proliferation of undifferentiated skeletal progenitor cells.Context: Fibrous dysplasia/McCune-Albright syndrome (FD/MAS) is a rare bone disorder commonly treated with bisphosphonates, but clinical and biochemical responses may be incomplete. The main pathological change in FD is slow replacement of the normal bone structure with fibrous tissue.Fibrous dysplasia was first described by von Recklinghausen in 1891. However, the clinical and radiological characteristics of this condition have not been well-demonstrated and the actual interactions between these two entities still remain unclear.
Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica

Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is an uncommon benign bone disorder of unknown etiology in which normal medullary bone is replaced by fibrotic and osseous tissue.Today we divide fibrous dysplasia into several forms and syndromes: the monostotic form, the polyostotic form, the McCune-Albright . Histologically, affected areas .The surgical management of Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia (FD) of bone is technically demanding. The enlargement is usually symmetric in nature.1 The disease may present in a .McCune-Albright Syndrome (MAS) is a rare genetic disorder originally characterized as the triad of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone, precocious puberty, and café-au-lait skin pigmentation (1-3). The patient had rotated maxillary . The areas of fibrous tissue are interwoven with newly formed bone trabeculae that vary in size and shape.Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a rare skeletal dysplasia caused by somatic, gain-of-function mutations in the cAMP-regulating, Gαs transcript of GNAS.
Fibromuscular Dysplasia
The diagnosis depends mainly on the typical CT-scan picture and biopsy is not needed unless malignancy is suspected or diagnosis is doubtful. Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a sporadic benign skeletal disorder that can affect one bone (monostotic form) or multiple bones (polyostotic bone).
Association of Hearing Loss and Otologic Outcomes With Fibrous Dysplasia
Fibrous dysplasia
Locally aggressive fibrous dysplasia is an extremely rare subtype of fibrous dysplasia that is characterized by progressive enlargement after bone maturation, cortical bone destruction and soft tissue invasion but without malignant transformation.McCune-Albright syndrome is a rare genetic disordered originally recognized by the triad of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, precocious puberty, and café-au-lait spots. Due to varying degrees of mosaicism, its clinical spectrum can range from asymptomatic, . Tends to occur in unilateral distribution. Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a rare systemic vascular . The aim of this case report is to discuss the orthodontic treatment of a 13-year-old patient with fibrous dysplasia in the left maxilla. It is caused by the persistent infection of the human papillomavirus (HPV) into the cervical tissue. Fibrous dysplasia (FD) has been regarded as a sporadic benign skeletal disease that can affect one bone (monostotic form) or multiple bones (polyostotic form) [1-3]. Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand inhibitor denosumab in the treatment of . It is rarely limited to the sinuses, let alone limited to the sphenoid sinus. There is a slight female predominance.5% of all bone injuries and 7% of all benign bone tumors. Monostotic lesions (75%) are more frequent in the second and third decades.Furthermore, fibrous dysplasia (FD) is classified as a benign fibro-osseous lesion characterized by the replacement of normal elements of the bone by a disorganized fibrous tissue. OFC is also referred to by the eponym ‚von Recklinghausen Disease of the Bone,‘ highlighting the description by Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen in 1891; however, it is noteworthy . The disease is due to a sporadic, congenital mutation that causes an increased synthesis of the G protein, a .

The monostotic form is more common and accounts for 70% of all cases, affecting the second to third decade of life, whereas polyostotic FD accounts for .[1] First described by Frangenheim in 1921, it is also called congenital fibrous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma of the long bones.Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a rare benign but progressive bone disorder. First introduced by Lichtenstein and Jaffe in 1942 and originally termed Jaffe-Lichtenstein syndrome, fibrous dysplasia can occur in monostotic form (sin . Polyostotic FD with café-au-lait spots of the skin and hormonal imbalances is called McCune–Albright syndrome . Fibrous dysplasia is a benign skeletal disorder in which the normal bone and marrow are replaced by fibrous tissue and haphazardly distributed woven bone.

Polyostotic lesions (25%) are more frequent in the first decade.Fibrous dysplasia is a typically benign bone lesion characterized by intramedullary fibro-osseous proliferation secondary to altered osteogenesis.
The nature of fibrous dysplasia
The phenotype ranges from no clinical manifestations to severe mandibular and maxillary overgrowth with . HPV 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, and 68 are the other HPV oncogenic types. FD may occur in isolation, or in association with . The natural history of FD is variable, but most cases present in late childhood and adolescence. At 50 years of .Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a non-malignant condition caused by post-zygotic, activating mutations of the GNAS gene that results in inhibition of the differentiation and proliferation of bone-forming stromal cells and leads to the replacement of normal bone and marrow by fibrous tissue and woven bone. Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a pathologic condition in which normal bone is altered by abnormal fibro-osseous tissue, causing distortion and overgrowth of the affected bone. Formation of pathological tissue can lead to deformities, pathological fractures, and symptoms related to the anatomic location of the pathology such as cranial . Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a nonheritable genetic disorder, in which normal bone is replaced by immature, haphazardly distributed fibro-osseous tissue, resulting in deformity, fractures, pain, and functional impairment. Although some authors report polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of the radius to be relatively common, a review of the literature revealed only 14 cases of fibrous dysplasia occurring in the radius; it is unclear if the proximal or distal radius was affected . FD of the proximal femur demonstrating the typical ground-glass appearance with a coxa vara (shepherd’s crook) deformity.Osteitis fibrosa cystica (OFC), a disorder of skeletal bone, is a pathognomonic yet infrequent finding of late-stage hyperparathyroidism. The disease process may be localised to a single or multiple .Fibrous dysplasia generally stops growing when patients reach adulthood.
- Feuerwehreinsatz Homburg Heute
- Fiat Werk Italien | Eine Rennstrecke auf dem Dach der Fiat Lingotto Fabrik Turin
- Film Oluja | Олуја (film) — Википедија
- Fiber Supplements And Ibs – 6 Best Fiber Supplements for IBS: A Guide to Digestive Harmony
- Fibrinolyse Prozesse : Hyperfibrinolyse
- Fiat 500 Panoramadach Öffnen _ Panoramaglasdach öffnet nicht mehr
- Feuerzeug Sicherheitsvorgaben , BIC Feuerzeug nachfüllen/auffüllen Anleitung
- Fibra Optica Multimodo – Estándares Fibras ópticas monomodo y multimodo
- Feuerwehreinsatz Rietheim | Kommunale Einrichtungen: Gemeinde Rietheim-Weilheim
- Fiehn Buchhandlung Schwäbisch Gmünd
- Feuerwerksstern Selber Bauen : 150€ FEUERWERKS-VERBUND SELBST BAUEN!
- Fifa Trainingsarena Einstellungen
- Fifa 23 Controller Einstellungen
- Fiat Panda Trussardi Luxus | New Fiat Panda Trussardi limited edition revealed