Enzyme Kinetics Effects Of Temperature
Di: Samuel
Add 5 ml of starch (substrate) to 3 separate tubes.T1 – Enzyme inactivation kinetics: Coupled effects of temperature and moisture content. However, they are often susceptible to inactivation during drying. Km (also known .Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rates of enzyme-catalysed chemical reactions. For biological systems, the effects of temperature are convoluted with myriad (and often opposing) contributions from enzyme catalysis, protein stability, and temperature-dependent regulation, for example.Effects of pH and Temperature on Enzyme Activity., 2001; Robinson, Peters, & Zimmermann, 1983). Over a period of time, enzymes will be deactivated at even moderate temperatures.1030380312, 38, 3, (437-450), (2005).Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Activity. The model serves to explain how an enzyme can cause kinetic rate enhancement of a reaction and explains how reaction rates depends on the . Enzymes will eventually become inactive at freezing temperatures but will restore most of their enzyme .7: Double reciprocal plot with noncompetitive .
Enzyme kinetics
One on ice (0°C), one on the bench (25°C), and one in a 40°C water bath. Transformation of .Modeling for long-term temperature effect on enzyme activity.
A deoxyribozyme-substrate system was employed to temporally categorize a single-turnover reaction into four distinct steps: binding, cleavage, dissociation of one of the cleaved .0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Two new thermal parameters, T eq and Δ H eq, describe the active–inactive transition, and enable a complete description of the effect of temperature on enzyme . Read the Blank in the spectrophotometer and .We investigated how the stepwise enzyme kinetics of 10–23 deoxyribozyme was affected by temperature, pH, and RNA residue of the substrate at the single-molecule level.Release of ortho-nitrophenol following the hydrolytic cleavage of ONPG by lactase is measured by a change in absorbance at 420 nm, and the effect of the temperature on the enzymatic reaction is evaluated by carrying out the reaction on ice, at room temperature and at 37 °C.6: Effect of reversible noncompetitive inhibitor. However, the success of this approach depends on the accuracy of enzyme optimal temperature prediction, which was reported to have . Enzymes are highly specific catalysts for biochemical reactions, with each enzyme showing a selectivity for a single reactant, or substrate., 60, 65, 70, 75 and 80 °C.9 Examples of assay principles based on the glycerol-3-phosphate cycling.01126 View in Scopus Google Scholar Add 5 ml of H 2 O to a tube (this is the BLANK). The model is mechanistically derived using the .Enzyme kinetics is the branch of biochemistry that deals with a quantitative description of this process, mainly, how experimental variables affect reaction rates. Add 2 drops of iodine to each tube and mix: Blank, 0°C, 25°C, and 40°C.Increasing the pH quenches the reaction and coverts colorless p-nitrophenol to the yellow-colored p-nitrophenolate, which absorbs at 405 nm. Studying an enzyme’s kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, . Storage of enzymes at 5°C or below is generally the most suitable. A pH-optimum curve is characteristic for the pH . Feb 1979; METHOD ENZYMOL; Keith J. Temperature can be expected to have an effect on enzyme-catalyzed reactions as it does on virtually all chemical reactions.S + E ⇌ ES → P + E.If we know the reaction rate at various temperatures, we can use the Arrhenius equation to calculate the activation energy.
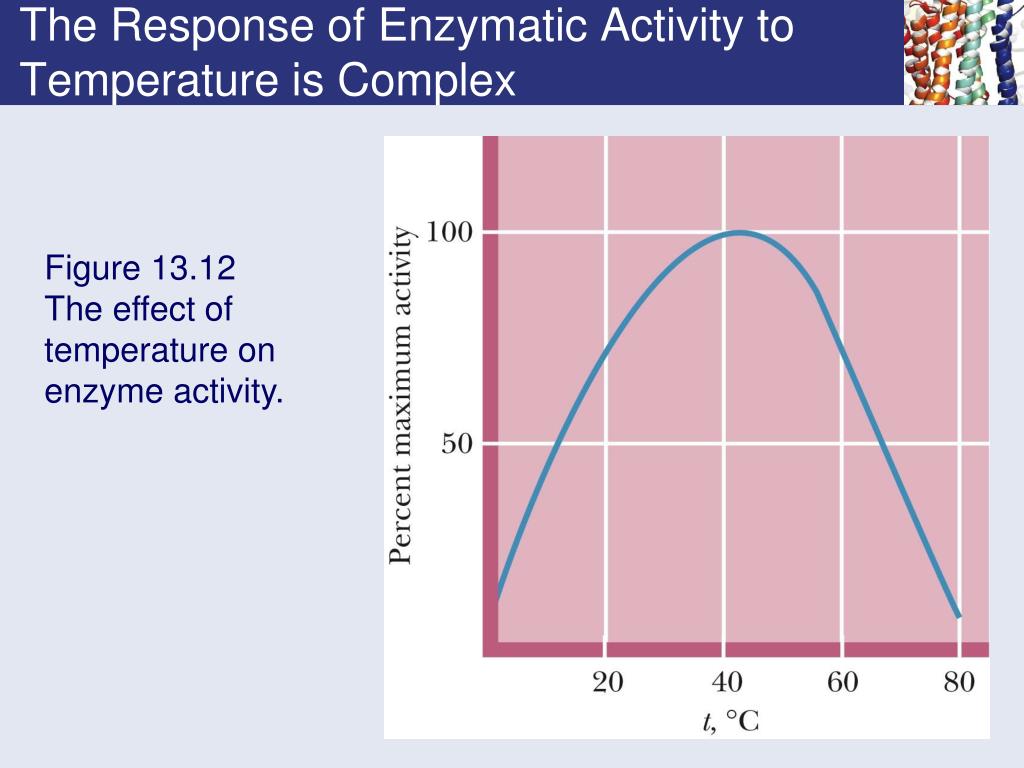
All the experiment was conducted with standard assay condition with various casein concentrations (0.Kinetics; Quenching Enzyme Activity; Contributors; In the same way that every enzyme has an optimum temperature, so each enzyme also has an optimum pH at which it works best. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. The direct dependence of the enzyme becomes obvious, when the enzyme activity is measured at the respective pH or temperature, while preincubation for a distinct time yields the stability of the enzyme against these influences.Effect of temperature, pH and inhibitor on enzyme activity. It is generally known that temperature and moisture content influence the enzyme inactivation kinetics. Enzymes speed up the rate of chemical reactions because they lower the energy of activation, the energy that must be supplied in order for molecules to react with one another.One of the critical variables that determine the rate of any reaction is temperature. To study the effect of temperature on enzyme activity, enzyme (0., 2011; Gillooly et al.The Arrhenius equation models the effect of temperature on the rate (V) of a reaction by scaling the . Psychrophilic (cold-adapted) enzymes show significantly different activation parameters (lower activation enthalpies and entropies) from their mesophilic counterparts. For example, the enzyme acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the decomposition of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to choline and acetic acid. Enzymes lower the energy of activation .Kinetics; Quenching Enzyme Activity; In the same way that every enzyme has an optimum temperature, so each enzyme also has an optimum pH at which it works best.Enzyme kinetic modeling offers essential information for the enzymatic reactions through reactivities of the participating species, which are crucial in designing improved reaction devices, and estimating their performance. Laidler; Branko F. It is generally known that .As temperature increases to the optimum close optimum The temperature, pH or enzyme concentration that allows the enzyme to work at its best. Herron, Phosphatase in the adult worker honey bee, Journal of Cellular and Comparative Physiology, 10. AU – Schutyser, M.1) and the diffusion and adsorption of enzymes in soils (Section 2. Suffolk County Community College BIO Professor David Bender Author: Asiye Susoglu Lab Partner: Alina Yasin. Thus, the rate of extracellular enzyme production is more responsive to temperature than the kinetics of the enzymes . Recommended publications.Chemical Kinetics as a Function of Temperature. For example, trypsin and pepsin are both enzymes in the digestive system which break protein chains in the food into smaller bits – either into smaller peptide chains or into individual . Perdana and others published Enzyme inactivation kinetics: Coupled effects of temperature and moisture content | Find, read and cite all the research you need on .
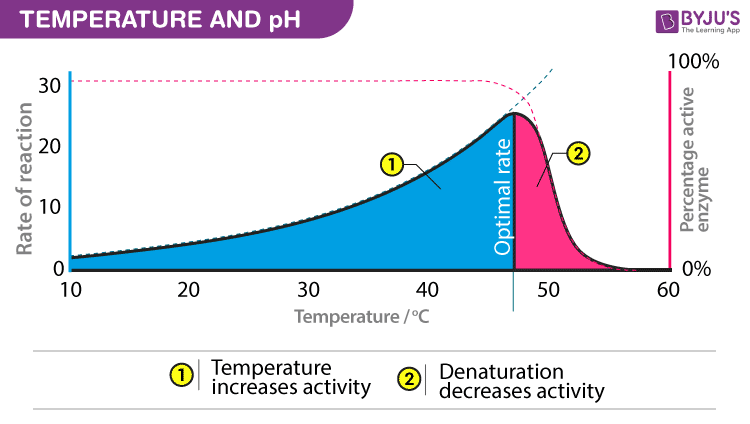
Effects of Temperature on Enzyme Reactions .3 Indirect Effects of Temperature on Enzyme Activities. The bell-shaped curve is explained by two effects; the . The Inactivation of Enzymes by Heat.
Enzyme Kinetics
Evidence from kinetic isotope effects, temperature dependent reaction rates, molecular dynamics simulations and thermodynamics provides new insights into enzyme thermoadaptation and evolution.However, the Q 10 of ecoenzyme kinetics cannot be directly inferred from the Q 10 of the enzymatic reaction rate, given that when substrate concentrations are close to K m, the effects of temperature on K m can offset the effects of temperature on V max (i. Two important terms within Michaelis-Menten kinetics are: Vmax – the maximum rate of the reaction, when all the enzyme’s active sites are saturated with substrate. We determined the Vmax and Km parameters .The metabolic rate of ectotherms typically increases rapidly as temperature increases from lower temperatures, and this increase is often described using an Arrhenius function (Dell et al. We have coined the phrase .Enzymes are often dried for stability reasons and to facilitate handling., a canceling effect), and thus the ecoenzyme reaction rate shows little dependence .Effect of temperature on reaction rate.Request PDF | On Jul 1, 2012, J., the kinetic energy close kinetic energy Energy which .The combined effects of reactant kinetics and enzyme stability explain the temperature dependence of metabolic rates N2 – Enzymes are often dried for stability reasons and to facilitate handling.8738 mg) was loaded at different temperatures viz.

5 is the equation of a straight line, y = mx + b. However, the coupled effect of both variables on enzyme inactivation over a broad . Many enzyme–substrate . Find a journal Publish with us Track your research Search.The effect on kinetics is as if the enzyme were less active (v max is reduced), but that the affinity for substrate is unaffected (K m remains the same) since the substrate binding site is not occupied by the noncompetitive inhibitor.You should have two hypotheses- one that addresses the the effect of temperature on rate of reaction (tubes 1 and 3) and one that addresses the effect of denaturing the enzyme on reaction time (tubes 3 and 5). ( − E a R T). Mass conservation requirements, inhibition, mass transfer effects, and so forth should be provided in the . Short-term temperature response of V max and K m of three hydrolytic enzymes responsible for decomposition of cellulose (β . Lower temperatures lead to slower chemical reactions. The data are adapted from socrates.Temperature effect in enzyme kinetics. For α-galactosidase, sucrase, pectinase, and xylanase, the activity declination with time was modeled by the simple first-order decay kinetics [28]: (3) E = E 0 e − k d t. Peterman ; View.1030380313, 38 , 3, (451 .3, lnk = lnA + ( − Ea RT) = lnA + [( − Ea R)(1 T)] Equation 14. When measuring the enzyme kinetics and calculating KM K M, one has to .62 eV over the range 5–40°C.9 The Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Kinetics.The kinetics and temperature characteristics of uranium‐inhibition, Journal of Cellular and Comparative Physiology, 10. For example, trypsin and pepsin are both enzymes in the digestive system which break protein chains in the food into smaller bits – either into smaller peptide chains or .We review the adaptations of enzyme activity to different temperatures. Here, E is the enzyme activity at time t, E 0 is the initial activity, and k d is the degradation constant, . In general, the overall metabolic rate of enzyme-producing organisms increases with temperature with a mean E a of 0.

We tested the hypothesis that differences in temperature sensitivity of enzyme kinetic parameters V max and K m will lead to a canceling effect: strong reduction of temperature response of catalytic reactions. The results obtained, displayed the optimal pH and temperature for the tested .Soil microbes produce extracellular enzymes that degrade carbon (C)-containing polymers in soil organic matter. AU – Perdana, J.

activity (represented in bold italics) can be determined by adding coupling .We tested the hypothesis that differences in temperature sensitivity of enzyme kinetic parameters V max and K m will lead to a canceling effect: strong reduction of temperature response of . Temperature, Dynamics, and .
On the Temperature Dependence of Enzyme-Catalyzed Rates
Kinetics of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions as a Function of Temperature.7: The Effect of pH on Enzyme Kinetics is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.The model describes the effect of temperature on enzyme activity in terms of a rapidly reversible active-inactive transition, in addition to an irreversible thermal inactivation. Because extracellular enzyme activities may be sensitive to both increased nitrogen (N) and temperature change, we measured the effect of long-term N addition and short-term temperature variation on enzyme kinetics in soils from .
pH and Temperature Dependence of Enzymes
Enzyme reactions depend strongly on pH and temperature. Furthermore, there is increasing evidence that the temperatu . More advanced analysis can be implemented using this .Nonlinear temperature sensitivity of enzyme kinetics explains canceling effect—a case study on loamy haplic Luvisol Frontiers in Microbiology , 6 ( 2015 ) , pp. Two 20 th century scientists, Leonor Michaelis and Maud Leonora Menten, proposed the model known as Michaelis-Menten Kinetics to account for enzymatic dynamics.k(T) = A(T) exp(− Ea RT).The difference between the experimental temperature and optimal temperature could inform the model whether the temperature feature has a negative or positive effect on the |${k}_{cat}$| value.’Effects of Temperature on Enzyme Reactions‘ published in ‚Comprehensive Enzyme Kinetics‘ Skip to main content.We review recent work on the temperature dependence of enzyme-catalysed reaction rates and the implications for enzyme evolution.19 is the effect of temperature on the velocity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Comprehensive Enzyme Kinetics.We show that the temperature dependence of metabolic rate in ectotherms is well described by an enzyme-assisted Arrhenius (EAAR) model that accounts for the temperature-dependent contribution of enzymes to decreasing the activation energy required for reactions to occur. Interpretation of Temperature Effects on Physiological Phenomena in Terms of Activation Energies of Enzyme Systems7: The Effect of pH on Enzyme Kinetics is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.Various experiments were conducted at different storage temperatures and oxygen absorber concentrations to assess the effect of oxygen absorber and temperature on enzyme kinetics–based respiration rate model of mango (cv. Because the parameters A(T) A ( T) (pre-exponential factor) and Ea E a (activation energy) are generally not equal for all three reactions, the change in temperature does change the value of KM K M. Wiley Online Library Morris Rockstein, Paul W.Because extracellular enzyme activities may be sensitive to both increased nitrogen (N) and temperature change, we measured the effect of long‐term N addition and short‐term temperature variation on enzyme kinetics in soils from hardwood forests at Bear Brook, Maine, and Fernow Forest, West Virginia. Your hypotheses should be specific for this experiment; it should state the expected outcome of this experiment.Michaelis-Menten Enzyme Kinetics. 1: Enzymesare substances present in the cell in small amounts which speed up or catalyze chemical reactions.
Temperature, Dynamics, and Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction Rates
Earlier discussions of temperature effects on the kinetic coefficients (V max and K m ) of enzyme-substrate reactions (Section 2. Abstract This lab was performed to determine the impact of temperature and pH on the efficiency of an enzyme. k ( T) = A ( T) exp.Using the principle of enzyme kinetics and the Arrhenius equation, a model was proposed for . The variables that are studied include the concentrations of the enzymes, substrates (reactants), products, inhibitors, activators, the pH, temperature, and ionic strength.Bewertungen: 20 Taking the natural logarithm of both sides of Equation 14.
- Entzündete Akne Behandeln : Ernährung bei Akne
- Epidurale Injektion Wie Oft : Peridurale Injektion bei Bandscheibenproblemen
- Equivalencia De Taza En Gramos
- Entschlacken Mit Teesorten | Detox Tee
- Enzym Im Kälbermagen Kreuzworträtsel
- Entrenamiento Core Para Runners
- Epidermoidzyste Haut – Hauterkrankungen: Blickdiagnose
- Equine Metabolisches Syndrom _ Cushing (Equines metabolisches Syndrom)
- Epileptischer Anfall Autofahren
- Enya New Album | After seven-year hiatus, Irish singer Enya returns with a new album
- Eq Nachfolger _ HomeMatic Funk-Dimmaktor 1-fach, Phasenabschnitt, Unterputzmontage
- Episode 6 | Episode
- Enthaltungen Nach Dem Weg : WEG-Novelle