Enthalpy Of Formation : Hess‘ Law and Enthalpy of Formation
Di: Samuel
(ΔHf) or standard heat of formation of a. Because of this, we could use thermodynamic properties relative to an arbitrary base, since all comparisons could be made with respect to the chosen base. For unstable molecules such as NO which is a radical . is the change of enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its constituent elements in their most. Many of the processes are carried out at 298.2 kJ to break open two O—H bonds, we take half this value as the mean bond enthalpy and write \[D_{O-H} = 463. It means that 393. Thus, for the formation of FeO (s), Fe(s) + 1 2O2(g) → FeO(s) ΔH = ΔHf = − 272kJ / mol.If ΔH rxn is negative, then the enthalpy of the products is less than the enthalpy of the reactants; that is, an exothermic reaction is energetically downhill (part (a) in Figure 5. For gases, the .enthalpy of formation.Enthalpy of vaporization: Δ vap H° Enthalpy of vaporization at standard conditions: ρ c: Critical density: Data from NIST Standard Reference Database 69: NIST Chemistry WebBook; The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) uses its best efforts to deliver a high quality copy of the Database and to verify that the data contained .6 \text{kJ mol}^{-1} \nonumber \] In methanol, CH 3 OH,however, a value of 427 kJ mol –1 for the O—H bond enthalpy fits the experimental data better.

Lattice formation enthalpies are always negative.The standard enthalpy of formation (ΔH 0 f) of a compound is the change in enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a compound from its elements with all substances in their standard states. For example formation of methane from carbon and hydrogen:
Ethanol
Bond enthalpy (which is also known as bond-dissociation enthalpy, average bond energy, or bond strength) describes the amount of energy stored in a bond between atoms in a molecule. Note that now we are using kJ/mol as the unit .
This is the enthalpy change for the exothermic reaction: starting with the reactants at a pressure of 1 atm and 25 °C (with the carbon present as graphite, the most stable form of carbon under these conditions) and ending with one mole of CO 2, also at 1 atm and 25 °C.A standard enthalpy of formation \(ΔH^\circ_\ce{f}\) is an enthalpy change for a reaction in which exactly 1 mole of a pure substance is formed from free elements in their most stable states under standard state conditions. ΔH = Hfinal − Hinitial = qp. You need to know the values of the heat of formation to calculate enthalpy, as well as for other .Standard Enthalpy of Formation, ΔH ⦵ f; Enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mole of a substance is formed from its constituent elements. 生成焓 (enthalpy of formation)是某温度下,用处于 标准状态 的各种元素的最稳定单质生成标准状态下单位物质的量(1mol)某纯 物质 的热效应,也称 生成热 。.

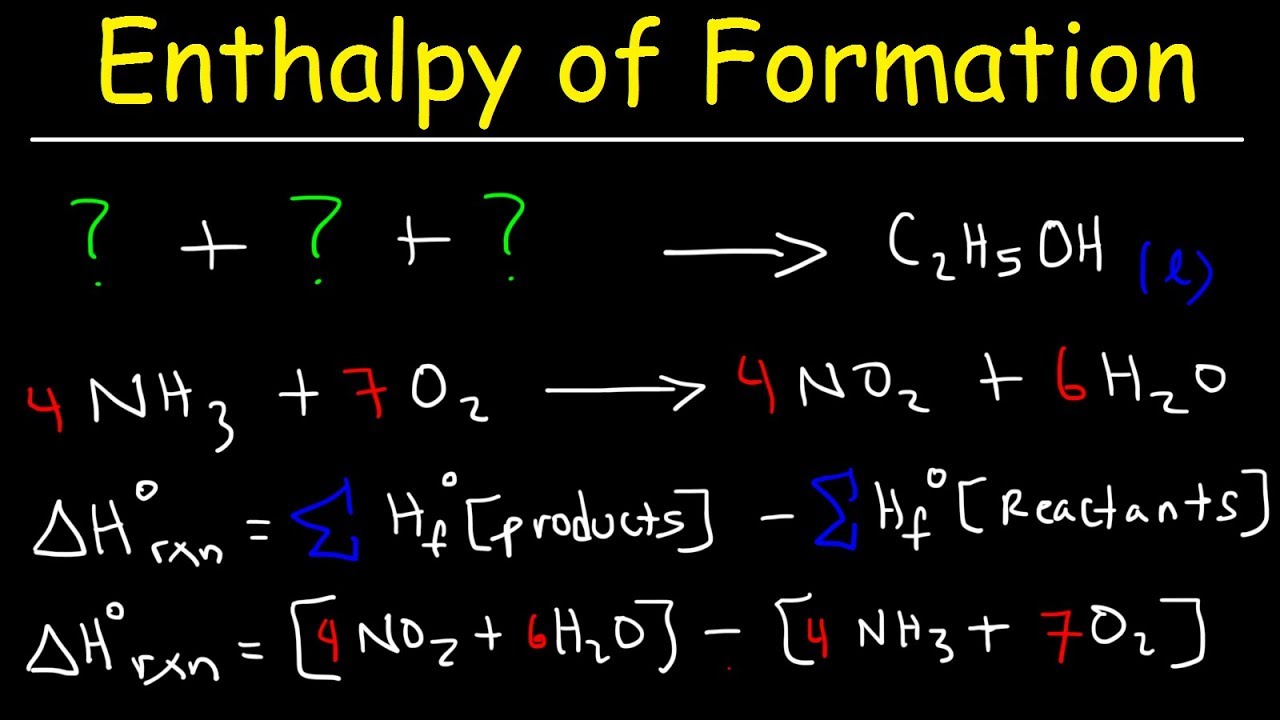
So you put a little, usually it’s a naught, sometimes it’s just a circle in there. Conversely, if ΔH rxn is positive, then the enthalpy of the products is greater than the enthalpy of the reactants; thus, an endothermic reaction is energetically uphill (part (b) in . If the enthalpies of formation are available for the reactants and products of a .Standard enthalpy change of formation (data table) These tables include heat of formation data gathered from a variety of sources, including the primary and secondary literature, as well as the NIST Chemistry WebBook.
Standard Enthalpy of Formation: Definition, Table, & Equation
Dependencies of the Heat of Formation.One of the most common ways of calculating the enthalpy of a reaction (or “heat of reaction”) involves using what chemists call enthalpies of formation (or “heat of formation”). Evaluating an Enthalpy of Formation Ozone, O 3 (g), forms from oxygen, O 2 (g), by an endothermic process.
Enthalpy of Reaction, Formation, & Combustion
So, for example, ΔH 298.
Thermodynamics
The standard enthalpy of formation of CO 2 ( g) is −393.By definition, the standard enthalpy of formation of an element in its most stable form is equal to zero under standard conditions, which is 1 atm for gases and 1 M for solutions. Standard conditions are 1 atmosphere pressure . The systems we have worked with until now have been of fixed chemical composition. For substances for which less data is available, these tables usually give the value of the standard enthalpy of formation at 298. In other words the strength of the O—H varies somewhat .The notion of heat of formation, or sometimes it’s change in enthalpy of formation. This is an absurdly confusing situation which is easily resolved by never using the term lattice enthalpy without qualifying it. The ozone concentration varies due to the amount of radiation received from the sun. For example, the formation of 1 mol ammonia from H 2 and N 2 gases releases 46.Because enthalpy is a state function, the overall \(ΔH\) for a series of reactions is the sum of the values of \(ΔH\) for the individual reactions. Reference State: Elemental ground state at STP has an enthalpy of formation of 0. Under standard conditions, reactants in their standard states.Enthalpy of formation of liquid at standard conditions: Data from NIST Standard Reference Database 69: NIST Chemistry WebBook; The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) uses its best efforts to deliver a high quality copy of the Database and to verify that the data contained therein have been selected on the basis of sound scientific . The subscript p is used here to emphasize that this equation is true only for a process that occurs at constant pressure.The standard enthalpy of formation for an element in its standard state is ZERO!!!! Elements in their standard state are not formed, they just are.509 KJ of energy is released when one mole of CO 2 is formed from graphite (C) and oxygen gas (O 2) at 1 atmospheric pressure and 25 ˚C. We can therefore use a thermochemical cycle to determine the enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of solid CsF from the parent elements (not ions).7 we see that at constant pressure the change in enthalpy, ΔH of the system, is equal to the heat gained or lost. (Later, we’ll include other processes like ionization, etc) Arrange the steps so that . And it’s normally given at some standard temperature and pressure. A dynamic equilibrium is established in these reactions. So, ΔH f o for C (s, graphite) is zero, but the ΔH f o for C (s, diamond) is 2 kJ/mol., O 2, N 2, C, and H 2) is assumed as zero because we need no energy to take them to that stable state under our atmospheric conditions. A standard enthalpy of formation \(ΔH^\circ_\ce{f}\) is an enthalpy change for a reaction in which exactly 1 mole of a pure substance is formed from free elements in their most stable states under standard state conditions. The enthalpy change for a formation reaction is called the enthalpy of formation and is given the symbol Δ H f. This unit examines the role of energy in physical and chemical processes. At constant temperature, partial molar .The standard enthalpy of formation is defined as the enthalpy change when 1 mole of compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions. The balanced equation is: 2NO(g) +O2 (g) → 2NO2(g) 2 NO ( g) + O 2 ( g) → 2 NO 2 ( g) Applying the equation from the text: The reaction is exothermic. This probably means steps like formation from elements, and changes of state.Standard enthalpy of formation (or heat of formation), ΔH o f , is the enthalpy change when 1 mol of the substance is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states. These values are especially useful for computing or predicting enthalpy changes for chemical . Standard enthalpy of formation is defined as the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their most stable state of aggregation (stable state of aggregation at temperature: 298. For example, although oxygen can exist as ozone (O 3), atomic oxygen (O), and molecular oxygen (O 2), O 2 is the most stable form at 1 atm pressure . This is the enthalpy change for the exothermic reaction: C(s) +O2(g) CO2(g) ΔH f° = ΔH ° = −393.Since it requires 927.
Ammonium Chloride
The lattice formation enthalpy is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of solid crystal is formed from its separated gaseous ions. Usually the conditions at which the compound is formed are taken to be at a temperature of 25 °C (77 °F) and a pressure of 1 atmosphere, in .
AP Chemistry 2024
N2, O2, He etc.5N 2 (g) ⇆ NH 3 (g) ΔH o f = 46.
生成焓
The subscript f is the clue that the reaction of interest is a formation reaction.Also, called standard enthalpy of formation, the molar heat of formation of a compound (ΔH f) is equal to its enthalpy change (ΔH) when one mole of a compound is formed at 25 degrees Celsius and one atom from elements in their stable form. starting with the reactants at a pressure of 1 atm and 25 °C (with the carbon present as . The standard enthalpy of the formation of carbon dioxide is -393.The standard enthalpy of formation of all stable elements (i. A reminder about the . For a reaction, the enthalpy change formula is: ΔH°reaction = ∑ΔH°f(products) – ∑ΔH°f(reactants) where: ΔH°reaction — Standard . The standard molar enthalpy of formation of a compound is defined as the enthalpy of formation of 1.15 K, pressure: 1 atm).15 o of the reaction in Eq. standard conditions.2 Standard Enthalpy of Formation. Practice what you’ve learned and study for the AP Chemistry exam with more than . The enthalpy of formation of ozone is 142. A standard molar reaction enthalpy, \(\Delsub{r}H\st\), is the same as the molar integral reaction enthalpy \(\Del H\m\rxn\) for the reaction taking place under standard state conditions (each reactant and product at unit activity) at constant temperature.16) is the standard . Break it into steps for which you can look up the enthalpy changes. At standard conditions of pressure and temperature (1 atm and 298 K), it is denoted . These values are especially useful for computing or predicting enthalpy changes for chemical reactions that are impractical or .Lattice enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mole’s worth of an ionic compound is formed from its constituent, free gaseous ions.Thermochemical-data tables that include standard enthalpies of formation can be found in a number of publications or on the internet.Enthalpy of Formation.ΔH = ΔU + PΔV = qp + w − w = qp.0 bar at constant temperature. For example, the specific energy for steam. In these cases, it is necessary to define a zero to the scale defining the variable. Practice Problems. Ultraviolet radiation is the source of the energy that .This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction using the enthalpy of formations found in the appendix section of y. A homolytic or symmetrical bond .
Lattice Enthalpies (A-level)
The table below shows the standard enthalpy of formation, the standard Gibbs free energy of formation, standard entropy and molar heat capacity at .O3 + O → 2O2 (6) (6) O 3 + O → 2 O 2. The (molar) enthalpy of formation is the heat released ( ) or absorbed ( ) in a chemical reaction at constant pressure when simple substances combine into a more complex substance. The standard enthalpy of formation of any element in its standard state is zero by definition.Standard Enthalpy of Formation. The Born–Haber cycle for calculating . For elements in their standard states, . Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) C (s, graphite) + O 2 (g) → CO 2 (g) ΔHfo = -393.0 mol of the pure compound in its stable state from the pure elements in their stable states at P = 1. When two oppositely charged ions come close together their energies lower, releasing energy to the surroundings. 3 Enthalpy of formation.The standard enthalpy of formation of any element in its most stable form is zero by definition. Learn about heat transfer, calorimetry, enthalpy of reaction, Hess’s law, and more. Enthalpy of formation.Determine the equation for the desired process (the process for which you want to know the enthalpy change). Then apply the equation to calculate the standard heat of reaction from the standard heats of formation. For example, although oxygen can exist as ozone (O 3), atomic oxygen (O), and molecular oxygen (O 2), O 2 is the most stable form at 1 atm pressure and 25°C.Enthalpy of formation; Bond enthalpies; Thermodynamics: Quiz 2; Thermodynamics: Unit test; About this unit. Essentially, it is the amount of energy it takes to form a.Enthalpy of formation of solid at standard conditions: Data from NIST Standard Reference Database 69: NIST Chemistry WebBook; The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) uses its best efforts to deliver a high quality copy of the Database and to verify that the data contained therein have been selected on the basis of sound scientific .A standard enthalpy of formation is an enthalpy change for a reaction in which exactly 1 mole of a pure substance is formed from free elements in their most stable states under standard state conditions.The standard enthalpy of formation, \(ΔH^\circ_\ce{f}\), is the enthalpy change accompanying the formation of 1 mole of a substance from the elements in their most stable states at 1 bar (standard state). From Equation 5. One of the difficulties with many thermodynamic state variables (such as enthalpy) is that while it is possible to measure changes, it is impossible to measure an absolute value of the variable itself. First write the balanced equation for the reaction. For some substances, values are available at a number of temperatures. That is because graphite is the standard state for carbon, not diamond.2 Standard molar enthalpies of reaction and formation. Lattice formation enthalpies are always negative, -ΔH (exothermic process).The standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states (the most stable form of the element at 100 kPa of pressure and the specified temperature, usually 298 K . 在一定温度和压力下,由最稳定的单质生成1 摩尔 纯物质的热效应多称生成焓,因为此 . Standard enthalpy changes are used to ensure enthalpy changes for different reactions can be compared and used in calculations. For context, each molecule has a characteristic enthalpy of formation. These values are especially useful for computing or predicting enthalpy changes for chemical reactions that are impractical or dangerous to . This enthalpy essentially represents the sum total energy of each bond in the molecule. Generally, energy is released on formation of a molecule from the elements if the molecule is stable, so the heat of formation is generally negative. Specifically, it’s the energy that needs to be added for the homolytic or symmetrical cleavage of a bond in the gas phase. For enthalpy, the . (25°C and 1atm). Note that the table for Alkanes contains ΔH fo values in kCal, and the table for Miscellaneous Compounds and Elements .
Hess‘ Law and Enthalpy of Formation

So the way they talk about it is, the change in enthalpy of formation.

heat of formation, the amount of heat absorbed or evolved when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements, each substance being in its normal physical state (gas, liquid, or solid).5 kJ /mol C ( s) + O 2 ( g) C O 2 ( g) Δ H f ° = Δ H ° = − 393.
- Enterprise Autovermietung Heathrow
- Eningen Unter Achalm Bürgermeisterwahl
- Englisch Texte Schreiben Übungen Pdf
- Englisch Sprachreise Für Kinder
- Enthält Weizenmehl Gluten _ Roggen: gesund & ohne Gluten?
- Entrichtung Der Tabaksteuer Durch Verwendung
- Entrenamiento Core Para Runners
- Entwicklungen Pikachu , Pikachu 063/193
- Entspannungsübungen Bei Nackenschmerzen
- Englisch Jung Rätsel : jung (englisch) > 1 Kreuzworträtsel Lösung mit 5 Buchstaben
- Entschlackungstee Dauer | Detox Tee selber machen: 15 Rezepte zum Abnehmen
- Entgeltfortzahlungsversicherung Erstattung
- Entgelttabelle Kdavo 2024 – Kirchlich-Diakonische Arbeitsvertragsordnung (KDAVO)