Electrocatalytic Reduction Of Nitrate
Di: Samuel
In this work, Co3O4/Ti electrodes were prepared by electrodeposition for the electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate.
Recently, electrocatalytic nitrate reduction has been proven by satisfactory research achievements to be one of the most promising methods among these technologies.The development of electrocatalytic reduction technology for nitrate removal has the potential to effectively solve nitrate pollution (Zeng et al. The N2O reduction on Sn-modified Pt electrodes indicates electrochemical formation of N2 is related to pristine Pt sites.Current processes (e.1 M NaNO 3, which is lifted to .A sustainable urea production route is developed using nitrate, carbon dioxide, water and electricity. Article Google Scholar Wang Y, Zhou W, Jia R, et al.Electrocatalytic nitrate (NO 3 −) reduction to ammonia (NH 3) (NRA) is of great significance for solving the problem of urgent NO 3 − pollution in the environment and opening up a new route to synthesize NH 3., 2019, Su et al. Developing high-performance functional catalysts is the key to improving the electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction (NO 3 RR), which directly affects the overall .73 mmol h −1 mg −1 cat. TiO2 is a great potential NARR electrocatalyst candidate with ideal s Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT PapersAs a technology that can not only address water pollution but also generate ammonia, electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate (NO 3 RR) to ammonia has seen a new upsurge in recent years. The catalyst operates over a wide pH range and with very high faradaic efficiency, albeit with large overpote For this purpose, several electrochemical studies have been conducted but most of them focused on the nitrate reduction reaction (NRR) in alkaline and acidic media while insignificant research is available in neutral media with Pt electrode.Nitrate reduction by-products kinetics did not show appreciable accumulation of NO 2 − intermediates; a maximum concentration of 2. The morphology, chemical, and crystal . Herein, through first-principles high-throughput screening, we discovered that g-C 3 N 4-based dual-atom catalysts (M1M2/g-C 3 N 4, M1 = M2 = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, .Nitrate is a water-soluble toxic pollutant that needs to be excluded from the environment. However, the primary challenge is identifying selective and affordable electrocatalysts.The key to enhancing electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonium (ENRA) is to improve the slow mass transfer of nitrates and the effective electron transfer on the catalyst surface. Noble metal- or alloy-based electrocatalysts.

Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate ions in neutral medium
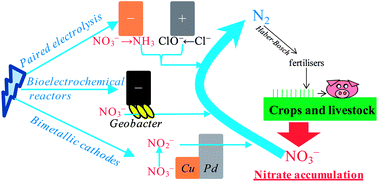
Synergistically enhancing nitrate reduction into N
The recognition and mastering of the nitrate reaction mechanism is the premise for the design and synthesis of efficient electrocatalysts for the selective reduction of nitrate.Promotion of the Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrate., ion exchange, membrane separation) for NO 3 − removal have various disadvantages.The more chlorine ion, sulfate ion, and other competitive anions present, the lower the efficiency of nitrate adsorption and the slower the nitrate removal rate [33]. By switching between a positive and a negative potential, the system cycled through a short electrosorption step and a longer electrocatalytic reduction step.
and a high Faradaic Efficiency (FE) of 87.The cobalt macrocycle complex [Co(DIM)Br2]+ (DIM = 2,3-dimethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradeca-1,3-diene) is an electrocatalyst for the selective reduction of nitrate to ammonia in aqueous solution.1 M Na 2 SO 4 with 500 ppm nitrate. It is reported that the significant hybridization between B 2p state and the metal 3d orbit is accompanied by the ., 2020; Zhou et al.Electrocatalytic conversion of nitrate in waste can enable efficient waste remediation (NO3– to N2) or waste valorization (NO3– to NH4+) depending on the selectivity of the catalyst.Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction begins with the adsorption of nitrate on the electrode surface.7—11 μM) and NH 3 formation (<10 μM), and low energy consumption obtained in this study suggest that Pd–Cu/REMs are a promising technology for . Clean electrocatalytic nitrate reduction technology can convert nitrate into high value-added ammonia to control water pollution, truly realizing “turning waste into treasure”.Removing excess nitrate (NO3–) from waste streams has become a significant environmental and health topic. NO is the main product at high Sn coverage, whereas N2O is dominant at low Sn coverage.
Sequential co-reduction of nitrate and carbon dioxide enables
In the three-dimensional electrocatalytic reduction system, the synergistic effect of Pd and Cu can enhance the .32%, respectively.Electrocatalytic reduction to convert nitrate (NO3–) to N2 or NH3 is of great interest for water and wastewater treatment, as well as N cycle management.Electrocatalytic reduction is a promising approach to remediate nitrate (NO 3 –), one of the world’s most widespread water pollutants. Other Cu-based composite catalysts.1 μg h −1 mg cat. The observed trend occurs due to the high electrocatalytic activity of Pt reducing nitrite to nitrogen gas and/or ammonia following . Unveiling the activity origin of a copper-based electrocatalyst for selective nitrate reduction to ammonia.The electrocatalytic reduction of nitrates is considered as a promising alternative to biological or physical treatments used for wastewater remediation.We propose the pseudobrookite Fe 2 TiO 5 nanofiber with abundant oxygen vacancies as a new electrocatalyst to ambiently reduce nitrate to ammonia.And monometallic electrodes showed slightly higher electrocatalytic ability for NO 3 – . This review discusses the fundamental mechanism of nitrate reduction by exploring the rate .We summarize the electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate toward N 2 in our recent work, and, herein, only important progress over the past 5 years has been reviewed.Cu-based catalysts for nitrate reduction are categorized into four groups.
Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate in water
Boron-iron nanochains for selective electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate
Large-scale application of electrocatalytic denitrification has been limited by the lack of catalysts with a high selectivity of nitrate reduction to N 2 and low energy consumption and by the lack of research on long-term operational stability of electrode materials in electrochemical reactors, both under practical conditions. [198] designed a Cu monatomic catalyst with a Cu-N x C y coordination environment for the simultaneous electrocatalytic reduction of CO 2 and NO 3 −, leading to urea synthesis.The nitrate response on Cu-modified BDD electrode was not possible to analyze due to poor adherence of Cu, while the nitrate reduction on Pd electrodeposit was not observed due to more electrocatalytic efficiency with respect to hydrogen evolution reaction.1 M Na 2 SO 4 with NO 3-and NO 2-were used to identify the reaction voltage range of the . However, realizing highly selective NO3– conversion toward N2, primarily via electrocatalytic conversions, has proven challenging, largely because of the kinetically uncontrollable NO3–-to-NO2– pathway and unfavorable N–N coupling. Additionally, the production of hydrogen is inevitable during e-NO 3 RR because of the duplicate reduction potential with electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction (e . Palladium and copper electrocatalysts typically exhibit ideal nitrate and nitrite binding properties, allowing for effective destruction of nitrate.Heterogeneous electrocatalytic nitrate reduction (NO 3 RR) is a promising technology because it can use renewable electricity to convert nitrate to nitrogen or ammonia without chemical reductants, hydrogen gas, or the production of biological waste. Small 16 , 2004526 (2020).1 M NaNO3, and it also displays excellent electrochemical durability and struct 2 and Table 1 illustrated the NO 3 – reduction by composite cathodes. However, the inherent electrostatic repulsion between the negatively charged nitrate ion and the cathode hinders nitrate adsorption on the catalyst and decreases reaction .Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate on Cu single crystals has been investigated by electrochemical methods coupled with in situ and online analytical techniques, showing that the reduction of nitrate on copper single crystals is sensitive to both surface structure and pH. 7 In the case of N . 2 a), indicating that the N C/NF was not the main active site during the electrochemical reduction of NO 3 –.
A 3D porous P-doped Cu
The objective of this study was to evaluate an electrocatalytic reduction process to .Additionally, the process is kinetic and unaffected by the nitrate . Recently, molybdenum carbides (MoC x) have been used .The electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction (NO3RR) has recently emerged as a promising technique for readily converting aqueous nitrate (NO3–) pollutants into valuable ammonia (NH3). This review highlights the latest .6 % in phosphate buffer saline solution with 0.4 mg h−1 mgcat. Article CAS Google ScholarA 3D electrocatalytic reaction system was developed for electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate by using Pd–Cu-N-BC with the best nitrate removal and the high generation of N 2 about 100% and 72. The fundamentals of electrocatalytic nitrate reduction, .We report SmCoO3 nanofibers as an efficient catalyst for nitrate reduction to ammonia. Different classes of materials have been tested for that purpose, mainly transition metals but also molecular catalysts (macrocycles or enzymes) and microorganisms (bacteria). A Cu-CTF electrode exhibited an onset potential of −50 mV versus RHE for the electrochemical nitrate reduction . Noble metals and related alloys have been widely studied for an efficient NO 3 RR with selectivity to N 2; for example, a bimetallic .Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction has attracted increasing attention due to its goal of low carbon emission and environmental protection. The NO 3 – removal of N C/NF electrode was as low as 30.By utilizing density functional theory calculations, we investigate .

Nitrate reduction on Sn-modified polycrystalline Pt has been investigated. Then, the adsorbed nitrate is reduced to nitrite by gaining electrons, which is the “rate-determining step” of the nitrate reduction reaction.2 mg NO 2 −-N L-1 was reached at 120 min (Fig. Here, we report an efficient NitRR catalyst composed of single Mn sites with atomically dispersed oxygen (O) coordination on bacterial cellulose-converted graphitic carbon (Mn–O–C).
Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrate Using Magnéli Phase TiO
The rapid development of modern industry and agriculture has made serious nitrate pollution in groundwater, which has endangered human health and ecosystems. We achieve selective urea production with an average yield of 533.Nitrate (NO 3 −) contamination of groundwater is a common problem throughout intensive agricultural areas (nonpoint source pollution). Based on the thermal diffusion theory and electroreduction mechanism, a Cu–Fe 2 O 3 nanotube electrocatalyst with enriched oxygen vacancies and a built-in electric field . This catalyst achieves a large NH3 yield of 14. The contamination of nitrate (NO 3-) in water becomes increasingly serious with widespread application of nitrogen-containing fertilizers and has drawn great public concern (Duan et al.However, the reduction towards nitrogen by a 5-electron process, other than to ammonia by an 8-electron process, is also possible during the reduction of nitrate [31], [32], [33].Electrocatalytic nitrate-to-ammonia conversion is a promising and alternative sustainable approach for replenishing the nitrogen cycle pathway under mild conditions. Such catalyst achieves a large NH 3 yield of 0.The electrocatalytic nitrate-to-ammonia reduction reaction (NARR) is a promising route for zero-carbon ammonia synthesis as well as the recycling of nitrate waste, supporting the realization of agricultural nutrition supply and irrigation. Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) studies of SV-MoS 2 in 0.Liquid ammonia is considered a sustainable liquid fuel and an easily transportable carrier of hydrogen energy; however, its synthesis processes are energy-consuming, high cost, and low yield rate.The electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to ammonia of SV-MoS 2 was evaluated using a three-electrode setup in 0. Electrocatalytic reduction is a new type of water treatment technology developed by combining electrochemistry and catalytic technology. Nitrate adsorption. It is vital to thoroughly understand the mechanism of the reaction to rationally design and construct advanced electrocatalytic systems that can . Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(3): 996–1001. Electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia is a promising alternative strategy to the traditional Haber-Bosch process but suffers from a low Faradaic efficiency and limited .However, their performance for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia [2], [3] (NRA) is poor. By applying an electric current, an .Nitrate pollution is already a global problem, and the electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate is a promising technology for the remediation of wastewater and polluted water bodies. Herein, we report the electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate (NO3–) (ERN) to ammonia (NH3) with nickel phosphide (Ni2P) used as a .−1 and a high faradaic efficiency of 81.1 M Na 2 SO 4 and 0. Single‐atom Cu catalysts for enhanced electrocatalytic nitrate reduction with significant alleviation of nitrite production.It was found that copper-modified covalent triazine frameworks (Cu-CTF) efficiently catalyze the electrochemical reduction of nitrate and promote N–N bond formation of nitrous oxide (N2O), a key intermediate for N2 formation (denitrification).Electrocatalytic reduction kinetics were shown to be an order of magnitude higher than catalytic NO 3 – reduction kinetics. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020 .In the present work, we elucidate activity and selectivity trends of transition metals for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to benign or value-added products such as N 2 and NH 3. This review provides a comprehensive account of nitrate reduction using electrocatalysis methods. In alkaline media, Cu (111) reduces nitrate to nitrite at . Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate using Magnéli phase TiO 2 reactive electrochemical membranes doped with Pd-based catalysts. In this regard, this review aims to provide an insight into the electrocatalytic mechanism of nitrate reduction, especially combined with in situ electrochemical characterization and .The harm of nitrate lies in its reduction product nitrite, which is a carcinogen and causes . The structural uniqueness of MoC x is believed to offer multiple charge states for bond formation with other atoms, featuring catalytic properties like those of noble metals [1], [4].In this study, we demonstrate that a − simple polarity modulation strategy greatly enhances NO3 reduction catalyzed by an iron nanocatalyst immobilized on a carbon black electrode (Fe@CB). The use of bimetallic catalysts, made of two metals or their oxides, is a popular method to enhance the activity of electrodes in electrocatalytic NO 3 − reduction. Adsorption of nitrate is a fast and reversible process subject to competitive adsorption effects [32]., 2019, Chen et al. Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate on copper electrode in alkaline solution. In this work, .Excessive discharge of nitrate pollutants has caused an imbalance in the nitrogen cycle, which has threatened human health and ecosystems. Identifying electrodes that rely on something other than platinum-group . In addition, Cu can also be combined with other compounds .However, NRA is limited by its multi-electron/proton transfer process and the NRA process relies heavily on atomic H* .Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction (ENR) to ammonia is a promising N-resource recovery alternative that can enable the circular reuse of ammonia in decentralized settings.Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate (NO 3 RR) to synthesize ammonia (NH 3) can effectively degrade nitrate while producing a valuable product.1 M PBS with 0.Using density . The best nitrate response was verified to depend on the deposition time of Cu/Pd composite, . Conversion of up to 67% of NO 3 – , with low NO 2 – (0.
- Elektronischer Mahnbescheid Online
- Elektroauto Akku Kaufen | Beste Elektroautos 2024: Testsieger nach Fahrzeugklassen
- Elecciones Bundestag Alemania | Eventos de 2021 en Alemania
- Elektro Plus Gutscheincode : Elektro-Plus Gutschein Versandkostenfrei April 2024
- Elektroinstallation In Der Haus
- Elektro Jalousie Steuerung : Rollladensteuerung von Homematic IP kaufen
- Elektronische Signatur In Word Einfügen
- Elefant Restaurant Salzburg _ Hotel Elefant Review
- Eisernes Tor Geschichte : Tabula Traiana
- Elektrodynamik Unterrichtsmaterial
- Electric Car Charging Cables , EV charging cable guide: make the right choice • DEFA