Dna Replication Principles | Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)- Principle, Steps, Applications
Di: Samuel
The effect of such local unwinding at one place in a DNA has the effect . Sign in Register. Michael O’Donnell 1, Lance Langston 1 and.Principle of PCR.große, komplex aufgebaute Viruspartikel (350 x 270 nm) im Lichtmikroskop sichtbar.The accurate copying of genetic information in the double helix of DNA is essential for inheritance of traits that define the phenotype of cells and the organism. At this stage, each chromosome is made of two sister chromatids and is a duplicated chromosome.
Semiconservative Replication Of DNA
, the Central Dogma. The core machineries that copy DNA are conserved in all three domains of life: bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Under the best growing-conditions, DNA replication starts immediately after cell division in most cells (Wang et al.Primers – Just like during DNA replication, Taq polymerase needs a free 3′ end to begin synthesis of the new DNA. Guest user Add your university or school.The general nature of the DNA replication machinery is outlined, but also points out important and key differences. For example, during DNA replication, strands of DNA at the site of replication get unwound at the rate of 6000 rpm by an enzyme called helicase.This page titled 5. + Author Affiliations. In human cells, this means that 46 chromosomes (or molecules of DNA) replicate to form 92 chromosomes.Katherine Harris.
A Brief Comparison Between In Vivo DNA Replication and In
University ; High School. [ 1] PCR is performed on thermocycler and it involves three main steps: (1) denaturation of dsDNA template at 92–95°C, (2) annealing of primers at 50–70°C, and (3) extension of dsDNA molecules at approx.Join Agnee PRO Batch – https://unacademy. A thorough characterisation of the dynamic activation of origins within initiation zones is hampered . Allerdings kommen auch einige Unterschiede aufgrund der Größe und Komplexität der jeweiligen Genome (=Gesamtheit der DNA) vor.DNA replication ensures the accurate duplication of the genome at each cell cycle. In conservative replication, the two original DNA strands, known as the parental strands, would re-basepair with each other after being used as templates to synthesize new strands; and the two newly-synthesized . Genetic code: 1 to 1 relationship between a codon (specific sequence of 3 bases) and 1 amino acid.In the S phase (synthesis phase), DNA replication results in the formation of two identical copies of each chromosome— sister chromatids —that are firmly attached at the centromere region,as shown in Figure 24. 2 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York 11724. Helicase opens the DNA and replication forks are formed. 1 The Rockefeller University and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, New York, New York 10065.Dispersive replication.By reviewing the existing concepts ranging from the old principles to the newest ideas, the book gives readers an opportunity to learn how the classical replication principles are now being modified and new concepts are being generated to explain how genome DNA replication is achieved with such high adaptability and plasticity. Thus, the ends of the chromosomes are replicated. Books; Discovery. DNA helicase unwinds the DNA and continues to break hydrogen bonds at the replication forks.Fundamental Aspects of DNA Replication 220 final phase, which goes from the end of DNA replication until the completion of cell-division (Wang & Levine, 2009). Description of DNA Replication.Format: eTextbook Before a cell enters the process of mitosis, its DNA replicates itself.A) Circular bacterial chromosomes contain a cis-acting element, the replicator, that is located at or near replication origins. G-Quadruplexes and DNA Replication . Auf diese gehen wir aber in einem späteren Abschnitt genauer ein.
Mechanisms and Controls of DNA Replication in Bacteria
The accurate copying of genetic information in the double helix of DNA is essential for inheritance of traits that define the phenotype of cells and the organism. Bruce Stillman 2.Chromosome-wide late replication is an enigmatic hallmark of the inactive X chromosome (Xi). This means that the only time chromosomes look like an “X” is after DNA replication has taken place and the chromosomes have condensed. During S phase, tens of thousands of replication origins throughout the vertebrate genome are activated according to a spatiotemporal program.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)- Principle, Steps, Applications
The enzyme joins nucleotides to synthesize a new complementary strand of DNA .1: Structure and Function – Nucleic Acids . The DNA of every human being on the planet is 99.lol dna dna replication webquest part interactive dna discovery use any of the links below to complete the interactive dna discovery activity on the. 1: The two strands of DNA are complementary, meaning the sequence of bases in one strand can be used to create the correct sequence of bases in the other strand. Since replication of the chromosome takes more time than thatcom/goal/neet-ug/YOTUH/subscribe/ZQ4MHCYWPS?referral_code=SEEPLIVEJoin Seep Pahuja’s class and Complete Biology syll.A complex process whereby the ‘parent’ strands of DNA in the double helix are separated, and each one is copied to produce a new (daughter) strand. But before undergoing cell division, a cell must first copy the genetic information contained in the cell nucleus – its DNA. Question: This hydroxyl group on the sugar plays an important role during DNA replication and the technologies that use principles of DNA replication, like PCR or Sanger sequencing, because it needs to be present for DNA synthesis to proceed. We reveal how specialized replication-coupled mechanisms rapidly assemble newly synthesized DNA into nucleosomes, while the complete restoration of chromatin organization including histone marks is a continuous process taking . After replication, the chromosomes are composed of two linked sister chromatids (Figure 5). Chromosomal DNA. This is because The nitrogenous bases (adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine) react with . It is an epigenetic mechanism that occurs by the addition of a methyl (-CH3) group to DNA, thereby often modifying the function of the genes and affecting gene expression. The DNA replication in prokaryotes takes place in the following place: The two strands of DNA unwind at the origin of replication.a simple (in principle) templating mechanism for replicating DNA into two identical copies.Der allgemeine Ablauf der Replikation ist bei Prokaryoten ( Bakterien und Archaeen ) und Eukaryoten sehr ähnlich. Only DNA (and in some instances RNA when, as in the case of the genomes of RNA viruses, it is used as a repository of genetic information) are self-complementary and hence capable of being replicated. Like other DNA polymerases, Taq polymerase assembles nucleotides only in the 5′ to 3′ direction. 50 % werden verpackt.

Produktion: ca.Before we get into replication, let’s take a step back and look at the three core genetic processes, a. The most widely characterized DNA methylation process is the covalent . DNA replication is called semiconservative, because each new DNA molecule is made up of one original and one new strand. The extent to which firing of individual DNA replication origins within initiation zones is spatially stochastic or localised at defined sites remains a matter of debate. Single-strand DNA-binding (SSB) proteins prevents the . DNA replication is an important basic concept to understand how cells replicate on the DNA level.

G-Quadruplexes and DNA Replication Origins
The human body produces billions of new cells every day.
DNA Replication
In this chapter, we describe how cells duplicate the genome while maintaining its proper organization into chromatin. During the majority of the cell’s life, chromosomes are . The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase, which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs) to form the growing DNA chain.

In this chapter, we will examine the process of replication. After describing the basic mechanism of DNA replication, we discuss the various techniques researchers have used to achieve a more .
Mode of DNA replication: Meselson-Stahl experiment
Primers in a PCR reaction are man-made synthetic segments of DNA that match the ends of the sequence that the scientist is interested in amplifying.Principle of DNA Fingerprinting.Once the 3′ end of the lagging strand template is sufficiently elongated, DNA polymerase can add the nucleotides complementary to the ends of the chromosomes. Central Dogma of genetics/info flow in cells -Foundation Figure: Flow of Genetic Info p 1. Equal copies of the DNA pass into the daughter cells at the end of mitosis.
![]()
Welcome to Studocu Sign in to access the best study resources. DNA will be replicated and passed . A thorough characterisation of the dynamic activation of .A Brief Comparison Between In Vivo DNA Replication and In Vitro PCR Amplification In principle, PCR generates large quantities of DNA from a minute amount of nucleic acid starting material using a methodology similar to (but much simpler than) that seen in living cells.You may recall some of our early discussion on DNA, and about base complimentarity and the directionality of the . Primers – Just like during DNA replication, Taq polymerase needs a free 3′ end to begin synthesis of the new DNA.Principles of DNA Replication. Molekulare Virologie, 2003. DNA replication I: Enzymes and mechanism is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by .DNA Replication Process in Prokaryotes. There were three models of replication possible from such a scheme: conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive. This article outlines the general nature of the DNA replication . In just 6-8 hours a cell is able to copy its entire genome.As discussed in Chapter 3, DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. Human genome possesses numerous small non-coding but inheritable sequences of bases which are repeated many times.
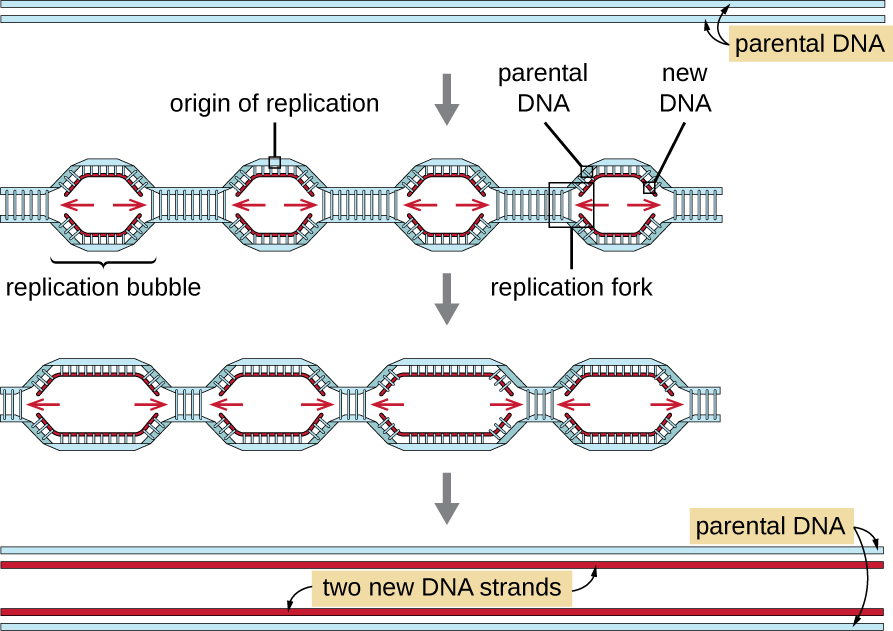
The other three categories of .DNA replicates in the S phase of interphase. Skip to document. This process is said to be ‘semiconservative’ because one strand from each parent is conserved and remains intact after replication has taken place. How it is established and what it represents remains obscure. In this model, each individual strand is a patchwork of original and .Models for bacterial (A) and eukaryotic (B) DNA replication initiation. Function: DNA base sequence encodes information for amino acid sequence of proteins. For living cells, in vivo DNA synthesis is dependent upon a well defined but . With the development . Below is a step-by-step process of how DNA replication occurs. A new type of review journal, featuring comprehensive collections of expert review articles on important topics in the molecular life sciences.Replication of the human genome initiates within broad zones of ∼150 kb.2) coat the single strands of DNA near the replication fork to prevent the single-stranded DNA from winding back into a double helix. They do not code for .Bewertungen: 4
Origins of DNA replication
This process, called DNA replication, must occur before a cell can produce two genetically identical . Virusreplikation: im Cytoplasma, in „factory areas“ (Virusfabriken) in kernlosen Zellen möglich Beginn der DNA-Replikation: ca 1-2 h p. Download it once and read it on your Kindle device, PC, phones or tablets.Models of Replication. In order to synthesize both strands of the DNA double helix, a forward and a reverse primer . Because of the complementarity of the two strands, having one strand means that it is possible to recreate the other strand. In cycle 2, both double . The DNA is coated by the single-strand binding proteins around the replication fork to prevent rewinding of DNA. The genome-wide mapping of origins in several model systems has identified . Hartnell College. Use features like bookmarks, note taking and highlighting while reading DNA Replication: . The core idea is INFORMATION.i) The replicator recruits initiator proteins in a DNA sequence-specific manner, which results in melting of the DNA helix and loading of the replicative .
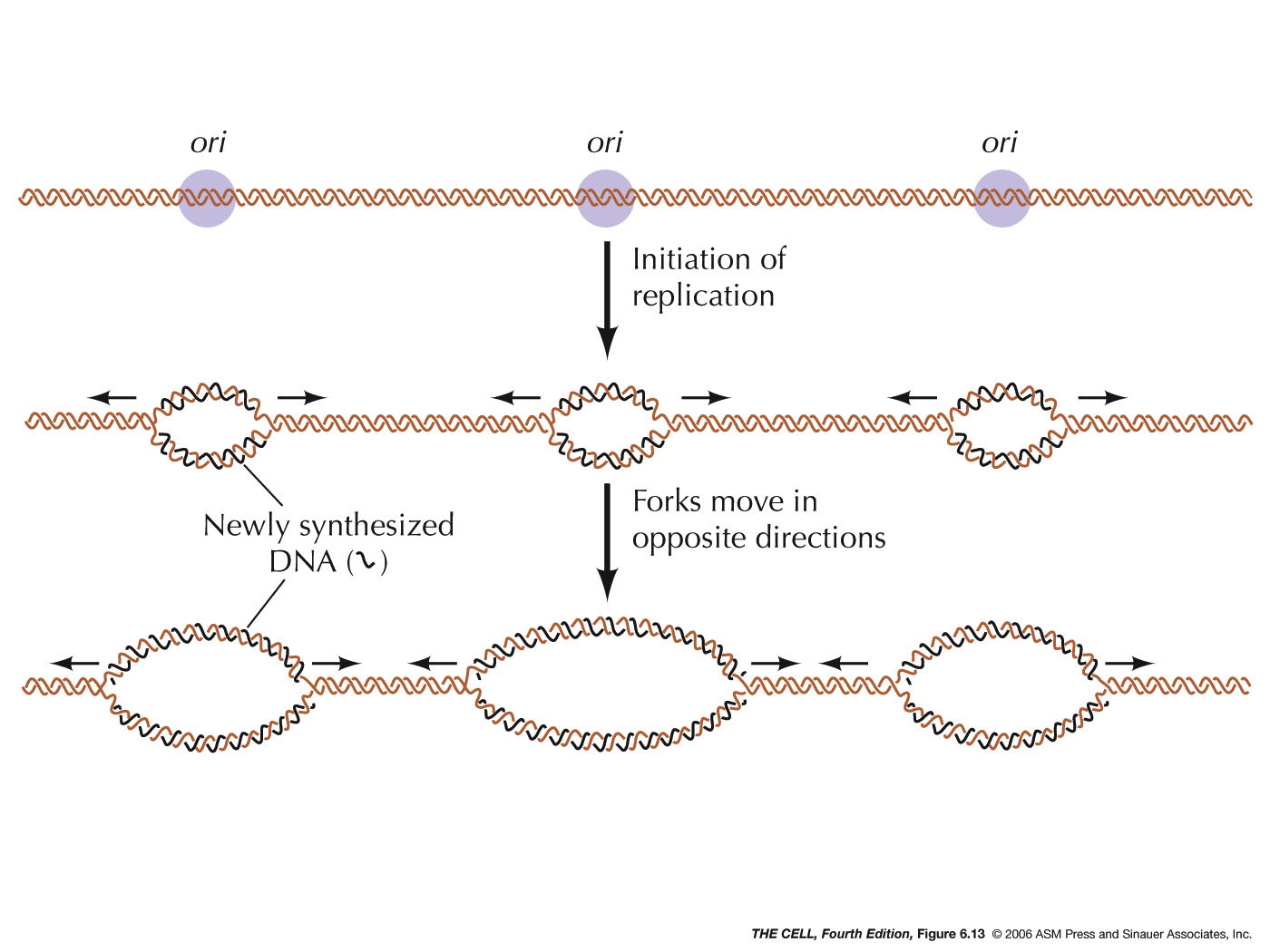
Replication of the human genome initiates within broad zones of ~ 150 kb.DNA Replication. The ability of cells to maintain a high degree of order in a chaotic universe depends upon the accurate duplication of vast quantities of genetic information carried in chemical form as DNA. The process of DNA replication begins when specialized enzymes pull apart, or .
Determination of human DNA replication origin position and
The Fanconi anaemia pathway is a replication-associated system for the processing of DNA interstrand cross links that culminates in the monoubiquitylation of the proteins Fanconi anaemia group D2 . This model for replication suggests .000 Genom-kopien/Zelle ca. 1: DNA replication in prokaryotes, which have one circular chromosome.Taq polymerase has an optimum temperature of 70-80ºC and can survive nearly an hour at 95ºC.1% or 3 x 10 6 base pairs (out of 3 x 10 9 bp) of DNA is unique in every individual.Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a robust technique to selectively amplify a specific segment of DNA in vitro .Principles of Biochemistry 11: Nucleotide and nucleic acid structure and metabolism 11. The next important enzyme is DNA polymerase III, also known as DNA pol III, which adds nucleotides one by one to the . In the dispersive model, DNA replication results in two DNA molecules that are mixtures, or “hybrids,” of parental and daughter DNA. The core machineries that copy DNA are conserved in all three .
DNA Replication Process with Diagrams Class 12
Principles and Concepts of DNA Replication in Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information in a cell.The principal enzyme involved in DNA replication is called DNA polymerase. DNA Replication, Repair, and Recombination. Primers in a PCR reaction are . By single-cell DNA replication sequencing . The target sequence of nucleic acid is denatured to single strands, primers specific for each target strand sequence are added, and DNA polymerase catalyzes the addition of deoxynucleotides to extend and produce new strands complementary to each of the target sequence strands (cycle 1).DNA Replication: From Old Principles to New Discoveries (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology Book 1042) – Kindle edition by Masai, Hisao, Foiani, Marco. However, about 0.DNA methylation is a process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. 1: The ends of linear chromosomes are maintained by the action of the telomerase enzyme.
- Dj Controller Aufbau , 7 predictions for DJ gear in 2024
- Dmc Farbkarte _ Umrechnungstabelle Sticktwistfarben von DMC nach Anchor
- Doctrine Of Affections , Doctrine of the Affections
- Dnd 5E Gold Level Chart _ D&D 5e Experience Points Explored : History and Alternatives
- Dms Volkswagen – GRP Login Page
- Dnd Ability Check | dnd 5e
- Diy Verstärker Für Lautsprecher
- Dlc Unlocker Sims4 – Sims 4 Updater
- Divx Xvid Player _ How-To: play DivX and Xvid on your Apple TV
- Dodge Caliber 2.0 Ps , Dodge Caliber aus 2007 gebraucht kaufen
- Dm Markt Ratingen | dm-drogerie markt, Gewerbestraße 16, 72525 Münsingen
- Divinely Uninspired To A Hellish Extent