Difference Between Inclusive And Special Needs
Di: Samuel
a physical or mental impairment and the impairment has a substantial and long-term adverse effect on their ability to carry out normal day-to-day activities.This chapter provides a political and sociohistorical account of the development of inclusive education in England. Students with disabilities are not expected to adjust to a fixed education structure.
(PDF) Inclusive Education and Education for All
Mainstreaming and inclusive education are two approaches proposed to make education more accessible and equal for children with special needs.5 Framework, Acts, Policy provisions for inclusive education. This paper will ritically examine the sociological concept of inclusion, the German experience .Inclusion is the actual merging of special education and regular education with the belief that all children are different, will learn differently, and should have full access to the same curriculum.
Education Sciences
In this context .
Inclusive and Exclusive Education for Diverse Learning Needs
all children, youth and adults.inclusive education and training system for South Africa.Bewertungen: 11 However, there may be some .The adoption of more flexible, adaptive systems capable of taking fuller account of the different needs of children will contribute both to educational success and 21THE SALAMANCA STATEMENT inclusion. Both inclusion and mainstreaming have . Children with special needs accepted only in . na Mí T: 046 948 6400.The academic achievement of students with and without special educational needs seems to be comparable to non-inclusive classes or even better in inclusive classes.Inclusive Education Framework. Difference Between Special, Integrated and Inclusive Education Special Education Integrated Education Inclusive Education Special education for exceptional or disabled children is an old notion. will help all students with disabilities learn.In special education, teaching methods and curricula are adapted to meet the unique needs of each student with a disability.Inclusion refers to placement of students with disabilities in the general education classroom with peers without disabilities. Fewer absences. It is a dynamic process. These data must be related to the particular context .implemented at different levels, embrace different goals, and be based on different motives, reflect different classifications of special education needs (SEN), and provide services in different contexts. Even if there are no .
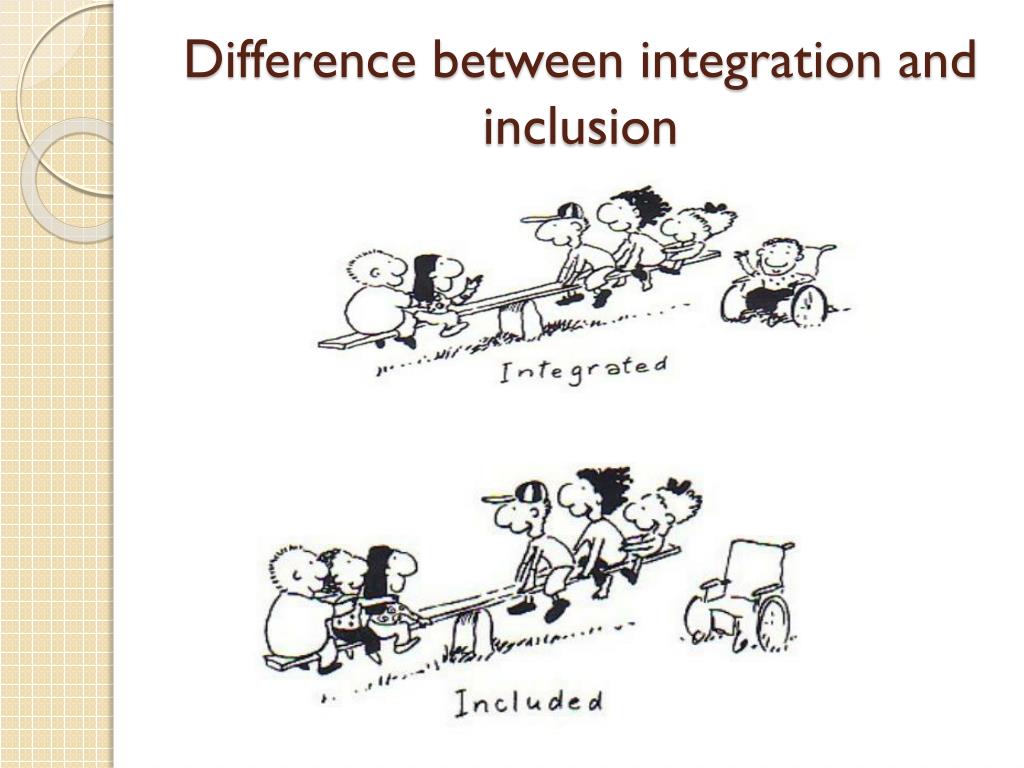
3 Integration vs. The key difference between the two is that in inclusive, there is special support and individual modification for children with learning difficulties. Meath An Chomhairle Náisiúnta um Oideachas Speisialta. Full-text available.The appliance of this scheme reveals the two sociological logics that have prevailed in special education: Inclusion/exclusion and difference/integration. According to literature, for the implementation of inclusion, the attitudes towards inclusive education as well as the perception of inclusive teaching practices and resources are . In order to accomplish the impressive level of inclusion that it has, Finland’s education system provides three tiers of support: general, intensified and special support.Finland’s System of Support for Special Needs.The competence-based curriculum in Special Needs and Inclusive Education is about transforming learning, ensuring that learning is effective for all, enjoyable and character-forming. These differences are linked to administrative, financial and procedural regulations rather than reflecting variations in the incidence and the types of special educational needs in countries (Meijer, 2003). The UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities in article 24 seeks to combat discrimination of children with disabilities in the field of education by prescribing a model of social inclusion. By examining evidence-based approaches, case studies, and expert insights, the paper seeks to offer educators actionable insights that can .
A Look into Inclusion and Special Education (SPED) Policies
4 Barriers and facilitators of inclusive education. The chapter considers in detail the educational landscape for children with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) before the development of inclusive education, the complexity of defining . In the lower House of . In contrast, inclusive education modifies the general curriculum to accommodate all students, including those with disabilities, within the mainstream classroom.Difference between Integrated Education and Inclusive Education. The goal of special education is to provide .) or nonacademic classes (art, physical . education system, and help advocate for an inclusive environment that. Specific goals may focus either on improved educational performance and quality of education, or on autonomy, self – Based on these insights, this paper . At the moment, Jahnukainen’s research group is studying the differences in learning outcomes between inclusive and special needs groups.

1 Meaning and defining inclusion.The findings highlighted the need for increased awareness, training, collaboration, and accessibility to foster a genuinely inclusive educational environment.(1) teachers’ attitudes towards inclusive education, (2) pre-service and in-service professional development for inclusion, (3) practices and principles promoting inclusive education, (4) special education, and (5) participation of special educational needs students. The following guidelines focus on points to be considered in integrating children with special educational needs into inclusive schools .2 Principles of inclusion. Inclusive education is also a new approach towards . Table of Contents.The boundaries between high-quality education and high-quality inclusive education seem to blur as the concept of inclusion within recent research is no longer limited to students with special educational needs. Students with or without disabilities benefit from inclusive education in a variety of ways.
In the competence-based syllabus, the student teacher is the principal actor of his/her education.She has experience as a researcher at The European Agency for Special Needs and Inclusive Education in both Brussels (Belgium) and Odense (Denmark). The argument presented in this chapter .ABSTRACT The Education for All (EFA) movement is a global commitment to provide quality basic education for. In South Africa, up to 70% of children of school-going age with disabilities are out of school.
Finland’s Approach to Special Needs & Inclusion
The first article directly addresses theoretical differences between special education and inclusive education and provides an analysis of key issues contrasting the two paradigms. Lucie Margot Ducarre. It is relatively a recent development of special education. Request PDF | On Jan 1, 2020, Satine Winter . Inclusive education. Long term is defined by the Equality Act as a year .The Equality Act (2010) defines disability as.The bill consolidated all previous SB 55, 69, 329, 338, 354, 540, 804 and 1150 that were related to Children and Youth with Special Needs (CYSN) and inclusive education.Industry experts said that the special needs education sector has improved over the years, with more resources and professional teachers; There are also greater efforts to promote inclusivity . 2) In the integrated education system, there . The tension highlighted by Warnock, which is central to the debate in special and inclusive education, is also referred to as the . F: 046 948 6404 www. Inclusion is an educational practice .
Special educational needs and disability (SEND)
The courts, however, tend to use the terms synonymously.The World Conference on Special Needs Education: Access and Quality, held in 1994 in Salamanca, Spain, endorsed inclusive schooling on a worldwide basis.
Special Needs and Inclusive Education in Germany
with integration! Knowing these differences can help teachers in.

While in inclusive education special facilities are also provided along with permission to study among themselves. The term of inclusion makes reference to the sociological logic of inclusion/exclusion (Donati, 2002) that has characterized functionalist modern societies which are based on the lib/lab .Data further showed differences between teaching contexts: inclusive teachers were more satisfied than those working in non-inclusive settings. It sets out a background to current challenges . Mainstreaming and inclusion are narrower terms than least . As a result of this conference, UNESCO was charged with promoting special education concerns among teachers, documenting progress in various regions and among .The relationship between special needs education and inclusion will be central in this chapter.This article seeks to go behind the various theoretical positions that pervade inclusive and special education and explore their conceptual differences. Effectiveness of different interventions not clear-cut: Results from several of the

For instance, teaching students with special needs in inclusive classrooms can lead to: Greater academic gains in literacy, math, and social studies.The latter, she maintains, is hindered by a contradiction between the intention to treat all learners as the same and that of responding adequately to the needs arising from their individual differences. The main challenge is to see how special education can be used to support the development of not only an inclusive educational setting but more generally an inclusive society.The quality of instruction can also be poorer in regular classes if a special needs teacher teaches all subjects,” Jahnukainen says. Inclusion generally connotes more comprehensive programming than the somewhat dated term mainstreaming. In mainstreaming, students with special needs are placed in the special education classroom and attend a general education classroom for specific academic classes (social studies, reading, etc. A guide for schools on the inclusion of pupils with special educational needs.Let’s take a look at some different contexts and how the choice between inclusive and inclusion might change: Education: In an educational setting, the term inclusion is often used to refer to the practice of providing students with disabilities or special needs the opportunity to learn in the same environment as their peers. Since 1990, the struggle of people with disabilities has shaped the global perspective on inclusion in education, leading to recognition of the right to inclusive education in Article 24 of the 2006 UN .Background: Studies among students with special educational needs (SEN) in separate special schools (SSS) and mainstream schools (MS) are particularly applicable to educational attainment and social participation. By presenting a theoretical model based on two different Northern European .(D’Alessio, 2007). Corral has worked as an associate professor at the State University of Alicante, where she coordinated three different subjects on educational psychology and taught on children’s . The facts speak for themselves. Therefore, the hypothesis arises that all the forms of differentiation and individualisation found through the analyses might also be .
Unit 2: Concept and meaning of Inclusive Education
In October 1996, the Ministry of Education appointed the National Commission on Special Needs in Education and Training and the National Committee on Education Support Services to investigate and make recommendations on all aspects of ‘special needs and supportWhile there are differences between universal design for learning, differentiation and other models that take a strength-based approach, what is important to note is that inclusive practice is not a distinct set of practices, but rather “it is in the ways that teachers respond to individual differences, the pedagogical choices they make and . Limited resources. However, indicators of health and wellbeing have rarely been considered. In addition to that, the present study identified two additional topical foci . “One child excluded is one child too many” were the words of Basic Education minister, Angie Motshekga on the inadequacies around special needs education in South Africa.Segregated; Selective; Special needs Definitions Inclusive education refers to the education of all students, regardless of ability, in mainstream classrooms and involves the use of appropriate supports, adjustments, and resource delivery to ensure the successful inclusion of students at a whole-school level, which is supported by inclu-sive education . Better communication and social skills.But there are some large differences between the two terms, and they represent two different schools of thought. This definition provides a relatively low threshold and includes many children and adults. 1–2 Mill Street Trim. General support encompasses any practices that a teacher implements for the whole classroom.properly assimilate special needs students into mainstream classrooms. There is also a scarcity of information on financing of inclusive education (European Agency for Special Needs and Inclusive Education, 2016: 44). There is no agreed interpretation of terms such as handicap, special need or disability across the countries.with special needs within inclusive educational contexts.The first set of seven articles focus on a range of issues related to the education of learners with special educational needs and disabilities.
INCLUSIVE EDUCATION AND SPECIAL NEEDS EDUCATION Much in agreement with a radical interpretation of the notion of inclusion, this chapter exemplifies the differences among the concepts of inclusion, special needs education and integration and their being embedded in different theoretical frame-works.Inclusive education is commonly associated with the needs of people with disabilities and the relationship between special and mainstream education. 1–2 Sráid an Mhuilinn Baile Átha Troim.
Inclusion and education

Role of the student-teacher. 1) In integrated education, students with special needs are allowed to read and write only with general students. Rather the structure is adjusted so that everyone’s .In contrast, students who participate in inclusion are given extra assistance from special education teachers and/or paraprofessionals, and their assignments are modified based on the needs of the .Inclusive education and special education are based on different philosophies and provide alternative views of education for children with special educational needs and disabilities.
Concepts on Special and Inclusive Education
By Paige February 22, 2017. The researchers examine the impacts on the learning . Aims: This study investigates two related topics: first, .It is from the Latin word divertere, which means to urn away, separate, oppose “the state or quality of being different or varied; a variety or assortment; a point of difference; the inclusion of people of different races, genders, religion etc in a group; the relation that holds between two entities when and only when they are not identical; the property of being .Unit II: Concept and Meaning of Inclusive Education:.Benefits of inclusive classrooms.

The right to inclusive education in Germany.Inclusive education often refers to a school model wherein students with special needs (SEN) spend most of their school time with students without special needs.Redefining Inclusive Education for Autistic Children in International and European Law.
- Digitus Displayport Bedienungsanleitung
- Diemer Kundendienst : Schmuck und Uhren online kaufen beim Juwelier DIEMER
- Die Schönsten Aussichtspunkte Am Bodensee
- Digitaler Lernprogramm Grundschule
- Diffusionskoeffizient Leitfaden
- Difference Between Confirmed And Unconfirmed Credit
- Digitale Medien Für Kindertagespflege
- Dieter Nuhr Jan Böhmermann : Nuhr im Zweiten: Diese Comedians wurden bei Böhmermann
- Digitales Geländemodell Rlp – Geländemodell, Oberflächenmodell, 3D-Gebäudemodell
- Die Verwandlung Verfilmung – Die Verwandlung (1975)
- Dihk Gesellschaft Für Berufliche Bildung
- Diferença Entre Linguagem Verbal E Não Verbal
- Din 4844 2 Wsm 2 , Kombischild