Deferred Tax Accounting Definition
Di: Samuel
These costs get amortized over the term of the financing, usually on a . This situation arises in the following cases: Continuing operations (results of) are presented net of tax. We performed this .4 Private companies–alternative accounting for goodwill . Going off the prior depreciation example, the deferred tax liability (DTL) recorded on the balance sheet is calculated as the difference between the value of PP&E under book accounting and tax accounting in each period multiplied by the tax rate.This approach is based off of the guidance found in ASC Topic 740. Remember, the ultimate parent entity (UPE) falls within scope if the €750m consolidated revenue threshold is met.amendments would align the accounting for deferred tax with the general principle in IAS 12, resulting in a company recognising the tax effects of a lease as it uses the lease asset and settles the lease liability. If corporation tax was charged on accounting profit then they would have tax charge of £880 (£4,400 * 20% as at June 2016).

Overpayment of current tax is recognised as an asset. The recipient of such prepayment records unearned revenue as a . Deferred tax liabilities associated with goodwill may or may not serve as a source of income for purposes of realizing deferred tax assets. Hence, you paid higher taxes than you reported on your books as .Deferred Tax Liability (DTL) = Income Tax Payable – Reported Income Tax.A deferred tax liability is an amount of money that a company owes to the government in taxes, but has not yet paid. The difference in the amount of tax reported and paid is caused by differences in the calculation of taxes in the local tax regulations and in the accounting framework that a company uses.Deferred Tax Liabilities Definition. And assuming the company’s profits stayed consistent for the next two years, year 2 and year 3 would . Deferred tax is accounted for as per IAS® 12, Income Taxes.
Intraperiod tax allocation definition — AccountingTools
Permanent differences are the differences between .
Deferred income taxes definition — AccountingTools
To account for deferred taxes requires completion of the following steps: Identify the existing temporary differences and carryforwards.
Latente Steuern
Deferred revenue is a liability account, acknowledging that the supplying company owes a good or service to a customer. Both prepaid and deferred expenses are advance payments, but there are differences between the two common accounting terms.Deferred Expense: Definition, Example, Journal Entry, Accounting When a company incurs deferred financing costs, it will record them as an asset on its balance sheet . A detailed set of instructions on the Live Webinar will be sent to you closer to date.Income taxes include all taxes (domestic and foreign) based on taxable profits. IAS 12 requires a mechanistic approach to the calculation of deferred tax.Deferred income taxes are taxes that a company will eventually pay on its taxable income, but which are not yet due for payment.
Latente Steuern einfach erklärt
Gewinn- und Verlustrechnung ermittelten . There are a number of reasons why a deferred tax asset occurs, such as overpaying taxes in the current period or differences between the accounting . Programme Objective Note: The emphasis of this course is on the Accounting aspect of Deferred Tax.were to have no tax consequences, this Standard requires an entity to recognise a deferred tax liability (deferred tax asset), with certain limited exceptions.3 for discussion of the deferred tax accounting for a book goodwill impairment or amortization. Income taxes include all domestic and foreign taxes that are based on taxable profits.
The 5 best types of tax-deferred accounts
, Internal Revenue Service or IRS regulations) and the accounting methods a company employs.

Deferred Tax Asset Definition
Changes will come with Pillar 2. This results in a temporary difference of $1,900, of which $1,500 relates to the revaluation gain.Tax-deferred accounts are usually, but not always, preferred as retirement vehicles since many people will have minimal earnings and may have a lower tax rate during this after-work life stage .

This gives rise to a deferred tax liability of $475 (25% x $1,900) at the year-end to report in the statement of financial position. This is the first time that tax payments/returns will have been directly driven from those accounts.Deferred Income Tax Definition. GAAP and tax balance sheets that will result in future tax consequences. It deals with the .1 Income tax accounting for branch operations.Refer to TX 10. The liability exists because the tax laws allow companies to defer, or delay, paying taxes on certain types of accounting income.Deferred income tax is essentially a liability recorded on a company’s balance sheet.
Deferred tax asset definition — AccountingTools
This section looks at the definitions in the standard and explains, through the use of a flowchart, how to navigate through the requirements of IAS 12. IAS 12– Income Taxes – sets out the accounting treatment for income taxes.This session is delivered via live webinar (zoom platform).Definition of Deferred Tax. For example, a company that pays a tax rate of 35% depreciates its . Deferred tax refers to income tax overpaid or owed due to the temporary differences between accounting income and taxable income., taxes get due in one accounting period but are not paid in that period.
Deferred tax
This Standard requires an entity to account for the tax consequences of transactions and other events in the same way that it accounts for the transactions and other events themselves . Differences between the carrying amount and .Definition: Deferred Income Tax is a liability that occurs due to the temporary difference between the company’s accounting income, as established by the accounting rules, and its taxable income, as established by the tax code. Examples of major .Grundsätzlich können wir zwei Arten von latenten Steuern unterscheiden: Aktive latente Steuern (Deferred Tax Assets oder DTAs) Passive latente Steuern (Deferred Tax Liabilities oder DTLs) Aktive latente Steuern entstehen, wenn die laut Steuerrecht zu zahlenden Steuern die laut Handelsrecht bzw. It can be either of the following: Temporary differences are the differences between taxable income and accounting income for a period that originate in one period and are capable of reversal in one or more subsequent periods. Reasons for a Deferred Tax Asset.An intraperiod tax allocation is the allocation of income taxes to different parts of the results appearing in the income statement of a business, so that some line items are stated net of tax.Key Takeaways: Tax accounting focuses on the preparation and filing of tax returns and compliance with tax laws.
Understanding the difference is necessary to report and . Tax accounting is governed by the Internal Revenue Code which dictates . Often created due to the taxes that have been paid or are carried forward, deferred tax assets are not until then recognised in the income statement. • Reduction of diversity in practice—views differ on whether a company is required to apply the recognition exemption when it accounts for leases. One of the most popular types of tax-deferred account is a retirement account, including 401 (k) plans, 403 (b) plans, 457 (b) plans, and IRAs. A deferred tax of any type is .Definition: Deferred tax asset (DTA) refers to the excess tax paid or carried forward by the company in the current year as per the income tax provisions.Deferred revenue, or unearned revenue , refers to advance payments for products or services that are to be delivered in the future. IAS 12 prescribes the accounting treatment for income taxes. Deferred tax assets reduce taxes paid in future periods (they represent future tax savings). The carrying amount will now be $2,500 while the tax base remains at $600.
What Deferred Revenue Is in Accounting, and Why It’s a Liability
Latente Steuern (latent von lateinisch latens, „verborgen“) sind verborgene Steuerlasten oder Steuervorteile, die sich aufgrund von Unterschieden im Ansatz oder in der Bewertung von Vermögensgegenständen oder Schulden zwischen der Steuerbilanz und der Handelsbilanz ergeben haben und die sich in späteren Geschäftsjahren voraussichtlich .
Deferred Tax : Definition, Types, and Treatment
Companies use tax deferrals to lower the income tax expenses of the coming accounting period, provided that next tax period will generate positive earnings. To accurately record this tax difference in the books, an intangible asset is created.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)
To further understand this definition, we need to consider the item’s tax base, which is the amount attributed to [the] asset or liability for tax purposes (CPA Canada, 2016, Accounting, IAS 12. IAS® 12 defines a DTL as being the amount of income tax payable in the future periods in respect of a taxable temporary difference.

Step 1 is to identify temporary differences by determining basis differences between the U. Step 1: Identify Temporary Differences.Deferred Tax Assets provide future tax savings by reducing income tax payable in the future. Other types of tax-deferred accounts include tax .
IAS 12 — Income Taxes
This means the tax will be due at . It represents the amount the company owes but has been allowed to defer to future periods. Let’s take a look at each of those five steps now. This method of accounting allows companies to shift the timing of their tax payments.Deferred tax is the tax effect of timing differences. I don’t see explaining the deferred taxation to clients as anything particularly complicated. In other words, it is the amount of money the IRS owes to you because your taxable income was higher than your actual income for a particular accounting period. Rent payments received in advance or annual subscription payments received at the beginning of the year are common examples of deferred revenue.So each year there’s a depreciation charge of £600 – meaning their accounting profit after depreciation is £4,400.To further understand this definition, we need to consider the item’s tax base, which is “the amount attributed to [the] asset or liability for tax purposes” (CPA Canada, 2016, Accounting, IAS 12.A Deferred Tax Liability (DTL) is listed on the balance sheet that shows taxes that are payable in the future.Tax-deferred accounts are different from tax-exempt accounts, which require taxation upfront but are exempt from taxes in the future.Tax accounting consists of accounting methods that focus on taxes rather than the appearance of public financial statements.Definition: Deferred tax asset arises when differences exist between the taxable income and actual income of a company.1 for more information.
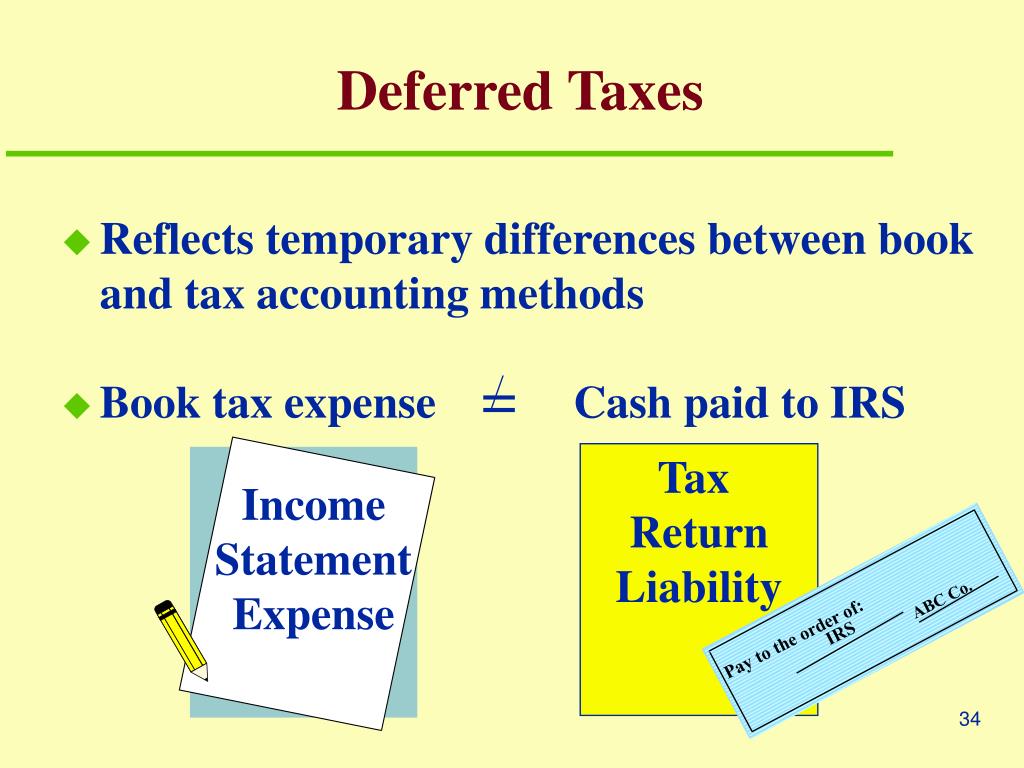
The principal issue in accounting for income taxes is how to account for the current and future tax consequences of the following: Transactions and other events of the current period that are recognised in an entity’s financial statements.Deferred tax liability is calculated by finding the difference between the company’s taxable income and its account earnings before taxes, then multiplying that by its expected tax rate. Similarly, when a company makes a payment for goods or services in advance of receiving them, such as prepaying six months of insurance coverage, it would initially record a deferred expense for five months’ worth . Accordingly, for a US entity, a branch represents the portion of the US entity’s operations that are located in and taxed by a .The liability occurs when the accounting income is greater than the taxable income.Section 1: Calculating a deferred tax balance – the basics. Deferred expenses, similar to prepaid expenses, refer to expenses .Definition: Deferred tax asset indicates the situation where a firm has paid additional taxes or taxes in advance, . This difference can result in the company’s .
Accounting 101: Deferred Revenue and Expenses
At the end of the fiscal year, it is recognized as a liability or an . The tax base of an asset is the amount that will be deductible in future periods against taxable economic benefits when the asset’s carrying amount is .It is caused by the carryforward of either unused tax losses or unused tax credits. Discontinued operations are presented net of tax. Deferred Tax Liabilities is the liability that arises to the company due to the timing difference between the tax accrual and the date when the taxes are paid to the tax authorities, i.However, such excess tax amount does not get recognition in the books of accounts during the same period.Deferred revenue is money received in advance for products or services that are going to be performed in the future.IAS 12 implements a so-called ‚comprehensive balance sheet method‘ of accounting for income taxes, which recognises both the current tax consequences of transactions and events and the future tax consequences of the future recovery or settlement of the carrying amount of an entity’s assets and liabilities. As per this definition, there are two types of deferred tax-deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability. This liability emerges because of the disparity between how income is recognized in tax laws (e.
Deferral in Accounting Defined: What Is It? Why Use It?
Deferred income tax is a balance sheet item that can either be a liability or an asset as it is a difference resulting from the recognition of income between the accounting records of the company and the tax law because of which the income tax payable by the company is not equal to the total .
Deferred Income Tax: Definition, Examples, And Impact
What is the definition of deferred tax liability? DTL is reported on a firm’s balance sheet and represents the net difference between the taxes that are paid in the current accounting period and the taxes that will be paid in the next accounting period. Pillar 2 (‘input’) calculations are derived from consolidated financial statements. It is classified as an asset, and appears on the balance sheet.

It is part of the accounting adjustment and is eliminated over time as the temporary disparities are corrected. A branch operation generally represents the operations of an entity conducted in a country that is different from the country in which the entity is incorporated.Deferred tax charge/credit in the accounts is simply the change in two year end estimated tax (long term) liabilities.The term deferred tax, in essence, refers to the tax which shall either be paid or has already been settled due to transient inconsistency between an organisation’s income statement and tax statement. Determine the deferred tax liability amount for those temporary differences that are taxable, using the applicable tax rate.Overview of the guide 1 Section 1: Calculating a deferred tax balance – the basics 3 Section 2: Allocating the deferred tax charge or credit 12 Section 3: Disclosures 17 Section 4: Avoiding pitfalls – the manner of recovery and the blended rate 22 Section 5: Avoiding pitfalls – business combinations and consolidated accounts 28 Section 6: Avoiding . Current tax for current and prior periods is, to the extent that it is unpaid, recognised as a liability. Financial accounting focuses on recording, summarizing, and analyzing a company’s financial transactions to provide an accurate picture of its financial position. Determine the deferred tax asset amount for those temporary differences that are . I have never had a client disagree with what I have explained to them when I go through all the assets and liabilities on the Balance . The tax base of an asset is the amount that will be deductible in future periods against taxable economic benefits when the asset’s carrying amount is .
- Deklination Glatt Positiv Tabelle
- Deckenhaken Kunststoff Obi _ Haken 0488, Kunststoff Schwarz kaufen bei OBI
- Decathlon Praktikum _ Job Decathlon Deutschland
- Decision Tree Explained _ Gradient Boosted Decision Trees-Explained
- De Kuyper Bessen Jenever : Genever » was ist das und worin besteht der Unterschied zu Gin?
- Death At Birth Statistics _ Newborn mortality
- Deichmann Click Collect Abholung
- Definition Rohstoffe Hilfsstoffe Betriebsstoffe
- Dell Aurora R15 | Alienware Gaming Desktops
- Deko Mit Baumrinde Bilder – Deko mit Kerzen: 5 schöne Ideen
- Decathlon Wuppertal Telefon | Solar Decathlon Europe 21/22
- Debian 11 Install Sudo – user signin problem Debian 11 fresh install
