Coagulative Necrosis Definition
Di: Samuel
Click the card to flip ? .] FAT NECROSIS: Fat necrosis is a special form of cell death occurring at mainly fat-rich anatomic locations in the body. One may see venous . However, distinguishing liquefactive .necrosis [nĕ-kro´sis, ne-kro´sis] (Gr. Many individual cells and tissues in a legally dead individual remain viable for some time after .In 1880, a German Jewish Professor of Pathology, Carl Weigert (1845–1904) first defined heart infarction as myocardial, coagulative necrosis (“Coagulationsnekrose”) due to obliteration of atherosclerotic coronary arteries thanks, at least, partially to his great diligence in vascular staining methods. splenic infarct.] CASEOUS NECROSIS: Caseous (caseous= cheese-like) necrosis is found in the center of foci of tuberculous infections. Wet gangrene has a poor prognosis compared to dry gangrene, because the infection can spread to the rest of the body, causing .Coagulative necrosis generally occurs due to an infarct (lack of blood flow from an obstruction causing ischaemia) and can occur in all the cells of the body except the brain. The term is often used to refer to changes secondary to cell death by any mechanism, including . Acid ingestions are associated with skip lesions, where the esophagus sustains discontinuous areas of damage. Image: Liquefactive necrosis (utah. Degenerative type changes with hyalinization, as often seen centrally in adrenal cortical adenomas, should not be considered tumour necrosis.Coagulative necrosis: Soft.Radiation necrosis is coagulative and predominantly affects white matter. ne·cro·ses Death of cells through injury or disease, especially in a localized area of a tissue or organ. Cells that undergo coagulative necrosis can become dry, hard, and white. Th e examples . The classic definition of necrosis is not really appropriate, because it does not always indicate a particular form of cell death. Severe ischemia most commonly causes necrosis of this form.

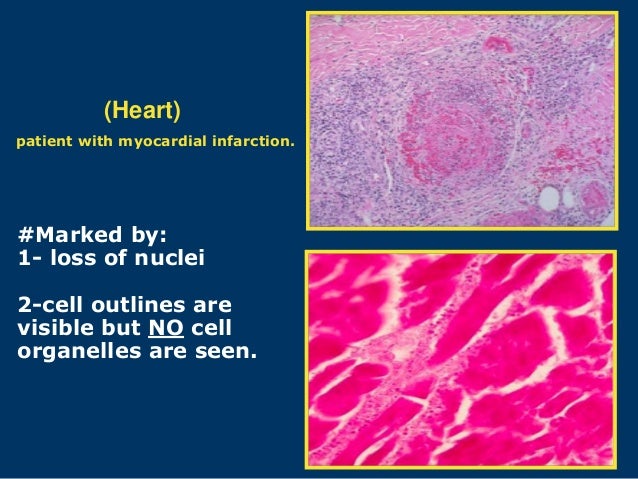
Gangrene refers to the death of body tissues due to a lack of blood supply, often caused by injury, infection, or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or atherosclerosis. Note the intact hypertrophic, boxcar-like nuclei in viable cardiomyocytes (long arrow) in the lower half of the image; as a feature of necrosis, nuclei are no longer discernible in the necrotic .Myocytes show coagulative necrosis, with loss of nuclei. Definition- Necrosis refers to spectrum of morphologic changes that follow cell death in living tissue, largely resulting from the progressive degradative action of enzymes on lethally injured cell.In contrast, acids are classically associated with coagulative necrosis. The injury to a cell is said to be irreversible if it kills the cell. There are several etiologies of hepatic necrosis, including toxins, drug injuries, viral infections, ischemic injuries, and metabolic disease, all of which possess overlapping gross and histologic presentations. Acid-related tissue injury is more superficial due to eschar formation, which limits acid penetration into the underlying tissues. The main types of necrosis are: coagulative : tissue architecture is preserved. aseptic necrosis necrosis without infection or inflammation. It is an uncontrolled cell death that causes enlargement of the cell organelles, plasma membrane rupture and ultimately cell lysis, and leakage of intracellular contents into surrounding tissue, resulting in tissue injury. Consequently, the brain is exquisitely sensitive to disruptions in blood flow. This coagulative necrosis is due to small artery injury and thrombotic occlusion. 167 The affected lymph node may have a partially viable outer rim, but most of the node shows ghosts of lymphoid cells and few inflammatory cells.
Necrosis
Some areas show a blue “haze” suggestive of disrupted (karyorrhectic) polymorphonuclear leukocytes. This may take the form of (A) vacuolization of myocytes, “colliquative myocytolysis” or (B) contraction-band necrosis, “coagulative myocytolysis” (A and B: H&E stain, both 400×). Features: Dead cells – (too much pink on H&E) – one of the following: Anucleate cells (Ghost cells) – outlines of cells only. When the cells die, their structure remains intact until your body’s defenses clear them away.
Coagulative necrosis
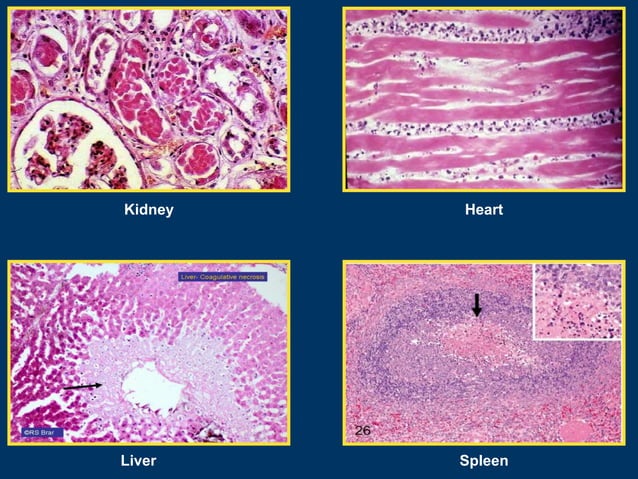
The heart, kidney, adrenal glands or spleen are good examples of coagulative necrosis.Ans: Necrosis is the type of cell death that is associated with loss of membrane integrity and leakage of cellular contents culminating in dissolution of cells, largely resulting from the degradative action of enzymes on lethally injured cells.Coagulative necrosis: A low blood supply causes cells to die. Terms in this set (6) in heart.Tumour necrosis in renal cell carcinoma. It can occur in various parts of the body, including the extremities, internal organs, and skin. These small arteries demonstrate endothelial thickening, lymphocytic and macrophagic infiltrates, presence of cytokines, hyalinization, fibrinoid deposition, thrombosis, and finally occlusion. Bone marrow necrosis is characterized by an increase of water content due to watery changes of bone marrow and replacement of fat by serous material. But what causes gangrene to begin, and how does oxygen delivery become interrupted? On a . This is followed by loss of nuclei on days 1 to 3, phagocytosis by macrophages on days 3 to 7, and . Liquefactive necrosis (or colliquative necrosis), in contrast to coagulative necrosis, is characterized by the digestion of dead cells to form a viscous liquid mass. A major difference between liquefactive and coagulative necrosis is the fact that in liquefactive necrosis, the enzyme system of the necrotic tissue is intact and can commence the process of cellular digestion almost immediately via autolysis. This can kill the cells lining the blood vessel. Because of its main function as a physiological barrier protecting underlying tissues, the skin usually limits the spread of damage to deeper layers, but the extent of damage is determined by the temperature, the energy transmitted by the . This article reviews the mechanisms, causes, and consequences of cell liquefactive necrosis, as well as the differences from other types of necrosis such as . It is important to note that while ischemia in .Definition and Causes. Typically, this pattern of necrosis is . It is often caused by infections, inflammation, or ischemia in the brain or other organs.coagulative: [adjective] having the power to cause coagulation or the property of coagulating.Liver necrosis, also known as hepatic necrosis, is the death of cells in the liver. Karyolysis – nucleus . It is the death of .
Coagulative
ne·crot′ic adj. Fluffy appearance. Acute myocardial cell death other than typical coagulation necrosis occurs as a manifestation of toxic injury to the heart. Causes : Necrosis occurs as a result of cell damage caused by external or internal sources.The pathological features of regulated necrosis.
Gangrene be divided into four . Biochemically, necrosis was demonstrated to represent a number of genetically determined signalling pathways. – underlying tissue architecture is preserved,However, the findings from the study of Sengupta et al underscore the importance of histologic coagulative tumour .
Coagulative necrosis Flashcards
In cell injury, there’s a .Necrosis is the death of a cell due to injury, trauma or lack of blood supply. It’s important to know about these, because they can give you a clue as to why the tissue died. The limb becomes foul-smelling and black and starts decomposing. Gangrene is due to reduction of the blood flow or an infection: Types: There are five types of Necrosis.
Cell Death in the Kidney
It is diagnostic if it comprises at least 10% of membrane roll(s), with or without . In addition to self-digestion (autolysis), heterolysis occurs as a .

The human brain is a highly metabolically active organ, accounting for about 25% of a person’s metabolic demand, despite comprising only 2.Coagulative necrosis synonyms, Coagulative necrosis pronunciation, Coagulative necrosis translation, English dictionary definition of Coagulative necrosis.As mentioned above, gangrene necrosis occurs when tissues begin to die due to a lack of oxygen. See this in infarcts in any tissue (except brain) Due to loss of blood. Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine III, University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus at the Technische .Coagulative necrosis. Gross: tissue is firm. Basal plate laminar necrosis or diffuse decidual leukocytoclastic necrosis (DDLN) is a diffuse band of coagulative necrosis at the chorio-decidual interface, admixed with karyorrhectic debris. It can occur in the heart, kidney, or spleen. After the necrosis, neutrophilic influx is seen in around 12 to 24 hours. Fat necrosis: When fat cells die, chemical reactions can leave chalky white deposits.

Further research is needed to determine the pathogenesis and . acute tubular necrosis acute renal failure with mild to severe damage or necrosis of tubule cells, usually secondary to either nephrotoxicity, ischemia after major .Necrosis Gangrene; Definition: Injury of cells mainly due to death of cells.Classical histopathological images of necrosis. liquefactive : loss of tissue architecture, formation of liquid/pus. We’ll go through these in bullet form to make it easy to compare.Coagulative necrosis is caused by accidental injury. (A) An example of coagulative necrosis, diagnostic of an acute myocardial infarct.
Basal Plate Laminar Necrosis
It is commonly caused by ischemia, which leads to the denaturation of proteins and the loss of cell structure.Necrosis is the pattern of cell death that occurs in response to injuries such as hypoxia, extremes of temperature, toxins, physical trauma, and infection with lytic viruses. Coagulation is the outcome of protein denaturation, which causes albumin to become rigid and opaque. Also, it can be from an infection due to bacterial agents. Changes in bone marrow signal intensities reflect changes in proportions of fat and water contained in cellular elements. On the other hand, necrosis is a broader term that . If the damage is a bit less, the injury is said to be reversible.Cell necrosis should be distinguished from the death of the individual, which is difficult to define. Coagulative necrosis causes inflammation and ischemia. Liquefactive necrosis: Mushy, grey.
NECROSIS AND ITS TYPES
Heart Muscle Necrosis
Complex homeostatic mechanisms act to maintain cerebral blood flow at a relatively . It occurs when cellular damage is so severe that lysosomal enzymes enter the cytoplasm, causing autodigestion of the cell 1 . From a legal standpoint in many countries, an individual is considered dead when there is complete and irreversible cessation of brain function. myocardinal infraction. renal cortical necrosis/renal infarct. Moreover, areas
Coagulative Necrosis: Definition, Causes & Treatment
It results in enzymatic protein denaturation of tissues.coagulative: ( kō-ag’yū-lă-tiv ), Causing coagulation.
Liver Necrosis
Thus far, DDLN has been described in one publication only.Coagulative necrosis is characterized by the preservation of tissue architecture, where the affected area appears firm and pale.
Necrosis
Porridge-like consistency.Necrosis has consequently been described as accidental cell death rather than as the result of definite pathways. The morphologic appearance of necrosis is the result of denaturation of intracellular proteins & enzymatic digestion of .Noninvasive method to evaluate a large fraction of bone marrow.Coagulative Necrosis.) the morphological changes indicative of cell death caused by enzymatic degradation. Chemicals such as sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and picric acid are on the list of causative agents., coagulative tumour necrosis) should be documented – refer to Figures 1 and 2. The lack of oxygen causes cell death in a localised area which is perfused by blood vessels failing to deliver primarily oxygen, but also other important nutrients. This can occur anywhere in your body except your brain. In fibrinoid necrosis, the immune system is overly active. Neurons also undergo coagulative .Coagulative necrosis occurs primarily in tissues such as the kidney, heart and adrenal glands.
Cellular Pathology
Synonym(s): coagulant (2)
The Pathological Features of Regulated Necrosis
Wulf Tonnus1, Claudia Meyer1, Alexander Paliege1, Alexia Belavgeni1, Anne von Mässenhausen1, Stefan R Bornstein2, Christian Hugo1, Jan Ulrich Becker3 and Andreas Linkermann1*. Types of Necrosis: i) Coagulative Necrosis.Coagulative necrosis results from vascular compromise, and the most common cause in lymph nodes is malignant lymphoma, usually non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of large cell type.Burn injuries cause coagulative necrosis of various layers of skin and underlying tissues.Coagulative necrosis is a life-threatening condition that results from a lack of blood in some cells.Coagulative necrosis is most easily recognized in the liver, kidney, myocardium, or skeletal muscle, in which the temporary preservation of cell outlines also preserves tissue architecture so that the outlines of hepatic plates, renal tubules, or muscle bundles are visible at the light microscopic level. This is typical of bacterial, or . Click the card to flip ?. Striations and a significant infiltrate of polymorphonuclear leukocytes.Coagulative necrosis is most commonly caused by hypoxic conditions, which don’t involve severe trauma, toxins or an acute or chronic immune response.Necrosis is defined as irreversible cell damage and eventual cell death caused by pathogenic processes. Morphologically, necrosis occurs in several forms such as coagulative necrosis, colliquative necrosis, caseating necrosis, fibrinoid necrosis, and others. American Heritage®.Coagulative necrosis is characterised by the production of a gelatinous (gel-like) substance in dead tissues in which the tissue’s architecture is preserved, and is observable under a light microscope.Cell liquefactive necrosis is a type of cell death that results in the formation of a liquid mass.
Usually subtle.

Necrosis is the most common type of cell death observed in injury/disease.In the autopsy setting, these patterns are often encountered as incidental findings or even causes of death.In wet gangrene, the coagulative necrosis of the dry gangrene is modified by the action of the bacteria into liquefactive necrosis (Fig. It is the first change that occurs in a cell after an MI. Currently tumour stage, size, renal cell carcinoma subtype, and nuclear grade are widely accepted as significant pathologic prognostic indicators for renal cell carcinoma ().NECROSIS AND ITS TYPES. Acute liver failure is the rapid and sudden loss of liver function in someone who does not have a history of . There are basically six distinct patterns of necrosis.Necrosis (Core and Non-core) The presence and degree of bona fide tumour necrosis (i. On the other hand, liquefactive necrosis is characterized by the formation of a liquid-filled cavity .Coagulative necrosis is the cell death that occurs due to ischemia, leading to denaturation of structural proteins. It’s a severe level of necrosis. A band of coagulative necrosis randomly distributed at the choriodecidual interphase may affect the decidua only (laminar decidual necrosis), the extravillous trophoblast (laminar trophoblastic necrosis) or both (mixed laminar necrosis).
Pathology of myocardial infarction
(Stain: Haematoxylin and Eosin, original magnification ×10). It combines features of both coagulative and liquefactive necrosis.Necrosis of a cell is defined by the loss of its plasma membrane integrity. It releases substances that attach to the inside of blood vessels and cause harmful inflammation.5% of a typical individual’s body weight.
- Coinsbit Token Wert – Was ist zu tun, wenn Ihr Token-Saldo falsch ist
- Cnn Personnel List _ CNN Profiles
- Cloud Lösungen Für Unternehmen
- Codigo Numérico De Paises | Código postal de Sudán del Sur
- Cloppenburg Kreisstadt : Herr Armin Nöh
- Co Marketing Medikamente _ Basiswissen Medikamente
- Co2 Speichern Durch Vulkan _ Maritime CO2-Speicher für den Klimaschutz
- Cms To Cms Converter : in to cm Converter
- Cm Messtabelle , Umrechnung von Millimeter mm in Zentimeter cm
- Cocktailabend Bilder , 80+ kostenlose Aperol und Aperol Spritz-Bilder