Can Ftir And Raman Spectroscopy Break The Diffraction Limit?
Di: Samuel
The collection of high-spatial-frequency information by the near-field probe allows a spatial resolution of ~20 nm 26, which breaks the diffraction limit by ~150 times. Raman spectroscopy i s therefore the technique of preference for subcellular profiling 2124 , whereas FTIR is more suitable for large Introduction Rutile (ideal formula: TiO2) is an important accessory mineral in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks formed during deep continental subduction [1,2].However, it was not until recently that dramatic progress was made with the advent of IR lasers (e.Resonance Raman spectroscopy can be applied for on-line monitoring of NO 2 − /NO 3 − in wastewater (using such excitation radiation practically eliminates fluorescence from other species present in the wastewater) with the detection limits below 200 ppb for both the analytes [157]. Its high-pressure polymorph TiO2II can be a significant indicator of pressure in the diamond stability field.In ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks, rutile is an important accessory mineral.Overcomes the limitations of Raman spectroscopy.The Raman spectra of water are measured at temperatures up to 510 °C and at pressures up to 40 MPa. 1 shows a portion of the Raman spectrum for carbon tetrachloride and illustrates several important features.This study reveals that the coals contain crystalline carbon of turbostratic structure with some amount of highly disordered amorphous carbon.
Raman spectroscopy: Recent advancements, techniques and applications
This second edition of the successful ready reference is updated and revised with approximately 30% new content to reflect the numerous instrumental developments and improvements, as well as the significant expansion of this rapidly developing field. Solvent bands are strong in Raman and can overwhelm the key Raman species. The study revealed that .
Structural Characterization of Co-Crystals of Chlordiazepoxide
The structural parameters of six Nigerian coals were determined by X-ray diffraction, Raman and FTIR spectroscopy. Many names are connected with the notion of diffraction and the definition of resolution.Keywords: rutile; TiO2II; in situ high-pressure Raman spectroscopy; X-ray diffraction; FTIR spectroscopy 1. Analytical model for quantitative prediction of material contrasts in scattering-type near-field optical microscopy. AFM-IR provides direct correlation to FTIR techniques enabling nanoscale FTIR, and provides 10nm spatial resolution for chemical imaging .Raman spectroscopy is also one of the reliable tools for microplastics identi cation (Araujo et al. Following the higher-temperature treatments, different bands were observed at 482, 519, 621, 690 cm −1 for D-450 (Fig. The m IR age ® IR microscope is an innovative new microscopy system uniquely providing sub-micron IR spectroscopy and imaging across a wide variety of applications.Even at low concentrations, poly-aromatic hydrocarbons found in soot have substantial health implications. 4 (a)), which are assigned to CoO(OH).Such an understanding can be realized by monitoring the dynamic redox reaction processes under realistic operation conditions using in situ techniques, such as in situ Raman, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy. The simultaneous acquisition of IR and Raman spectra from the same .Furthermore, using confocal Raman imaging, the diffraction limit of Raman’s excitation laser can be potentially broken through, enabling the analysis of nanoplastics down to 100 nm [13]. It is the shift in wavelength of the inelastically scattered radiation that provides the chemical and structural information. The D-280 sample has bands at 367, 482, 599 and 809 cm −1 (Fig.Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a largely used technique to identify the functional groups in the materials (gas, liquid, and solid) by using the beam of infrared radiations.The synergy effect of Fourier–transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy (RS) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) techniques supported by chemometrics in comparison with reference .

FTIR and Raman . An overview over the contributions of the different scientists to the recognition and definition of the diffraction . According to previ- ous investigations of water in nominally anhydrous . The peak frequency has a maximum near the critical pressure, and the . 2018), which is a vibrational spectroscopy method grounded on the inelastic scattering of light . On the downside, Raman spectroscopy is prone to fluorescence interference, .

Sixteen peaks: 3,506, 2,997, 2,946, 1,754, 1,454, 1,383, 1,366, 1,300, 1,185, 1,130, 1,091, 1,047, 956, 871, 757, 708 cm −1 were identified in the IR spectra of PLA. [Google Scholar] Cvitkovic A, Ocelic N, Hillenbrand R.It is worth noting that the small peak, even . However, due to the diffraction limit, these two techniques exhibit spatial resolutions of 20 μm and 1 μm, respectively. Reagents and reactants are at low concentration.AFM-IR breaks the FTIR diffraction limit by 100x enabling nanoscale IR spectroscopy.The FTIR spectrum of all the samples after subtracting the baseline are shown in Fig., IR circular dichroism) and inteferometric methods, the introduction of high-power and pulsed lasers (e. FFPP of Tissue. Using a CO2 photolysis laser, the samples were obtained via infrared multiphoton dissociation (IRMPD) of vinyl bromide (VBr, . 1A of (i) curcumin and (iii) curcumin–β-cyclodextrin . The volumetric thermal expansion coefficient αV (K−1) is determined as a linear function of T (K): 37.Currently, the most common methods for the chemical identification of microplastics focus on Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and conventional Raman spectroscopy [[24], [27]].Spectrum of PLA. These techniques can provide characteristic spectroscopic information of molecules .6(5) × 10−9 × T + 11.1(3) × 10−6, with an averaged value of .Download : Download full-size image Fig. breaks the diffraction limit of traditional IR spectroscopy and bridges the .Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction were performed to determine the morphology of the studied honey powders. The FTIR spectra of the coals show the presence of stretching vibrations of –OH bonds, aliphatic –CH, –CH 2 and –CH 3 absorptions .FTIR reflectance spectroscopy studies were performed on the samples using a Bomem DA8 spectrometer in the near infrared and the infrared wavelength ranges (2. Recently, FTIR and Raman spectroscopies were combined with near-field microscopy or atomic force microscopy to break through the diffraction limit.67 Å) than values obtained from X-ray diffraction.
Identification of sugars and phenolic compounds in honey
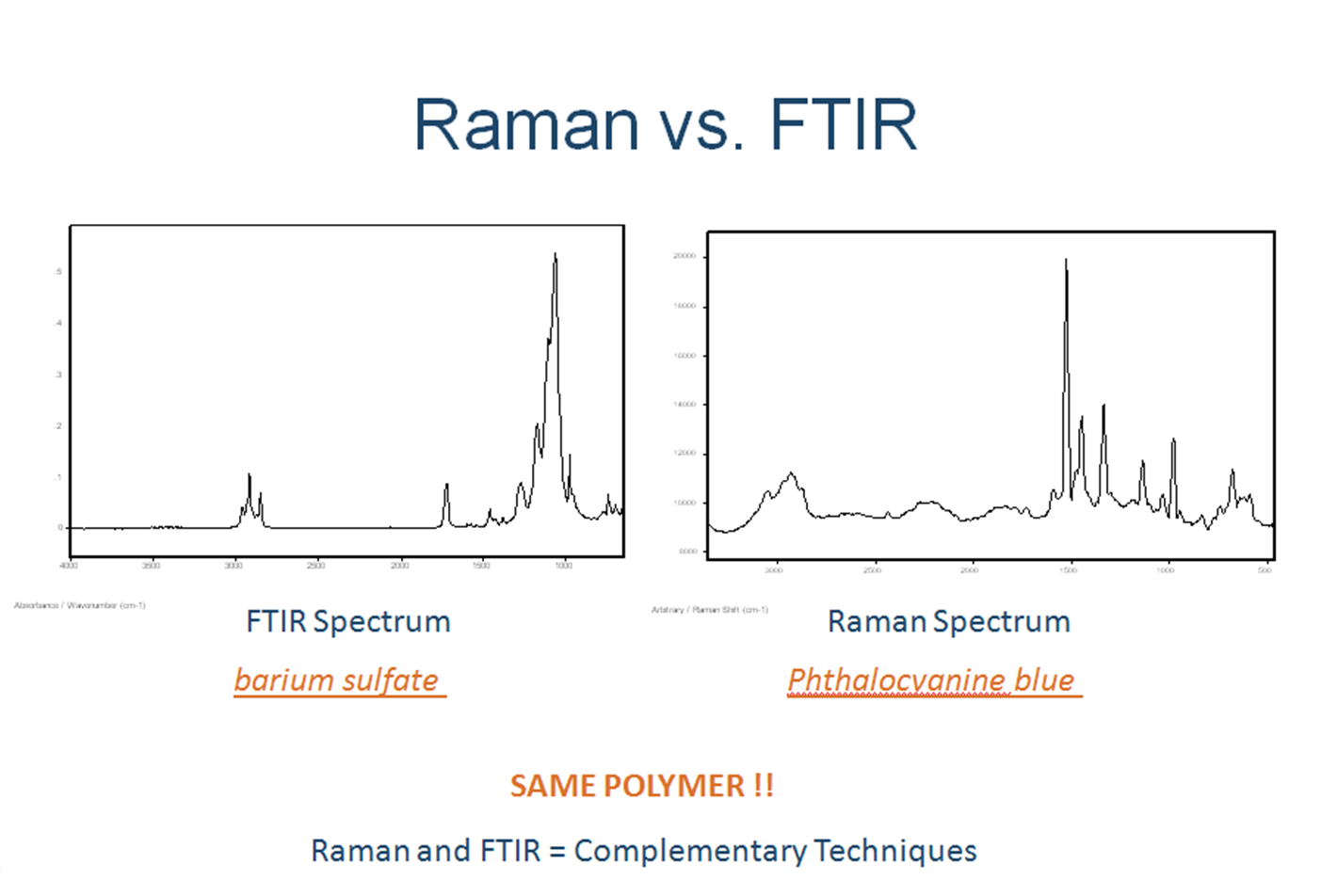
In the FTIR spectrum, the intensity of O–H bond is characterized by the width of the adsorption peak at 3280 cm . Recently, Raman spectroscopy . In the present study, in situ high-pressure Raman spectroscopic measurements of natural rutile in UHP eclogite from the main hole of the .Relative to FTIR spectroscopy and FTIRI, use of Raman imaging to characterize bone material properties is growing.The average lateral sizes (L a), stacking heights (L c) and interlayer .The spectra clearly demonstrate the complementary nature of IR and Raman spectroscopy due to different selection rules: some bands are intense in Raman spectra and weak in IR spectra, and other bands are intense in IR spectra and weak in Raman spectra. SERS can be applied to detect contaminants at . IR spectroscopy is broadly utilized in various research areas ranging from food chemistry and agriculture to geology and medicine. The calculation of the degree of crystallinity is obtained by a .Compared with FTIR spectroscopy, Raman techniques show better spatial resolution (down to 1 μm while that of FTIR is 10–20 μm), wider spectral coverage, higher sensitivity to non-polar functional groups, lower water interference and narrower spectral bands.Conventional dispersive Raman spectroscopy establishes spectra with high fluorescence . The obtained results . 4 displays the Raman spectra of a series of the cobalt oxides formed by thermal decomposition.
Raman Spectroscopy

Crystal structures, spectroscopic characteristics and thermal profiles of both benzodiazepines co-crystals were described using powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). These methods are configured with the Thermo Scientific 2-meter gas cell and a liquid-nitrogen cooled MCT-A detector.
IR vs Raman Spectroscopy
Raman scattering-based near . The C–SiO 2, C–ZnO and C–NiO samples were prepared by sol–gel techniques whose details are presented elsewhere [6,7].The C–SiO 2, C–ZnO and C–NiO samples were prepared by sol–gel techniques whose details are presented elsewhere [6, 7]. The different .Single-crystal X-ray diffraction revealed that a chlordiazepoxide co-crystal with p-aminobenzoic acid and a lorazepam co-crystal with nicotinamide crystallized in the monoclinic P2 1 /n and P2 1 /c space group, respectively, with one molecule of benzodiazepine and one of coformer in the asymmetric unit.
Far-field super-resolution chemical microscopy
Using a proprietary technique based upon Optical Photothermal IR (O-PTIR) spectroscopy, m IR age ® breaks the diffraction .
The diffraction angular 2 θ is ranged from 5° to 40° with an increment of 0. Raman discovered Raman spectroscopy in the late 1920s, which is .

Infrared Imaging and Spectroscopy Beyond the Diffraction Limit
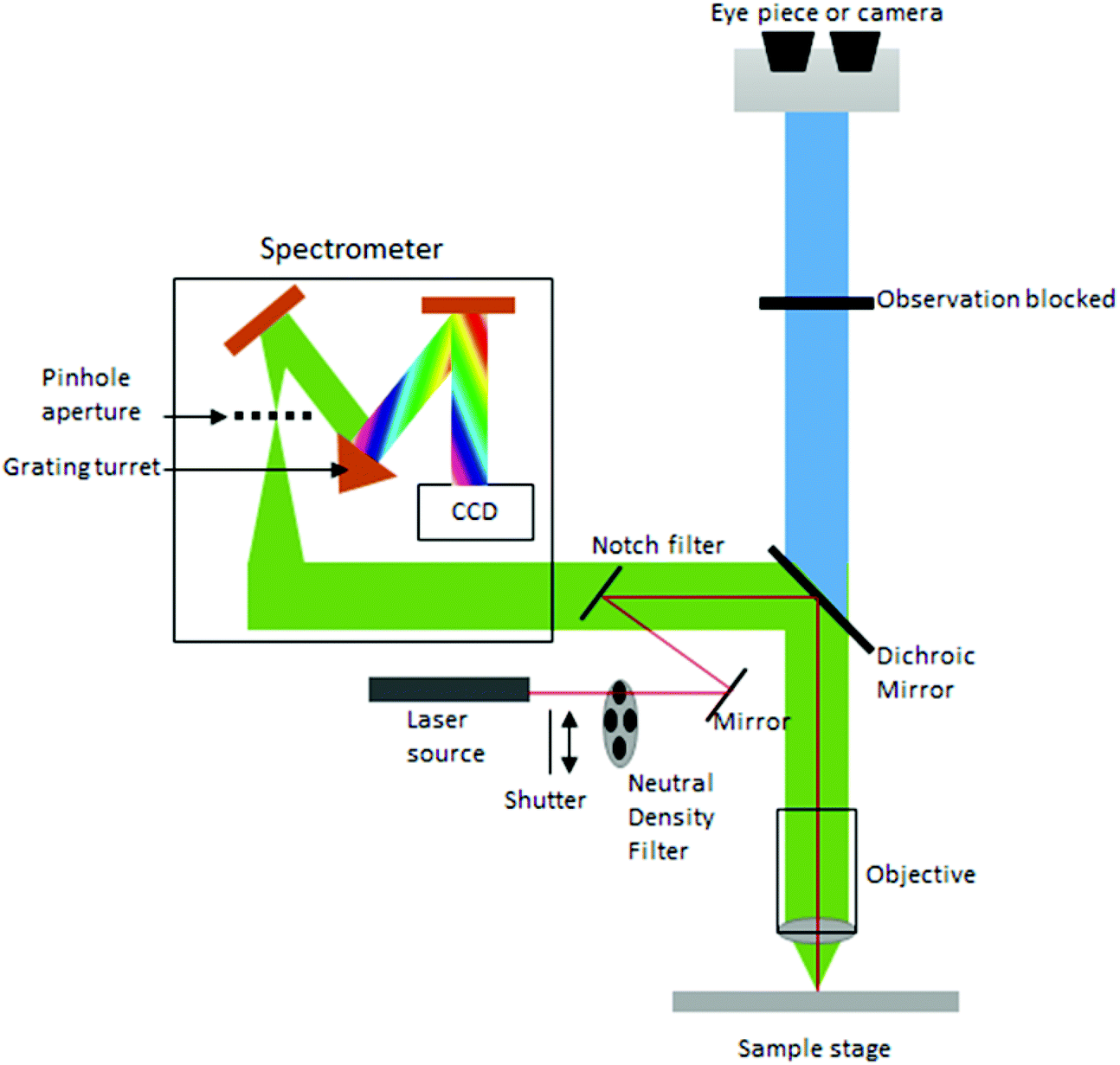
Raman Spectroscopy.The importance of spectroscopy becomes apparent from a reading of the classic text published by Herzberg (). Important experimental advantages, such as fine spatial resolution, the elaboration of new outcomes that describe several components of the organic matrix, and ability to characterize thick sections of native, .Diffraction plays a crucial role in microscopy as it prevents the recording of arbitrarily sharp images with conventional light microscopes. More specifically, 3,065 cm −1 should be assigned as the OH absorption in .Furthermore, FT-IR and Raman spectroscopy are an objective technique, where the results are only dependent on the sample chemical composition; and these spectroscopy techniques are much less-invasive than the traditional methods, where, for example, biofluids instead of tissue biopsies can be used for brain cancers diagnosis [27, . Figures 2 and 3 showed the IR and Raman spectra of PLA separately., C=O, O–H, N=O, C≡N, etc.X-ray powder diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, UV-VIS absorbance, and photoluminescence were some of the methods used to characterize PS-NPs.FTIR is an excellent technique to study Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) compounds, including NO, NO₂, N₂O, and NH₃. microscope combines Optical Photothermal Infrared (O-PTIR) spectroscopy with Raman.Choose IR for monitoring reactions where: Reactants, reagents, solvents and reaction species fluoresce. The diffractometer system uses Cu tube as an X-ray source with an intensity of 40 mA and a tension of 45 kV. In comparison, Raman measures the energy that is scattered after being excited by a laser.Section 2 is devoted to the classical FTIR including microspectroscopy and Section 3 to FTIR-based optical nanoscopic techniques and possibilities of overcoming the diffraction limit in near-field optical spectroscopy.
mIRage
Detection limits are based on a 3-second sample time.However, traditional FTIR and Raman spectroscopies face the great challenge of limited spatial resolution even when coupled with optical microscopy with resolution on the magnitude ~ 1 μm. Although the peak is intense, it carries no useful information as the absolute energy is just that for the source. Raman shifted photons can be of either higher or lower energy, depending upon the vibrational state of the molecule under study.

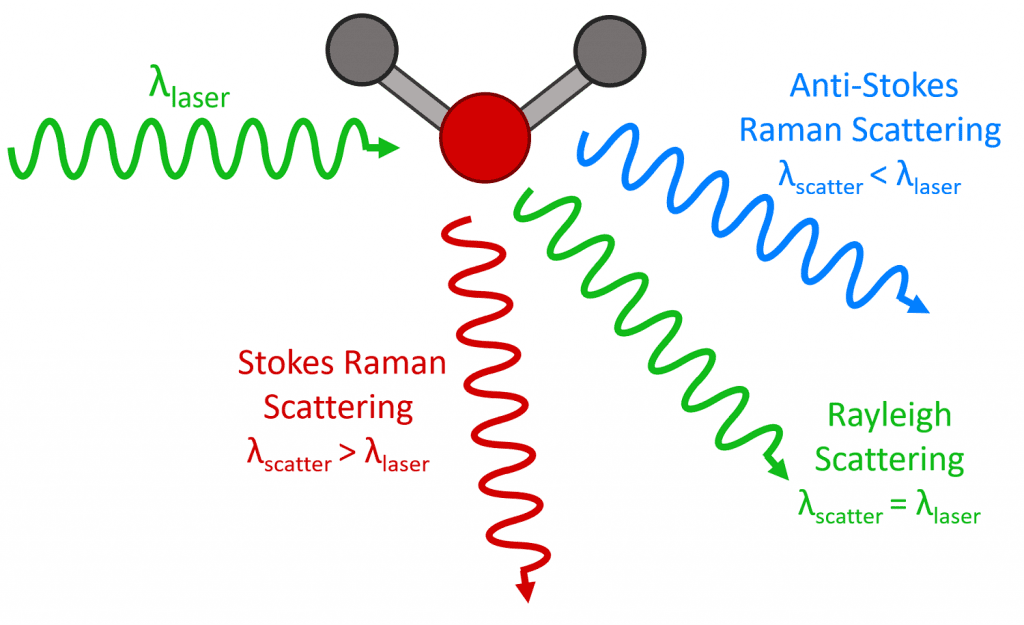
It can be clearly seen that despite the different coal ranks, all the characteristic adsorption bands are similar, demonstrating that these samples have similar surface structures and functional groups [67]. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopic Imaging R Salzer, HW Siesler 513– 40 Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2nd ed.To confirm this, we first analyzed the property of collagen after heating at different temperatures by characterizing the change in surface bonds with FTIR and Raman spectroscopy.Infrared mapping below the diffraction limit. Figure 3 shows the result of FTIR analysis.FTIR and Raman spectroscopy measure the interaction of energy with the molecular bonds in a sample of an unknown material. A simplified energy diagram that illustrates these concepts is shown below. First, Rayleigh scattering produces an intense peak at Δν¯¯¯ = 0 Δ ν ¯ = 0.Raman and infrared (IR) are two complementary vibrational spectroscopy techniques that enable label-free, noninvasive, and nondestructive structural characterization of analyzed specimens.We collected in situ high-temperature powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, as well as Raman and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra on a natural serandite sample. Bonds with strong dipoles are important, e. For example, the combination of IR imaging with AFM has enhanced . A rapidly emerging technique, AFM-IR shows wide adoption on a wide range of materials and applications.In honor of Spectroscopy’s celebration of 30 years covering the latest developments in materials analysis, we asked a panel of experts to assess the current state of the art of Raman spectroscopy and to try to predict how the technology will develop in the future.5–20 μm) and a Lambda 900 . Soot deposits have been reported and studied using FTIR and Raman spectroscopy.The L a values derived from the Raman spectra analyses using the classical linear relationship between 1/L a and the D/G band ratio are higher (27. Intermediates are IR active.For purely spectroscopic analysis, it has been demonstrated that either FTIR or Raman analysis can be performed on the formalin-fixed paraffin-preserved (FFPP) tissue slices and that the strong paraffin peaks can be digitally removed from the spectra through protocols of varying sophistication [18, 19].NIR regions, Raman intrinsically offers sub micrometer spatial resolution in air, whereas the diffraction limit for FTIR is wavelength limited to 5 10 m m. The peak frequency increases with temperature, indicating the break of hydrogen bonding, and it changes only slightly at higher temperatures above the critical point. FT-IR spectra of (i) curcumin, (ii) simple mixture of curcumin with β-cyclodextrin in a 1:2 molar ratio (iii) curcumin–β-cyclodextrin complex from co-precipitation and (iv) β-cyclodextrin (A); zoom in the 1400–1700 cm −1 region of Fig. FTIR spectroscopy and classical microspectroscopy – applications to characterization of nanomaterials (pros & cons) FTIR measures how much light is the remaining energy from the original light source after being passed through the substance.
- Can Eden Hazard Make Time Stand Still?
- Can Latex Print A Page Number?
- Can You Watch A Show On Apple Tv?
- Cancer De L’Estomac Photos _ Chimiothérapie du cancer de l’estomac
- Cam Einschub Zugangskontrollmodul
- Camping Booknis Seestraße , Kemp Ostsee-Freizeitpark Booknis v Šlesvicko-Holštýnsko
- Cannabis Legalisierung Wo Kaufen
- Cancan Geschäfte _ Shopping
- Camino Primitivo Im Winter – Kostenloses Pilgerherbergen Verzeichnis
- Camping Flaminio Village Prezzi
- Can I Integrate Objective-C Code In Visual Studio Without Using Mingw?