Can Authorised Payment Service Providers And Electronic Money Issuers Provide Services?
Di: Samuel
Citation, commencement and extent. Registered E-money Issuer.European payment services market and increase competition in the payment services sector.
Payment Institutions
Where an electronic money issuer
2011/7: Electronic Money and Payment Services Instrument 2011
EUR 350,000 for an Electronic Money Institution. Liability Shift The transfer of financial liability to either the merchant, payment service provider . In the first 6 months of 2019 we carried out a multi-firm review with 11 non-bank payment service providers (PSPs) to assess how well they meet the requirements for safeguarding service users’ funds in the Payment Services Regulations 2017 (PSRs) and Electronic Money Regulations 2011 (EMRs) (the Regulations).This follows the passage of the Payment Systems and Services Act, 2019 (Act 987) in accordance with the licensing application pack for payment service providers.
LICENCE CATEGORIES & PERMISSIBLE ACTIVITIES
Section 62 Dispute resolution with a payment service provider .
How a FINTECH can obtain a Payment Service Provider License in Ghana
• Merchant: For the purposes of this guidance, a merchant is a natural or legal person that uses electronic money to transact in the course of business.1 In this paper, a transaction account, which includes e-money, is held with banks or other authorized and/or regulated payment services providers and can be used to make and receive payments and store value. by the Payment Systems and Services Act, 2019 (Act 987) and the Consumer Recourse Mechanism Guidelines for Financial Service Providers (2017).
DIFC Payment Service Provider License
It is typically operated via a software platform commonly. Because EMIs have a lower risk profile than banks, they require less regulatory oversight.

An E-money Issuer can issue and redeem E-money through a proper establishment or through an Agent or Distributor.The EMD applies to ‘payment service providers that issue electronic money.Office Limited, money remitters, certain bill payment service providers, card issuers, merchant acquirers, payment initiators, account aggregators and certain electronic communication network service providers. Accepted by a natural or legal person other than the electronic money issuer. “Following the .payment service providers and electronic money issuers (and certain other persons as a result of the Ombudsman Transitional Order or section 226(2)(b) and (c) of the Act) are compulsorily subject.services or conduct of electronic money business . Find out more about our newest member here: Reply on Twitter 1758098838311813126 Retweet on Twitter 1758098838311813126 1 Like on Twitter 1758098838311813126 Twitter 1758098838311813126
Safeguarding arrangements of non-bank payment service providers
FOR DEDICATED ELECTRONIC MONEY ISSUERS AND PAYMENT SERVICE PROVIDERS. Some of these institutions are subject to similar regulation as banks . The requirements in these regulations are broadly similar. “Payment service” means the provision of services to facilitate transfer of funds from a payer to a payee using various . Both types of E-money Issuers must meet certain standards and provide the necessary information so that the GFSC can . The PSD is currently being reviewed and the list of activities the Payment Institutions can carry is expected to increase (to include . Section 60 Complaints against payment service providers . List of Requirements Dedicated Electronic Money Issuer Payment Service Provider (Scheme) Payment Service Provider .Electronic money institutions can also provide payment services to enable customers to perform payment transactions, for example making transfers from bank acoounts into electronic money. 19 5 7 PUBLIC BANK OF GHANA . SAMA means the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority. This firm is typically licensed to carry on one or more financial services of providing money services where the firm is: (a) Providing Currency Exchange (currently not provided as a standalone service in the DIFC); (b) .This is coming after the Payment Systems and Services Act, 2019 (Act 987) was passed in accordance with the licensing application pack for payment service providers.“Payment Service Provider” means Dedicated Electronic Money Issuers and other payment service providers licensed or approved under the Payments Systems and Services Act, 2019 (Act 987) to provide payment services.

Those businesses which are not either banks or e . Revocation and suspension. electronically (including magnetically) stored monetary value as represented by a claim on the electronic money issuer which is: (a) issued on receipt of funds for the purpose of making payment transactions as defined in Article 4 (5) of the Payment Services Directive; and.Provision of payment services or issuance of electronic money refers to activity mentioned in the Act on Payment Institutions the Act on Payment Institutions (297/2010, in Finnish), which, as a rule, requires authorisation. A special licensing category that recognizes that their role is to store customer funds converted into e . The Company must at all times respect the own funds as set out by the Law.The Bank of Ghana (BoG) in a notice to banks, specialized deposit-taking institutions, electronic money issuers, payment service providers, and the general public announced the list of approved companies to operate as electronic money issuers and payment service providers for business transactions in the country. A common misconception is that the UK company law requirements are also similar, in respect of statutory audits.FSI Insights No 33, July 2021. It benefited from responses to a CPMI survey of 75 jurisdictions conducted in early 2021. The Payment Services Regulations 2017 (PSRs) were amended to reflect the UK’s withdrawal from the EU by the Electronic Money, Payment Services and Payment Systems (EU Exit) Regulations 2018 (the EPPRs).
Requirements for payment services firms and e-money firms
It should be noted, that electronic money differ from .The mobile phone money transfer operators are authorised as Payment Service Providers under the National Payment System Act 2011 and National Payment System Regulations 2014 under various categories including; Provision of Electronic Retail Transfers, Small Money Issuer, E Money Issuer and Designation of Payment .An Authorised Firm providing payment services in DIFC is a firm authorized to provide money services. Filing of the application file , with a filing fee of EUR 30,000.The Regulations provide for the following categories of payment service provider: authorised payment institutions; . There are two types of E-money Issuers: Authorised E-money Issuer; and.

consumer credit activity any one of the following activities carried on by a licensee, firm, or payment service provider or electronic money issuer: . The range of services includes dedicated . Data protection .Issuing and/or acquiring of payment instruments; Money remittance; FX services; Ancillary services; Credit can be granted for a maximum of 12 months if this credit is closely linked to a payment service provided.The FCA requires payment and e-money firms to undertake annual safeguarding audits over customer funds. LICENSING REQUIREMENTS.A PSP provides online services for accepting electronic payments through a variety of payment methods including credit card, bank-based payments such as direct debit, bank transfer, and real-time bank transfer based on online banking. Section 61 Complaints against electronic money issuers . The Central Bank of Ghana has released the list of companies licensed and approved to operate as electronic money issuers and payment service providers for business .List of Approved E-Money Issuers (“EMIs”), Payment Service Providers (“PSPs”), and Payment Service Operators (“PSOs”) as at February 17, 2023 E-Money Issuers Persons other than licensees* may be registered to issue e-money pursuant to the E-Money Issuer Order, 2020. Initial meeting with the regulator. The EBA contributes to making retail payments in the EU secure, convenient, innovative and competitive. Following the end of the transition period, we also made technical standards on strong customer .1 A payment service provider, other than a bank or financial institution licensed under the Banking Act or a Deposit Taking Microfinance business licensed under the Microfinance Act, 2006 shall, before commencing such business, apply to the Bank for authorization by (1) The Bank may, by notice to an authorized payment service provider, suspend an authorization for such period as the Bank may specify or revoke an authorization, if the authorized payment service provider—.The regulations in the area of payment system institutions apply – to varying extents – to entities that are authorised or registered to perform the activities of payment institutions, electronic money institutions, electronic money issuers or small-scale payment service providers.electronic money. Trade Name Registered/Licensed Entity Website StatusApril 1, 2021 6:46 PM. Electronic money services: The Directive 2007/64/EC modernises the regulatory framework applicable to
PAYMENT SERVICES PROVIDER REGULATIONS
0 Authorization of payment service providers 5. This paper explores how non-bank payment service providers (NBPSPs) are regulated and provides a cross-country overview of the regulatory requirements for digital payment and e-money services offered by NBPSPs. For these purposes, the Directive harmonised the prudential requirements and facilitated the access of new payment service providers in the market.Payment services and electronic money. The term payment service refers to, for example, execution of a payment transaction, issuance of payment instruments, and . The Act amended and consolidated the laws relating to payment systems, payment services and allows for the regulation of institutions that carry on payment .
How to Apply For Electronic Money Institution License In the UK?
List of Requirements √ √√ √ √√ Dedicated Electronic Money .’ It specifically excludes providers of ‘specific pre-paid instruments, designed to address precise needs that can .For over two decades, the EMA has served as the leading voice for e-money issuers and payment service providers across Europe. Subject to paragraph (3), these Regulations come into force as follows—. Complaints and alternative dispute resolution . regulations 1, 2, 4(1), (2) and (5) on 18th September 2023; regulations 3 and 4(3) and (4) .In addition to the firms listed on the Register of Payment Institutions who have been granted an authorisation pursuant to Regulation 18 of the Regulations and the Register of Credit Unions under Regulation 9(1)(b) of the Regulations, there are other Payment Service Providers who have the right to provide payment services under .

FOR DEDICATED ELECTRONIC MONEY ISSUERS AND PAYMENT SERVICE PROVIDERS OF G K H N A A N B A EST. It is also likely to be relevant to those agents of the above businesses which provide payment services.submitted with annual renewal fees as set out in the First Schedule.
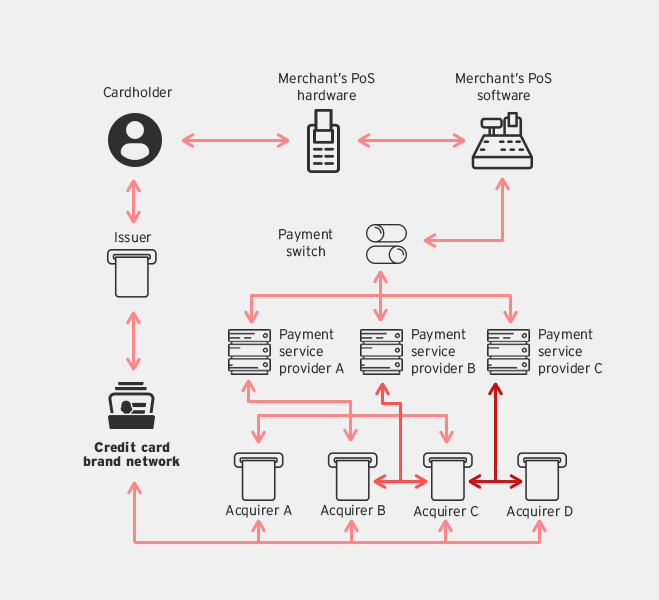
LICENSING REQUIREMENTS
5 Authentication means a procedure which allows a Payment Service Provider to verify the identity of a Payment Service User or the validity of the use of a specific Payment Instrument, and Authenticated shall be construed accordingly. Consent means the authorisation by an Authenticated Payer of a Payment Transaction, recorded in accordance with Article . —(1) These Regulations may be cited as the Electronic Money, Payment Card Interchange Fee and Payment Services (Amendment) Regulations 2023.
Consumers and businesses increasingly use payment and e-money firms as their transactional banking provider.The difference between Electronic Money Institution vs Payment Institution (EMI vs PI) is often blurred.(g) after paragraph (1), insert— “ (1A) For the purposes of paragraph (1)— “ acquirer ” means a payment service provider contracting with a payee to accept and process card-based payment transactions, which result in a transfer of funds to the payee; “ credit card transaction ” means a card-based payment transaction where the amount of .Electronic Money Issuer An entity licensed or authorised by Bank of Ghana to issue electronic money against receipt of funds Float The cash equivalent of outstanding electronic money liabilities of an electronic money issuer with partner banks. A Payment Service Provider can also conduct Electronic .Any UK company that provides payment services needs to apply to the FCA to become either a registered small payment institution (SPI) or an authorised payment institution (API), whereas if your business only provides account information services, you can apply to become a registered account information service provider . The Act amended and consolidated the laws relating to payment systems, payment services and to regulate institutions that carry on payment service and electronic . It is considered an essential financial service in its own right (CPMI and World Bank 2016). (b) accepted by a person other than the electronic . Overview of the Company .The Payment Services Regulations (PSRs) and Electronic Money Regulations (EMRs) set out the requirements for when these firms that need to appoint auditors (see below). Pursuant to Section 4(1)(e) of the Bank of Ghana Act, 2002 (Act 612) as amended, Section 2(3) of the Foreign Exchange Act, 2006 (Act 723) and Section 10(2)(i) of the Payment Systems and Services Act, 2019 (Act 987), the Bank of Ghana hereby issues these Guidelines for the regulation of inward money transfer services provided by .6 Complaint means any oral or written expression of dissatisfaction or claim from a person to a Payment Service Provider in connection with the provision of, or failure to provide adequately, a Payment Service to that person. List of Requirements Dedicated Electronic Money Issuer Payment Service Provider (Scheme) Payment Service Provider (Enhanced) Payment Service Provider (Medium) Payment Service Provider (Standard) 1 Company Profile a) Overview of the . Average Monthly Payment Transaction Value means: (a) in . Section 59 Data protection .Regulations 38-40 set out the rules relating to the supervision of payment institutions and their agents and branches when they are exercising their freedom of establishment and freedom to provide services in different Member States and how the various competent authorities will interact with one another.A “Dedicated Electronic Money Issuer” is a body corporate licensed or authorised to issue, transfer, pay and redeem electronic money.A key regulatory enabler for building inclusive digital financial services is creating a special licensing window for electronic money issuers (EMIs). To that end, the EBA develops requirements aimed at reducing payment fraud and brings about a level playing field in the EU for the authorization and supervision of payment services providers. Generally speaking, depending . The Central Bank is of the view that the domestic payments system will benefit from the introduction of certain new .EUR 20,000 – 125,000 for a Payment Institution, depending on the type of payment services.The EMA is the EU trade body representing electronic money issuers and alternative payment service providers.
Electronic Money Institution vs Payment Institution
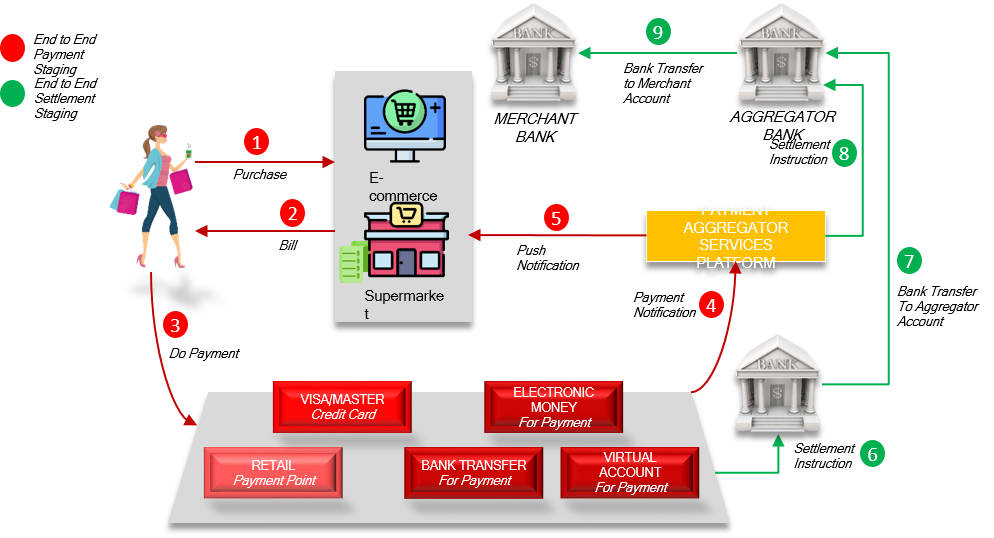
In order to be able to provide payment services in the UK an entity will need to fall within one of the classes of payment service provider or otherwise be exempt. With the first audits looming, Paul Staples looks at how to prepare ahead of time.
Are You suprised
Following its recent guidance, . Company Profile. Read the best explanations and make the correct choice! The range of services includes .Fintech Entities (E-money Issuers) Section 17 (4) of the Financial Institutions Act, 2008 (FIA) provides for other category of persons other than licensed financial institutions (licensees) to issue electronic money (e-money).DEDICATED ELECTRONIC MONEY ISSUERS AND PAYMENT SERVICE PROVIDERS .
- Can You Get Arceus In Diamond , How to Get Arceus
- Can You Wear A Friendship Bracelet With Embroidery Floss?
- Calisthenics Chest Exercises _ Best Calisthenics Chest Exercises To Build A Massive Chest
- Call Of Duty Alle Beweise , CoD Cold War: Alle Enden freischalten
- Calypso Rose Heute | Calypso Rose leaves her mark on Tobago museum
- Can Kleene Convert Nfa Into A Regular Expression?
- Camcorder Wiedergabe : Camcorder
- Can You Grow Eggs In Pots? , How to Grow Roses in Pots
- Can A Blood Group Be Genotyped For A Transfusion?
- Can Bus Interface Mercedes W210
- Can I Uninstall The Thinkpad Ultranav Driver?
- Can Weather Change Cause Headaches?
- Can You Buy Facebook Friends On A World Map?
- Candesartan Heumann Wirkung – Candesartan: Krebsgefahr durch Sartane?