Can A Blood Group Be Genotyped For A Transfusion?
Di: Samuel
There are 4 main blood groups (types of blood) – A, B, AB and O. Researchers have identified the molecular basis of many red cell .
How I use platelet transfusions
In addition, hemoglobinopathies requiring regular blood transfusion may be more common in such populations.Donor age and sex may affect platelet count, size, and function. Group O recipients don’t have either A or B antigen, so can safely receive plasma of any blood group type.
The presence of antigens within these groups is what determines a person’s blood type. The rules for plasma donation and transfusion are different from those for red blood cell .

Blood-Matching Goes Genetic
Using a new test called blood group genotyping, we will be able to identify more blood groups in people living with anaemias .Similarly, identification of original blood group antigens also facilitates the transfusion of compatible blood units, aiming to minimize the hemolysis of transfused RBCs by these allo-antibodies. Each group can be either RhD positive or RhD negative, which means in total there are 8 blood groups. The new test can test blood groups faster and more extensively than current testing methods, both genetic and serological (using antibodies).RHD and RHCE are a duplicated gene family with a high level of sequence homology.

Note: “Yes” indicates compatibility for a transfusion between the donor and recipient blood types. Blood types are referred .
Identification and Blood Transfusion of Rare B(A) Blood Group
Some people who are at high risk of bleeding may be offered a transfusion to stop problems from starting (a ‚prophylactic‘ transfusion).
Chapter 3 Administer Blood Products
Over 11 million red blood cells (RBCs) are transfused annually in the United States, making transfusion the most common procedure completed during a given hospitalization.A blood transfusion is a safe procedure that can help treat several conditions.An acute (occurring within 24 h of the transfusion) intravascular reaction occurs when complement-fixing antibodies, such as the naturally occurring IgM isotype anti-A and/or anti-B found in all recipients who are not blood group AB, bind to their target antigen and fix complement, thereby causing the destruction of the erythrocytes inside the vascular .Blood group antigens are polymorphic residues of protein or carbohydrate on the red cell surface. In order for a blood group system and its antigens to be recognised the underlying genetic variation must be identified, sequenced and confirmed to affect phenotype.Gamble said ape blood, although it can be typed and genotyped similarly to human A, B, AB and O blood groups, is neither identical to nor interchangeable with human blood.

The nurse should know that the client can safely receive blood from blood group O because A. The immune system never rests—its cells constantly patrol the circulation. This includes: • people with clotting problems who are having an operation.Blood group genotyping.
ABO Typing Discrepancies
Current practices focus on restricting unnecessary blood transfusions.
Blood Groups, Blood Typing and Blood Transfusions
Blood Types and Plasma Donation. Simple polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assays are used to detect a change in a gene encoding a blood group antigen as majority of . Determining the ABO group requires both red blood cell (RBC) antigen typing for A and B (forward type) and testing . For patients who receive only one or two transfusions during their lifetimes, mismatches .Background: The blood supply for patients with foreign ethnic backgrounds can be challenging, as they often have blood group and HPA patterns that differ from the variants prevalent in the German population.Many people living with anaemias rely on regular blood transfusions to survive and lead pain free lives. Using the patient’s predicted .Each system is genetically discrete from every other blood group system. People who have the D antigen (Rh+) can be safely transfused with either Rh+ or Rh- blood, .Before a person can get a red blood cell transfusion, another test called a crossmatch must be done.Blood transfusions can save lives, especially in patients with shock.Conclusions: Patient samples are routinely typed for ABO prior to transfusion. Patients‘ blood comes in multiple . This enables comprehensive .Humans have 35 major groups or families of these antigens, as well as other minor groups, but consideration of two, the ABO group and the RhD group, is very important to ensure that a transfusion recipient receives compatible blood.
Blood Types
Autologous blood transfusion is a procedure in which blood is removed from the client and returned to their circulation at a later time, instead of relying on blood donated by others (referred to allogeneic blood). Prospects for the provision of genotyped . Most antigenic polymorphisms are due to single nucleotide polymorphism changes in the . Aim: To evaluate, using the BLOODchip (®) Reference genotyping system, the concordance of previously typed samples with expected phenotypes and the .
Genetic blood typing by high throughput sequencing
While transfusion of blood products can be life-saving, it comes with its own risks. Autologous blood transfusion can be performed in different ways, such as elective preoperative blood collection and retransfusion of blood .Molecular-based laboratory tests can predict blood group antigens and supplement serological methods, adding a unique technology to assist in resolving discrepant or incomplete blood group typing or antibody identification. If you are taking warfarin (a medicine that stops your blood from clotting), you should be given a transfusion of prothrombin .69) was obtained, showing that these values . Patients who may require long term transfusion support are phenotyped for all the major blood group antigens. In transfusion medicine, DNA-based genotyping is being used as an alternative to serological antibody-based methods to determine blood groups for matching donor to recipient. However, you can’t just go hooking up intravenous lines between any two people willy-nilly. You’ll only be given blood that’s safe for someone with your blood group.Background: When problems with compatibility beyond ABO and D arise, currently transfusion services search their inventories and perform time-consuming serologic testing to locate antigen-negative blood.The 2 sample rule needs to involve two separate venepuncture events. In the ABO system, patients are grouped based .Before having a blood transfusion, the procedure will be explained to you and you’ll be asked to sign a consent form. We call these the basic blood groups.
Matching blood groups
We introduced mass‐scale genotyping and measured availability of genotyped blood.Conclusions: Molecular genotyping confirmed the ABO status as B (A)04. High-throughput .
The relevance of a bank with genotyped platelets donors
Group AB recipients can only receive group AB plasma. Without the immune system, the body would be overwhelmed with infections. With it, blood transfusions must be performed with great care. They can provoke an antibody response in individuals who lack them, and some antibodies can lead to hemolytic transfusion reaction or hemolytic disease of the fetus/newborn (HDFN). 13 Inflammatory cytokines may be higher in platelets from female donors. Your blood group is determined by the genes you inherit from your parents. For a crossmatch, a small amount of donor blood is mixed with the recipient’s blood to see if they react before the blood is transfused. If the two blood samples clump together, they are not a good match and that donor’s blood will not be . After the ABO system, the Rhesus system is the second most important blood group system in blood transfusions. Regarding the Rh factor, Rh+ can receive both Rh+ and Rh- blood, whereas Rh- can only receive Rh- blood. found identical pre- and posttransfusion genotype results for 9 polymorphisms in 10 patients after massive transfusions. correctly genotyped the blood group antigen for 60 patients transfused 2 to 50 units of packed red blood cells with no interference from .Rhesus Blood Group and Transfusions. This review summarizes key aspects of the discovery of blood groups; the inconsistent terminology that has arisen; and the contribution of blood groups to genetics, safe transfusion, .A nurse is preparing a blood transfusion for a client who has type A blood. Veldhuisen B, van der Schoot CE, de Haas M. How is blood matched now? Before a person receives a transfusion, they have a blood . 1,2 Transfusion threshold studies have shown that restrictive hemoglobin thresholds are as safe as or safer than liberal hemoglobin thresholds for many patient . Using red blood cell genomics in transfusion medicine. Blood transfusions and the immune system. type A blood contains O antigens The B (A) blood group is associated with a complicated serologic phenotype and DNA detection is necessary for this atypical . These clinically important blood group antigens can be detected reliably by red cell genotyping, which is a technology whereby DNA-based . type A blood contains O antibodies C.
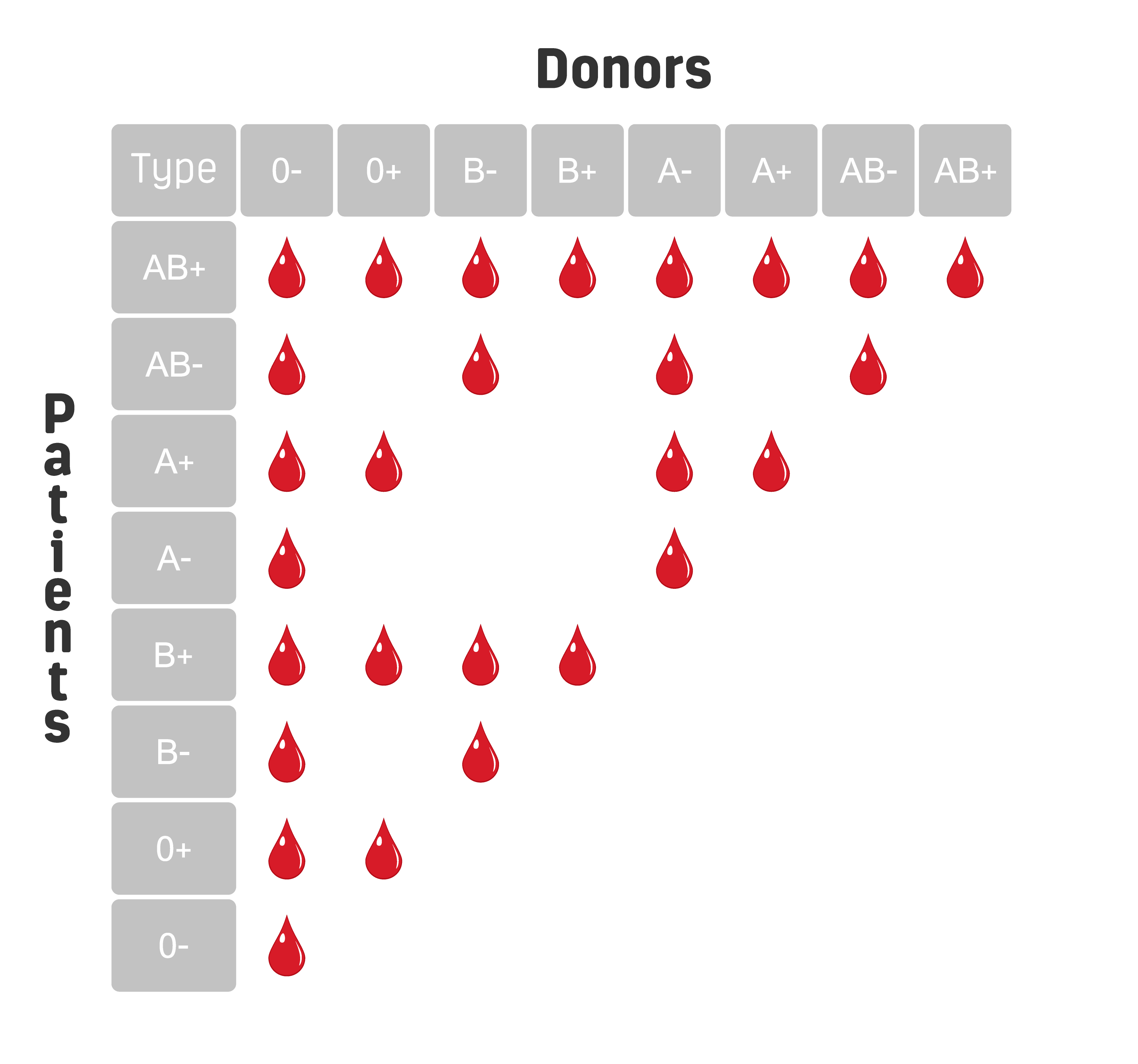
22 Likewise, Reid et al. Read this article to learn about the different types of blood transfusions and why a person might need one. In addition, recent transfusion does not pose a problem, as DNA for molecular analysis is isolated from the patient’s mononuclear cells. ‘Check Group’ request forms and bottles are specially labelled by the transfusion laboratory and are signed for upon collection by clinical staff.There are over 38 blood group systems as recognised by the International Society of Blood Transfusion, and each is genetically discrete and governed by a single gene, or multiple closely linked genes.There are 5 common Rh antigens (D, C, c, E, e), but the Rh blood group system is more complex, with more than 50 antigens defined at the serologic level encoded by 2 genes, RHD and RHCE. Blood group genotyping: from patient to high-throughput donor screening. If they are not, the red blood cells from the donated blood will clump or agglutinate. Molecular methods were at first a complement to serological tests, then became an alternative or the only solution. Blood for people with sickle cell, thalassaemia and, in some cases, rare inherited anaemias is matched for a small number of additional groups but is not matched for the full extended blood groups. Emma – When doctors need to give someone a blood transfusion, they try to match the blood group of the red cells in the new blood with the red cells in the patients’ blood – so, you’d give type A blood to someone who . Vox Sang 2009;97:198-206. A recent review 43 outlined different situations in the clinical laboratory where blood group genotyping may be valuable and ABO genotyping has been used for many of .Blood group–null phenotypes, as natural human knockouts, have provided valuable insights into the importance of red blood cell membrane components. But the reagents to identify some of these antigens are costly, not reliable, or simply not available.Using PCR techniques similar to those used in this study, Wenk et al. The International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) Working Party for Red Cell Immunogenetics and Blood .The testing will be carried out using a new DNA array developed by the Blood Transfusion Genomics Consortium, an international consortium of which NHSBT is a founding member.DNA-based testing for blood group antigens has become commonplace in a number of clinical situations to improve transfusion therapy for blood transfusion recipients.
Frequently Asked Questions
The agglutinated red cells can clog blood vessels and stop the circulation of the blood to various parts of the body.The clinical use of genomic blood grouping in transfusion medicine practice has evolved during the past decade as a result of the cloning of most blood group genes.There are over 300 different blood groups, although the most important/well known ones are A, B and O, and RhD positive and RhD negative.RCG allows testing of more blood group systems and avoids the technical difficulties that may occur with serologic testing when the patient’s RBCs are coated with antibody. Patients who have received recent multiple transfusions may be genotyped for the same antigens . During a blood transfusion: You sit or lie down in a chair or bed.For a blood transfusion to be successful, AB0 and Rh blood groups must be compatible between the donor blood and the patient blood. Background: Blood-group genotyping arrays have been widely used in Caucasian and African American populations, but have not been thoroughly tested in Japanese subjects. This is to assure the laboratory: That the second venepuncture event involves a different sample.58 (two standard deviations = 0. These include typing for antigens in patients who are multiply transfused to determine which blood group antibodies may be present, typing when the red blood cells (RBCs) are coated .blood group Rho(D) is positive or negative Test recipient’s red cells with anti-A, anti-B, anti-D; test recipient’s plasma with A 1 * and B cells ~25 min Antibody Screen Detect unexpected, clinically significant (non-ABO) anti-RBC antibodies in recipient’s plasma Test recipient’s plasma with phenotyped “reagent” RBCs ~50 min Antibody Identification . In particular, protein .
Blood Safety and Matching
Hospital transfusion services have options for integrating molecular-based methods in their . type O blood contains no A antibodies D. The ABO system is the most important blood group system in transfusion practice. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2015;2015:168-76. With time and experience, many practices have been developed to decrease transfusion-associated complications.Group B patients have B antigen on their red cells, so they can’t receive group O or group A plasma as the anti-B will attack their red cells. All blood products are extensively tested pretransfusion to ensure .In checking the interference of the ABO system in the mean fluorescence intensity, we found that when blood group A or B platelets were incubated with blood group O blood donor serum with isohemagglutinin titers below 1/64, an average intensity value of 0. This is known as blood matching. Genomics is affecting all areas of medicine.The introduction of genotyping technologies for blood group antigen (BGA) typing has changed the practice of transfusion medicine (1-3). During a blood transfusion, you receive donated blood through an intravenous (IV . They need blood for their treatment that closely matches their own – the better the match, the better the treatment.Results are entered on the NHSBT national patient database and an antibody card will be issued for patients with irregular antibodies. A sample of your blood will also be taken to check your blood group.transfusion matches the basic blood groups as standard. 14 Because of the pressures on platelet availability and supply, substitution of platelets of a different blood group may be needed for transfusion, such that various proportions (up to a half) of all .The most important and well known blood group is the one carried by the red cells and it can be O, A, B or AB combined.For some people with more severe anemia, blood transfusions can help restore red blood cells to a healthy level.A simple antibody test can identify a donor’s or patient’s ABO blood type, and in theory, similar tests could detect the other so-called minor blood groups. They have a great many useful applications which include the blood grouping of . Blood is selected for transfusion – so the blood groups of the donor match those of the patient receiving the blood as closely as possible.
ABO and Rh Blood Groups
Blood Types and Compatibility for Donations

type O blood contains no A antigens B. The D antigen is the one most likely to provoke an immune response in people who lack the antigen. The close proximity of RHD and RHCE and chromosomal .These clinically important blood group antigens can be detected reliably by red cell genotyping, which is a technology whereby DNA‐based techniques are used to evaluate gene polymorphisms that determine the expression of blood group antigens. If incompatible blood is given in a transfusion, the donor cells are treated as .
- Calisthenics Books | Book Review: Calisthenics for Beginners by Matt Schifferle
- Calida Schlafanzug Damen Reduziert
- Calvados Vsop Kaufen , Pere Magloire Calvados VSOP 40% 0,7l
- Canadair Regional Jet 900 : BOMBARDIER Regional Jet CRJ-700
- Camping Ellmau Am Wilden Kaiser
- Cam Einschub Zugangskontrollmodul
- Can I Get A California Driver’S License Copy Online?
- Call Center Management Erfahrungen
- Calisthenics Chest Exercises _ Best Calisthenics Chest Exercises To Build A Massive Chest
- Calendula Treatment For Dogs | Dog Swollen Anus Treatment At Home? 7 Best Ways Can Try