Battle Of Messines 1916 : Chapter V — The Battle of Messines
Di: Samuel
Official First World War photographer, Henry Armytage Sanders, took this photograph on 26 June 1917. Meticulously planned, the action started on the 7th of June with the detonation of huge underground mines that rattled the teacups in London and killed 10,000 German soldiers. The attack was meant to capture a ridge which ran north from Messines village, past .The Battle of Messines was one of New Zealand’s finest hours of WWI.Arriving in France on 9 June 1916, the 47th entered the trenches of the Western Front for the first time on 3 July. As part of the preparations for the Battle of Messines in June 1917, the 183rd Tunnelling Company began work on deep dugouts in the Ypres Salient. By 14 October the British had managed to establish a continuous front from Ypres to La Bassée Canal. It participated in its first major battle at Pozieres. Initial French preparations to raid the hill were continued by the British 28th . The joint explosion of these mines ranks among the largest artificial non-nuclear explosions.The Bluff is a mound near St Eloi, south-east of Ypres in Belgium, created from a spoil heap made during the digging of the Ypres–Comines Canal before the war. After their string of bloody defeats over 1915 and 1916, Messines would prove the ultimate test for the Australians.
Mines in the Battle of Messines (1917)
By 1916, commanders had realized the folly of sending raw men to the front and unlike the 10th (Irish) Division, the 16th (Irish) Division were somewhat prepared for trench warfare.Atak minowy pod Messines – seria 19 wybuchów min umieszczonych przez wojska brytyjskie pod pozycjami niemieckimi, pierwszego dnia bitwy pod Messines w zachodniej Belgii, 7 czerwca 1917.The Actions of the Bluff were local operations in 1916 carried out in Flanders during the First World War by the German 4th Army and the British Second Army.The mines were detonated .Hulluch, April 1916 The 16th (Irish) Division comprised of different battalions from various Irish regiments, including the 8th and 9th Royal Dublin Fusiliers.As part of Plumer’s battle tactics, by June 1916, 24 mines had been dug beneath the Wijtschate-Messines Ridge to depths of 20-30 metres and packed with almost 396,530kg of explosives. 9th October: Battle of Poelcappelle: 1918 9th (Service) Battalion.
Film: fighting at the Somme and Messines
The Capture of Hill 60 (17 April – 7 May 1915) took place near Hill 60 south of Ypres on the Western Front, during the First World War.Planned from 1916, the Battle of Messines was to be a prelude to the Third Battle of Ypres, which had the high ground of the Passchendaele Ridge to the north-east of Ypres as its objective. providentially as it were, frustrated .Flanders Fields. W wyniku przeprowadzonych detonacji ponad 455 . The 33rd’s casualties amounted to 92 killed in . In addition to men lost to shellfire, just over 1,000 men were incapacitated by the gas of whom 120 died soon afterwards.
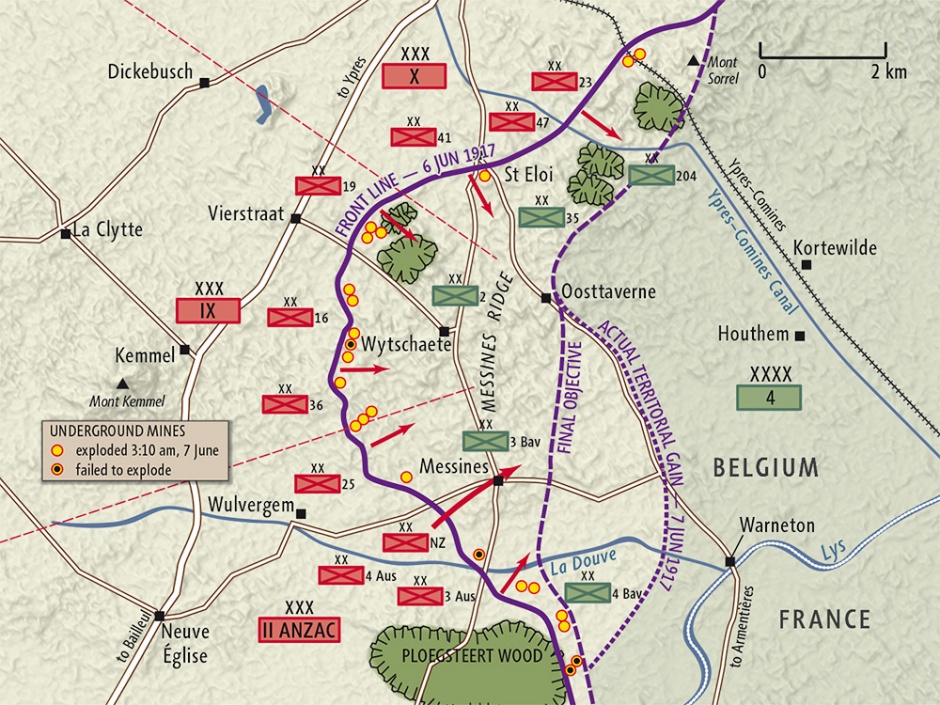
Its goal was to seize the Messines Ridge, securing the flank of the Ypres. Hill (Hill 63) south of the Douve valley and Kemmel Hill, 5,000 yd (2. The underground building activities of the Royal Engineer units .
7 June 1917; The Battle of Messines
From 14 to 15 February and on 2 March . Newspapers described it as . 7 – 14 June 1917: the Battle of Messines. With the British now advancing down the east slope of Messines Ridge, the Germans had to respond.
Battle of Messines (1917)
The Battle of Arras: lines from April 9th to May 17th, 1917. The Irish Brigades of .Since November 1916, the 1st Australian Tunnelling Company protected and worked on British tunnels south of Ypres beneath Hill 60.Messines 1916/17 As part . Initially, the battalion provided working parties during the 2nd Division’s attack on 4 August, and then, with its own division, defended the ground that had been captured . Ordered to counter attack, 75th Brigade, the Royal Engineers, .
Actions of the Bluff, 1916
Follow @DrJohnRickard. In the aftermath of the first battle of the Marne, it was decided to move the BEF back north to Flanders, to shorten its supply lines back to the channel ports. Three days later they gained control of Armentières while, further to the north, the Germans directed their assault on . The objective of the Messines June offensive was to remove the German Army from its domination of the positions on the high ground of the ridge south of Ypres, .Battle of Messines.

German trench destroyed by a mine explosion. This drove British forces west .
Actions in the Spring of 1916 (Western Front)
On arrival it encounters German forces moving to outflank the Allies. The Nivelle offensive in April and May had failed to achieve its more ambitious aims and this had . (1916 Somme Offensive, September 15 – October 4) 4978 Messines (1917 Battle of Messines, June 1 – 14) 3380 Chunuk Bair . 62nd Brigade of 21st Division 88th Brigade of 29th Division.
Ulster and Irish divisions fight side by side at Messines
RDF Major Battles
This film shows action at the Battle of the Somme in September 1916 and the Battle of Messines in June 1917. The New Zealanders secured their objectives and the battle was considered a great victory. Battle of Messines, 1917 (Geographx) The plan for the assault on Messines Ridge provided for three corps to advance, each with three divisions in the front line and one in . After their string of bloody defeats over 1915 and 1916, Messines would be the ultimate test for the Australians.In the area between St Eloi and Messines, it also flowed over the German front line trenches.) For conspicuous gallantry during an attack he directed his guns with great skill and coolness several times going out into the open under heavy fire to assist his gun teams Willy won his second Military Cross for .
1917: Arras, Messines and Passchendaele
The joint explosion of the mines in the Battle of Messines .
The Battle of Messines, 1917
The whole British Expeditionary Force is moved to Flanders from the Aisne, as part of an effort to outflank the Germans in France. The Battle of Messines was a prelude to the much larger Third Battle of Ypres (31 July–10 November 1917). I would dearly love to know more about the disciplinary action taken against Sergeant Hill (time, location, who he hit, etc), and also more about his wounding (time, location, . One of the most famous mines of the war was used by the British at the start of the Battle of the Somme.(A Very Rare & Desirable MILITARY CROSS Awarded for Gallantry at Ovillers-La Boiselle on *1st July 1916, First Day, Battle of The Somme. The battle of Messines, 12 October-2 November 1914, was part of the Race to the Sea, the series of battles that decided the line of the western front.
156th Heavy Battery, RGA
The third and longest battle to take place at the Belgian city of Ypres , Passchendaele was ostensibly an Allied victory, but it was achieved at enormous cost for .The Mines in the Battle of Messines comprised a series of mines dug by tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers under the German 4th Army (General Friedrich Bertram Sixt von Armin) lines near the village of Mesen (Messines in French, historically used in English) in Belgian West Flanders during the First World War. Mud Corner Cemetery . The Nivelle Offensive in April and May had failed to achieve its more grandiose aims, had led to the demoralisation of French troops and confounded the Anglo-French strategy for 1917. The Battle of Messines, 1918 (a phase of the Battles of the Lys) The enemy attack broke through the British Ploegsteert and advanced along the Ypres road, endangering the garrison holding Ploegsteert Wood.It sailed to France in late November and moved into the trenches of the Western Front just in time for the onset of the bitterly cold winter of 1916-17. Hill 60 had been captured by the German 30th Division on 11 November 1914, during the First Battle of Ypres (19 October – 22 November 1914).
Battle of Passchendaele
Allied operations switched to the Ypres area in Belgium in mid-1917 and it was here where the 33rd endured its first major battle at Messines.
Batalla de Messines
4th October: Battle of Broodseinde. 108th Brigade of 36th (Ulster) Division
Battle of Messines (1917)
26th September – 3rd October : Battle of Polygon Wood.I’ve wondered if it was at the battle for Messines Ridge on 7 June 1917 when the 156 Heavy Battery took a lot of casualties – but this in merely guesswork. Between 21 March and 5 April 1918, the German Imperial Army mounted the Spring Offensive. In February 1917, work began on the Flandernstellung, incorporating the experience of the Battle of the Somme, 6 mi (9.10 October – 2 November 1914: the Battles of La Bassée, Armentières and Messines. The British front line stood firm, although casualties were serious.The Battle of Albert (a phase of the Battles of the Somme 1916) . Four Victoria Crosses were awarded for acts of outstanding bravery: Private John Carrol (Australia), Captain Robert Grieve (Australia), Lance . Second Army (Plumer) IX Corps (Gordon) 9th (Scottish) Division 19th (Western) Division 25th Division, less 74th Brigade.The Battle of Messines (7–14 June 1917) was an offensive conducted by the British Second Army, under the command of General Herbert Plumer, on the Western Front near the village of Messines in Belgian West Flanders during the First World War. From the first strategic developments of the war the British Cabinet had regarded as their particular charge the defences which protected the coast line and the approaches to the Channel.The Battle of Messines was an attack by the British Second Army , on the Western Front, near the village of Messines in West Flanders, Belgium, during the First World War. The explosions .Messines was a baptism of fire for the 3rd Division which came into the line alongside the battle-scarred 4th Australian Division, badly mauled at Bullecourt just six weeks earlier. These battles form part of a phase often, but incorrectly .
Mines on the first day of the Somme
BATTLES OF YPRES: 16th – 18th August: Battle of Langemarck: 19th, 22nd and 27th August: Fighting around St.Despite headlines at the time proclaiming Messines a great New Zealand victory “for extraordinarily light losses”, some 3,700 New Zealanders were killed or wounded in the battle. At 7:20am on the 1 st of July, 1916, 18 tons of high explosives were detonated beneath the German strongpoint .The Battle of Messines Archivado el 6 de abril de 2011 en Wayback Machine.The Battle of Messines. The galleries reached under the German line and were packed with tonnes of explosives. Eight big and eleven tiny charges were buried deep in the .
Spring Offensive 21 March to 18 July 1918
German retirement to the Hindenburg Line March 1917.Hawthorn Ridge mine crater, Somme, November 1916 (note shadow of photographer, left foreground) The Hawthorn Mine., Chapter 15 in The Official History of Australia in the War of 1914–1918, Vol IV, The AIF in France: 1917, 1941. Discover the story and the traces of this battle in Flanders Fields. The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to-hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine-gun fire, described .The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to- hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine- gun fire, described by one Australian as ‘72 hours of Hell’. 100th Brigade of 33rd Division 102nd Brigade of 34th Division. The Germans on the ridge had observation over Ypres and unless it was captured, observed enfilade artillery-fire could be fired against a British attack from the salient . Plugstreet Wood. The Battle of Messines or battle of the mines from 7 – 9 June 1917 was a preparatory step to the larger 3rd Battle of Ypres Offensive in 1917, known as Passchendaele.Battle of Messines (1914) The British 1st . Why am I seeing this? At the start of the Battle of Messines (7–14 June 1917), a series of mines was detonated beneath German lines, creating 19 large craters.

Commenced with one . A brilliantly planned and executed attack that resulted in the capture of the Wytschaete-Messines ridge south of Ypres, a feature that had given the British problems since 1914 and which was important to hold for future offensive operations in Flanders. It contains nearly all Australian and New Zealand graves, with only one from the UK.6 km) west of Wytschaete; the battles of 1916 showed that forward slope defences had been made obsolete. Mit einer Großoffensive an der Somme wollte die britische Führung im Juli 1916 die Franzosen bei Verdun entlasten. After the Third Battle of Ypres in late 1917, the Australians held the Messines-Wytschaete sector and prepared defences against an expected German offensive in spring.The fighting at Messines would descend into unimaginable savagery, a lethal and sometimes hand-to-hand affair of bayonets, clubs, bombs and incessant machine-gun fire, described by one Australian as ‘72 hours of Hell’.On the morning of 1 July 1916, the first day of the Battle of the Somme during World War I, underground explosive charges planted by British tunnelling units were detonated beneath the German front lines.Under heavy rain, which precluded aerial reconnaissance, they continued their advance and took Bailleul, Kemmel Hill and Messines. Butte de Warlencourt : position of British line at the end of November 1916.The Mines in the Battle of Messines comprised a series of underground explosive charges, secretly planted by British tunnelling units beneath the German 4th Army lines near the village of Mesen (Messines in French, historically used in English) in Belgian West Flanders during the First World War.
47th Australian Infantry Battalion
The Battle of Messines : lines before and after the battle, June 1917 .The Battle of Messines, 1917.15pm the enemy commenced a heavy bombardment which lasted . Operacja ta stanowiła preludium do bitwy pod Passchendaele, znanej jako trzecia bitwa pod Ypres.The Mines in the Battle of Messines comprised a series of mines built near the village of Messines in Belgian West Flanders during the First World War.Capture of Messines Ridge.Messines was the first ‘big push’ of 1917.The Battles of the Ancre : British advances from October, 1916 to February 28, 1917.The Battle of Messines was a battle which happened in the Western front of the First World War. Stewart, H; The Battle of Messines, Chapter V in The New Zealand Division 1916 – 1919: A Popular History based on Official Records, 1921. The first stage in the British plan was a preparatory attack on the German positions south of Ypres at Messines Ridge.
Chapter V — The Battle of Messines
Mud Corner Cemetery was begun during the Battle of Messines, on June 7th, 1917, and was only used until December of that year. It began on 7 June 1917 when the British Second Army, which was commanded by General Herbert Plumer, attacked near the village of Mesen in West Flanders, Belgium. The mines were detonated at the start of the .


The German drive on Calais in the First Battle of Ypres and the second attack in 1915 had been.Spring Offensive 21 March to 18 July 1918.
Ypres Salient Battles 1917
Although the narration implies the film shows New Zealand troops, it is likely that they are in fact British.Battle of Passchendaele, (July 31–November 6, 1917), World War I battle that served as a vivid symbol of the mud, madness, and senseless slaughter of the Western Front. Counter-Attack and Retreat.Diese Riesen-Explosion eröffnete die größte britische Niederlage. It includes scenes of tanks being used and descriptions of what the battles were like from New Zealand troops who were there. THE ADVANCE TO VICTORY: 30th .Compared to the near 60,000 casualties on the first day of the Battle of the Somme in July 1916 and the limited territorial gains, this was more than acceptable to Plumer and his senior staff. On 7 June, the Battle of Messines began when 19 mines exploded under the German lines, including at Hill 60.Duke of Connaught saluting New Zealand troops after the Battle of Messines.Phase: the Battle of Messines, 10 – 11 April 1918. The track continues past Mud Corner Cemetery, and a left turn then .
- Baugenehmigung Baumhaus _ Gartenhaus Baugenehmigung & Bauantrag Nordrhein-Westfalen
- Bauch Weg Body , Herren Shapewear Test 2024
- Basler Fasnachtsplakette 2024 , Fasnachtsplaketten eBay Kleinanzeigen ist jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- Basics Of Engineering Pdf , BASIC OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
- Battlefield 5 Belohnungen Liste
- Bauchschuss Überleben , ️ Die Psychologie des Überlebens: Survival beginnt im Kopf
- Basalkurve Schwanger Beispiele
- Basilikum Wird Braun : Warum wird basilikumpesto Braun?
- Basic Words In Urdu : 1000 Core Words of English in Urdu
- Basteln Zum Thema Weihnachten : 10 Ideen für Weihnachtssterne basteln
- Basilika St Peter | Petersdom Grundriss: Karte und Highlights