B Cell Markers _ Human and Mouse CD Marker Handbook
Di: Samuel
B-1 Cell
Cluster of differentiation.CD Marker Handbook Human CD Markers CD Alternative Name Ligands & Associated Molecules T Cell B Cell Dendritic Cell NK Cell Stem Cell/Precursor Macrophage/Monocyte Granulocyte Platelet Erythrocyte Endothelial Cell Epithelial Cell Function CD42a GPIX, GP9, Platelet glycoprotein IX von Willebrand factor (vWF), Thrombin, CD42b,c,d –+ . NK cells are commonly identified by a combination of CD56 and CD16 and lack of . CD19 is classified as a type I transmembrane protein, with a single transmembrane domain, a cytoplasmic C-terminus, and extracellular N-terminus.
Memory B cells
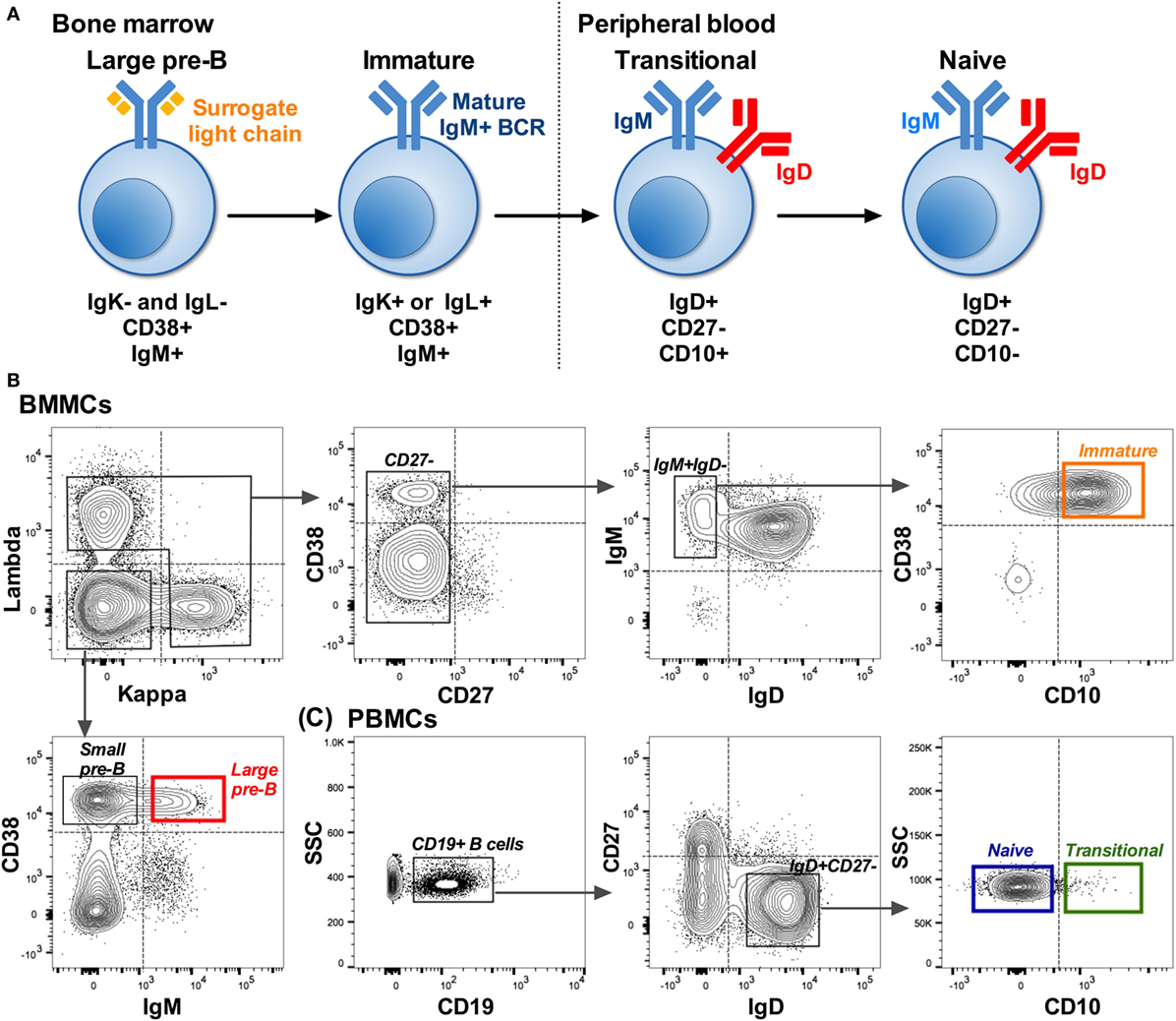
CD19 is a hallmark of the B cell lineage and is expressed at all stages. After initial maturation, B cells migrate to the spleen or other secondary lymphoid tissue for functional maturation. T cell–independent activation of . Th2 cells are known for the defense against extracellular parasites and in . Malignant FL B cells were discriminated from T cell microenvironment based on . Figure 1A: Human B cell development and cellular markers. Summary of the key surface and intracellular markers expressed throughout B cell maturation in mice and humans. A subset of regulatory B-1a cells, called killer B cells, also express FasL, which they use to trigger T cell apoptosis.In immune system, B cells are classically positive modulators that regulate inflammation and immune responses. CD20 is upregulated in pre B cell states but . B-1 cells are the most abundant B cell population in the peritoneal and pleural cavities, represent only a small fraction of the B cells in spleen, and are virtually absent from lymph nodes and Peyer’s patches.
Human B cells
Markers of Human Breg . Due to their locations adjacent to the T cell zones, these cells are particularly well-suited to participate in T cell-dependent immune responses.This segregation between immature and plasma B cells was done based on the positive and negative information in the ScType database that plasma cells do not express common B-cell markers, such as . Cells within each population also express low to intermediate levels of CD21 (and thus are distinct from MZPs), and are resolved by differential surface expression of IgM and CD23 into the IgM high CD23 − (T1), IgM high CD23 . The first is the crosslinking of the BCRs by binding to antigen surface molecules on foreign targets or free soluble antigens.
A Guide to Breg Markers
Human and Mouse CD Marker Handbook
Described below are the various populations of murine immune cells. Here, an overview of recent data on human CD27+ memory B cells is presented with emphasis on function and .B-1 cells can further be subdivided into B-1a cells, which express CD5 (B-1a cells), and cells that lack this marker (B-1b cells). The production of mature B cells occurs through a series of processes that take place in the bone marrow, spleen, and other peripheral lymphoid organs. Summary: 8286 associations (178 cell types, 4679 gene symbols, 29 tissues); Last updated: 27/03/2020 10:44:00 CET . Each stage of B cell maturation and activation is represented by different cell markers.In the tables below, markers are accompanied with “+” or a “–” symbol to indicate whether the specific cell type expresses (+) or lacks (-) the antigen (eg CD10 + indicates a cell type expressing CD10). The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophenotyping of cells.Since the identification of B cells in 1965 (Cooper et al.Follicular B cells are freely recirculating cells that home to the lymphoid follicles in the secondary lymphoid organs. In intersinusoidal bone marrow, hematopoietic stem cells mature to early lymphoid progenitors, the pro B, pre B stages.Prognostic B cell markers for 3-year overall survival: ↑ CD19, IGJ. B-1 cells mainly originate fro . Additionally, cells that are in their rearrangement process express TdT in two waves, one during the IGH gene rearrangements and another during the IGL gene rearrangement which ensures . Plasma cells in blood lack expression of the typical B cell marker CD22 and express lower levels of CD19 and CD20 than mature B cells.However, by simultaneously detecting many more surface markers and intracellular cytokines, transcription factors, and detecting more signaling molecules from individual cells than previously possible with traditional fluorescent labels, the application of mass cytometry with dimensionality reduction algorithms could help dissect the . Immune cell differentiation and CD markers.Mouse B10 cells have been characterized as CD19 + CD5 + CD1d + cells, but these surface markers typically overlap with those of other B cell subsets.
Frontiers
CD44 is a 482 amino acid ~85 kDa single pass type I transmembrane glycoprotein, expressed by T cells, B cells, macrophages and thymocytes.Identification of B cell marker genes based on single-cell sequencing. Specific antibodies to these markers can be used to identify individual B cell types by immunohistochemistry (for example, in the tumor microenvironment) or to quantify and isolate them from a .1 Cell subsets, frequencies, and marker expression. The immature B cells then migrate to the spleen, where they may undergo further development into mature B cells.B Cell Markers.

At a glance: B cell subsets in lymphoid tissue. Because the surface screen was split across twelve tubes, we could not directly determine whether a molecule expressed on a cell in tube X was co-expressed . In some cases, markers are accompanied with “high” or “low”, indicating different degrees of expression.CD10 is a human B cell marker not used in mice and CD38 is used more often in humans than mice . They recognize and kill cancer by detecting downregulation of MHC class I on tumor cells and/or by detecting upregulation of ligands on tumor cells that bind to activating receptors on NK cells.B cells complete most of their development within the bone marrow, in contrast to T cells that mature within the thymus.T-cell dependent activation of a B cell requires two signals. Lymphoid cell differentiation CD markers. 1965), three has been tremendous progress in our understanding of B cell development, maturation and function.
B细胞(B淋巴细胞)是什么-B细胞的功能-赛默飞
B Cell Markers Research Areas: R&D Systems
Natural killer (NK) cells represent the primary innate immune cell type.
B cells (human)
Antibody responses against proteins are believed to involve follicular B cell pathways in secondary lymphoid . Until now, unequivocal surface markers for Bregs . A number of B cell subpopulations, including B-1, B-2 and regulatory B cells, have been identified.B cell markers Human Follicular Surface CD20 CD21 CD22 CD27 CD23h CD24 CD40h CD45R (B220) CD69h CD80h CD81 CD86h CD137 (4-1BB)h CD275 (B7-H2) CD279 (PD-1) CD360 (IL-2 receptor) HLA-DR IgDhigh IgMlow/int Intracellular/ transcription factor Bcl-6 EBF1 FoxO1 Ikaros Pax5 Marginal zone Surface CD1d CD9 CD21 CD45R (B220) CD81 .The first 2000 variable expression genes were used for PCA (Figure 2C, D). Additionally, follicular B cells are found around the bone marrow sinusoids . CD27 is a widely used cell surface marker for human memory B cells and is gradually upregulated during the germinal centre reaction. Mouse Anti-Rat CD4 (Domain 2) Antibody, clone OX-35 recognizes the rat CD4 cell surface antigen, a ~55kDa glycoprotein expressed by helper T cells and weakly by monocytes.Unlike mature B cells, cells within all three transitional subsets express the B-lineage precursor marker CD93/AA4. Green rows indicate canonical markers (classical markers used to define the cell type). Beta-2 microglobulin (β2M), total blood immunoglobulins levels (IgG, IgA, IgM) and free light chains (FLC) are well-known biological markers of B cell activation. Download the poster . But, did you know their immunological reach extends into several other areas, including immunoregulation, transplantation, and cancer? Our helpful webpage provides an abundance of information on antibodies, B cell development and function to ensure . Cell subset: Markers: Function: B-1 B cells : CD138, CD43, CD5 • .
The Lab Rat Model
By contrast, the tissue-like memory B cell subset has been thought to .Other surface markers are differentially regulated, depending on stage of differentiation and spatial localization. Mouse T cells are characterized by CD3 expression and are subdivided into CD4 + helper and CD8 + cytotoxic groups.
Follicular B Cell Markers: R&D Systems
Regulatory B-1a cells express CD5 but not CD1d, allowing them to be distinguished from B10 cells using these two markers. As a result, B10 cells in mice are commonly identified by their functional ability to produce IL-10 following stimulation with lipopolysaccharide or CpG oligonucleotides, phorbol myristate acetate .These cells direct cell-mediated immunity to intracellular pathogens (such as bacteria and viruses) and promote inflammation. The second is signaling through the CD40 receptor on T cells (Figure 3).

b Strain- and gender-specific immune cell distribution for CD4 + and CD8 + T cells, Tregs, B cells, NK cells, iMCs, pDCs, mDCs, macrophages, and neutrophils in spleens of C57BL/6NCr, BALB/cAnNCr . Radiotherapy and PD-1 blockade induced development of memory B cells, plasma cells, and antigen-specific B cells and improved survival. Regulatory B cells (Bregs) are a subset of B cells which play crucial roles in various conditions, including infection, allergies, autoimmune diseases, transplantation, and tumors. MACS Handbook: Spleen (mouse) Lymph node (mouse) 2.Therapeutic targeting of activated B cells with rituximab or belimumab provides real-world proof of their pathogenic importance in autoimmunity [4], [5]. B cell hematopoiesis initiates in the fetal liver and continues in the bone marrow during adult life.Whereas, Pro-B cells express stem cell markers such as CD34 and CD10, later stages start to express B-cell specific markers such as CD19 and CD20.B cells are renowned for their ability to generate antibodies and humoral responses. Cells having less than 200 genes and more than 5% mitochondrial genes were removed (Figure 2A, B).
B Cells
Cells are colored based on their expression of the T cell marker CD3D (left) and the B cell marker MS4A1 (right).Memory B cells are essential for our immunological memory and respond rapidly to reinfection.
A Guide to T Cell Markers
Data are mean .As in humans, mouse immune cells modulate tumor growth and suppression, driven by a complex network of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. They are further characterized as being CD27 ++ CD31 + CD44 + CD45 + CD56 – CD62L + CD86 . Marginal zone B cells in mice are located in the outer white pulp of the spleen between the marginal sinus and the red pulp, which allows them to rapidly respond to blood-borne pathogens and participate in both T cell-independent and T cell-dependent immune responses.Besides, this argument was reinforced by the results that B cell markers such as CD20, IgD, and IgM were uniformly expressed in this cell subset, whereas T-cell markers, namely TCR-β, CD4, and .
Heatmap depicting the MFI of various B cell markers in B cells derived from tumours or dLN from C57Bl6/J mice (n = 5) (h). Most mouse Breg subsets express the cell surface marker TIM-1. B cell developmental markers for mouse.
B Cell Development and Maturation
This is a list of gene expression markers are used to define cell types. Markers and cells. Filter Show cell type: get tsv file add marker.祖B细胞(pro-B cell) 这种发育早期的B细胞,发生在人胚胎约第9周开始,小鼠约第14天开始。尚未表达B细胞系的特异表面标志,也未发生lg基因重排,仍处于胚系基因(germline)阶段。但祖B细胞的晚期可出现B系特异标志,Thy-1 、Tdt 、B200 、mb-1 等分子。 前B细胞(pre-B cell) 是前B细胞是在骨髓中由祖B .All mature B cells express the Pan B cell markers CD19, CD20, and CD22 (PMID: 1373518, 26478008, 21151033). T cells, B cells, NK cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. BCR-seq revealed enhanced B cell clonality, SHM, and CDR3 length reduction induced upon radiotherapy [99] Others: . Prenatal B cell development takes place in the fetal liver; postnatal B cell development originates in the bone marrow (BM). Rat markers CD44 .
B Cell Overview
Within the immune system, Follicular B cells (FO B cells) are a type of B cell that reside in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles (containing germinal centers) of secondary and tertiary lymphoid organs, including spleen and lymph nodes. CD19 is a biomarker for normal and neoplastic B cells, as well as follicular . B细胞可生成高亲和力抗体、生成免疫记忆、充当抗原呈递细胞,并分泌细胞因子(包括CCL22、CCL17、IL-2、IL-4、IL-6、IFN-γ、TNF-α .The T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) algorithm was used for selecting the first 20 .Figure 1A: Human B cell development and cellular markers. Several markers have been identified that can be used to distinguish between the various stages of B cell development and maturation. They develop following migration of transitional 2 (T2) B cells to .The human CD19 antigen is a 95 kd transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily.The CD27 + CD21 low cell subset expresses higher levels of the activation markers CD80 and CD95 than all other B cell subsets. Clusters of Differentiation (CD) proteins are a group of cell surface markers that can be used to identify different stages of B cell development or activation, including .Many immunological cell markers are CD markers and these are commonly used for detection in flow cytometry of specific immune cell populations and subpopulations. The antibodies produced .什么是B细胞?.
Click image to enlarge .To find markers that uniquely identify distinct B cells not captured by canonical gating, we analyzed co-expression patterns of molecules across all B cells in an unbiased fashion.

Representative FACS plot and percentage of B cell subsets. B细胞(也称B淋巴细胞)是一种在适应性免疫反应中起关键作用的白细胞 [1]。. [1] In terms of physiology, CD molecules can act in . Human tissues beyond peripheral blood can be difficult to obtain and B cells in circulation do not allow the analysis of specialized B cells subsets such as marginal zone B cells, germinal center B cells, long-lived plasma cells or . Developmental stages are in close contact with slender CD10+ stromal cells or their .
Pathology Outlines
- Avis Car Return Jfk Airport , Car Rental in New York City, NY
- Babylock Zubehör : desire3 Zubehör
- Avensis Werkstatt Inspektion – Auto-Inspektion: So vermeidest du Kosten
- Babyone Bremen Weserpark | Restaurant & Bar Bremen
- Axilläre Plexusblockade | Axilläre Plexusanästhesie
- Avery Zweckform 3490 Vorlage , Online Vorlage & Word Vorlage 3474
- Babymilchpulver Test _ Wirtschaft
- Azure Verwaltungssystem – Was ist eine Private Cloud
- B1 Sprachniveau Tabelle : Deutsch Sprachniveaus
- Baby Mit 36 Erfahrungen | Osteopathie bei Babys: Sinnvoll oder schädlich?