Aterial Pressure | Physiology and Pathophysiology of Arterial Flow
Di: Samuel
Thus with a common atrial pressure of 6 to 10 mm Hg (the expectation in the presence of preserved ventricular function, adequate arterial blood pressure, and other evidence of adequate systemic cardiac output), the proximal pressure in the SVC will be in the range of 12 to 18 mm Hg. Der systolische Pulmonalarteriendruck (sPAP) kann mittels Echokardiographie abgeschätzt .BP monitoring is a mainstay of hemodynamic monitoring in various fields of medicine, including intensive care medicine, anesthesiology, and emergency medicine.To calculate mean arterial pressure, start by taking both your diastolic and systolic blood pressures. The damage slows blood flow through the lungs. The patient will require further testing, preferably a CTA.Der mittlere arterielle Blutdruck (MAD) liegt zwischen dem systolischen und dem diastolischen arteriellen Druck. It is the arterial pressure wave that is felt as the radial pulse, not the blood flow wave. Perhaps more useful, however, is the direct cannulation of an artery, which allows quantitative information to .동맥압(Artery Pressure) 원인①: 동맥 바늘의 부적절한 위치→ 바늘이 혈관에 들어가지 않거나 혈관벽에 닿아있는 경우 . 원인④: 동맥라인의 꺾임 혹은 잠김이나 .Arterial, Central Venous, and Pulmonary Artery Catheters. 원인③: 혈관 통로의 경련 혹은 동맥 쪽 바늘이나 혈관통로의 clot. Few quantities can be noninvasively measured; they encompass cardiac frequency and peripheral arterial blood pressure as well as velocity and flow .
Chapter 9: Regulation of Arterial Pressure
, 120/80 is a normal adult blood pressure), expressed as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure.Our systematic review aims to determine (a) the average MAP OPT in these patients, (b) the feasibility of identifying . The dynamic component, pulse pressure (PP), is the variation around the mean state and is influenced by large artery stiffness, early pulse-wave reflection, left ventricular ejection, and heart . Blood flows through the heart, arteries Arteries Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body.
Mean Arterial Pressure
Physiology and Pathophysiology of Arterial Flow
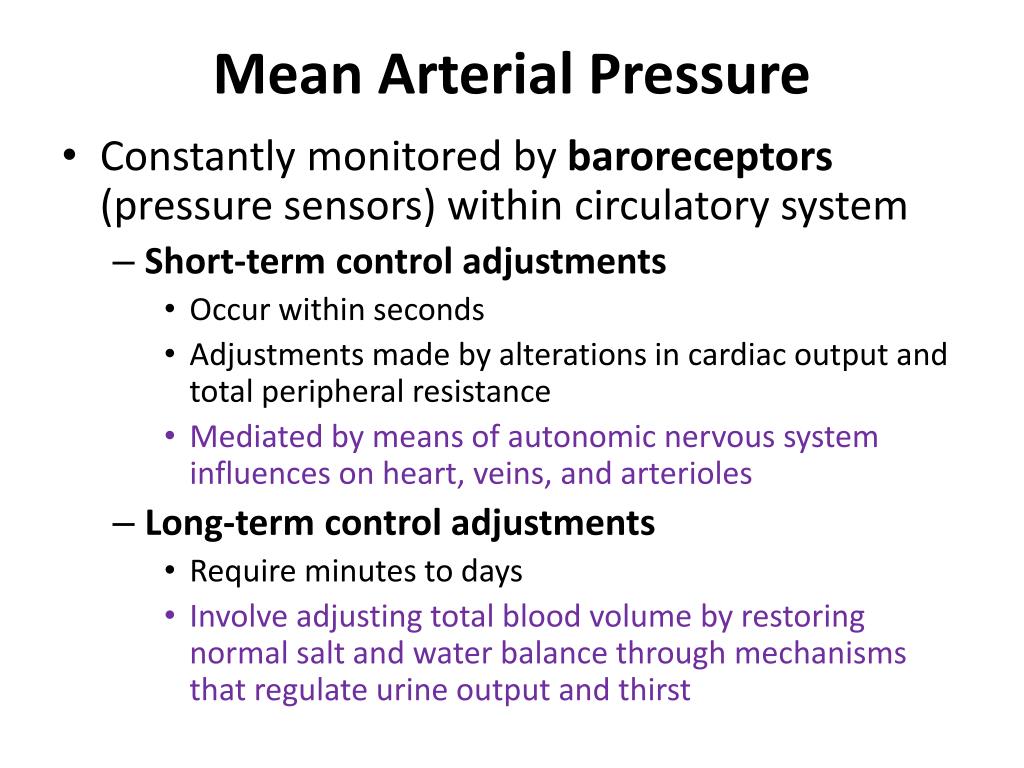
Once the brachial artery pressure curve is taken, the integral of the pressure curve is calculated, corresponding to the real mean arterial pressure. An arterial catheter connected to a fluid-filled tubing system and a pressure transducer is the clinical . is considered to be the perfusion pressure seen by organs in the body. electronic transducer amplifier display.Finally, systemic arterial pressure values are used for systemic vascular resistance (SVR) calculation as the main numerator constituent of the ΔP/Q fraction. In one form of pulmonary hypertension, called pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), blood vessels in the lungs are narrowed, blocked or destroyed. A blood pressure between 140/80 mmHg to 159/99 mmHg is classified to as stage 1 .A sphygmomanometer also referred to as a blood pressure cuff or monitor, is typically used to measure both diastolic and systolic blood pressure. Venous return to the heart is . People who stand upright all day and are inactive overall have very little skeletal muscle activity in the legs. The difference between the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure is the pulse pressure. For example, an individual with a systolic blood pressure (BP) of 120 mm Hg and a diastolic BP of 80 mm Hg would have a pulse .Arterial flow is a three-dimensional unsteady process that is analyzed by measurements as well as physiological, biological, and mechanical experiments and numerical simulations.Heart Atrium Pressure. the point of maximum oscillation = MAP (most reliable measurement) Consequently, multiple mechanisms exist for regulating mean arterial pressure to a normal value of about 100 mm Hg. It is believed that a that is greater than 60 mmHg is enough to sustain the organs of the average person.
Regulation of Arterial Pressure
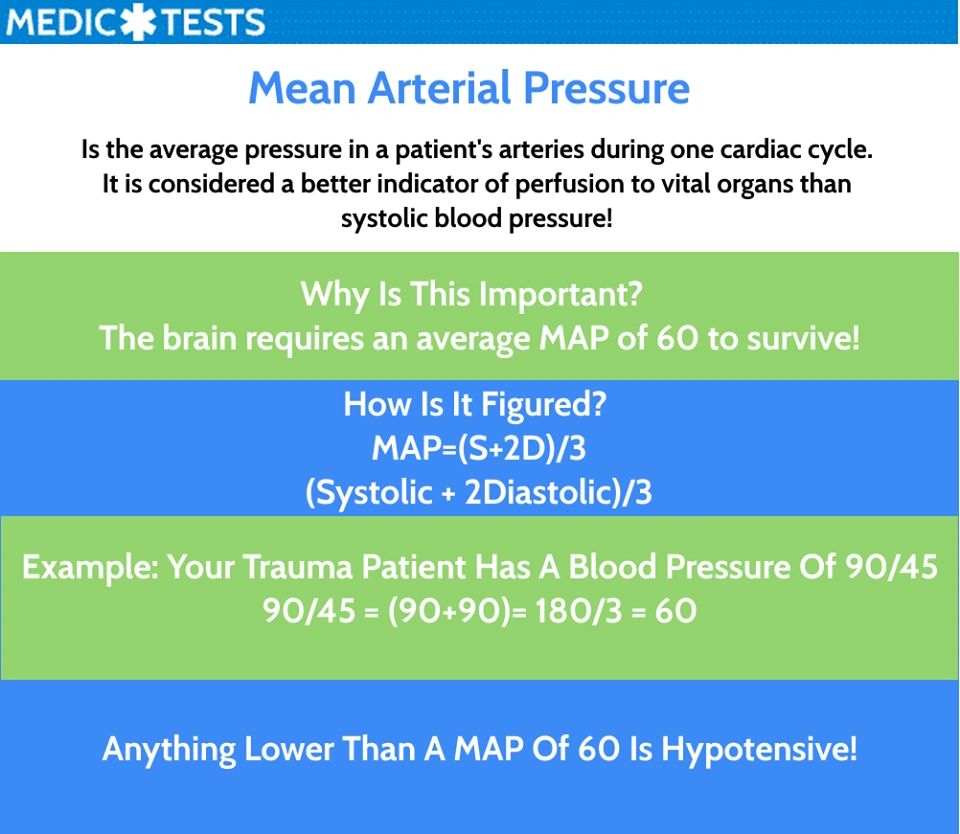
Peripheral artery disease treatment includes . Er berechnet sich annäherungsweise nach folgender Formel: für herznahe Arterien gilt: MAD = Diastolischer Druck + 1/2 (systolischer Druck – diastolischer Druck). Next, multiply your diastolic by 2 and add it to your systolic. In this article, we provide you with a definition of MAP, the normal mean arterial pressure level, teach you how to calculate the mean . pressure transducer and automatic flushing system.Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is determined by cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance (PVR) and is the steady-state component of blood pressure.
Heart Atrium Pressure
Arterial pressure fluctuates with respiration, rising by 15–20 mmHg during each inspiration. Recall that the usual components of a reflex pathway include sensory receptors, afferent pathways, integrating centers in the central nervous system (CNS), efferent pathways, and effector organs. These will be discussed further under the Mechanism heading of this article. Clinical significance.The definition of mean arterial pressure (MAP) is the average arterial pressure throughout one cardiac cycle, systole, and diastole. Pulse Pressure. The wave propagates down the arterial tree at a much faster rate (around 4 m/s) than the mean aortic blood velocity (20 cm/s).The arterial pressure wave is caused by the distension of the elastic walls of the aorta during systole.Arterial pressure directly corresponds to cardiac output, arterial elasticity, and peripheral vascular resistance. Studies have shown that the reduction of arterial stiffness is associated with an improvement in the survival of patients with arterial hypertension and other diseases [ 8 , 37 ]. The transient increases in intrathoracic pressure influence venous return in patients who . If the API is less than 0. Maintaining blood pressure within normal limits is essential.
Arterial Diseases: Risk Factors, Causes, and Symptoms
A medical-grade BP monitoring device, Finapres NOVA, was used to measure the subject’s control BP during the experiments.
Arterial Bleeding: Emergency Care And How To Stop Them
Der Pulmonalarteriendruck, kurz PAP, ist der in der Arteria pulmonalis herrschende Blutdruck. The size of that gradient (ΔP) equals the rate of .
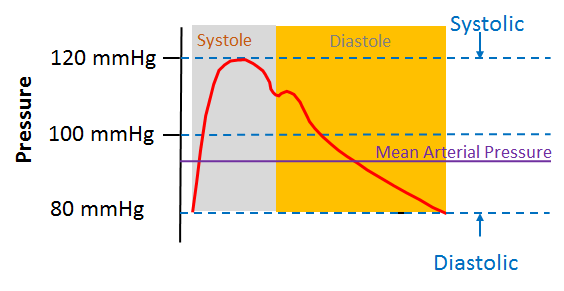
The patient’s mean arterial pressure is 85 + 1/3 (45) = 85 + 15 = 100. On average, each participant underwent 4±1 hours of continuous BP monitoring. Second, invasive systolic blood pressure (Sys-IBP), diastolic blood pressure .Although several guidelines . The definition of mean arterial pressure (MAP) is the average arterial pressure throughout one cardiac cycle, systole, and diastole. Observe or discharge depending on the severity of the injury/patient. Atherosclerosis causes narrowing of the arteries that can reduce blood flow in the legs and, sometimes, the arms. Its value is derived from a patient’s systolic and diastolic blood pressures.
Mittlerer arterieller Blutdruck
To measure blood pressure, the cuff is placed around the bare and stretched out upper arm, and inflated until no blood can flow through the brachial artery. single cuff inflated above systolic and then incrementally deflated while the amplitudes of cuff pressure oscillations measured by pressure transducer.Arterial pressure monitoring. Formulas for mean arterial pressure: MAP = DP + 1/3 (SP – DP) MAP = DP + 1/3 (PP) Classification after calculating MAP: Normal : < 90 mmHg.This may cause leg pain when walking (claudication) and other symptoms. Fluid Responsiveness. Increasing blood pressure: 90 to < 92 mmHg. pressure bag and automated slow infusion (1-3mL/h) of pressurised saline. Jean-Louis Vincent, in Critical Care Medicine (Third Edition), 2008. + +
Blood pressure
toegenomen arbeid voor het hart. Wat zegt de map? MAP gemiddelde arteriele druk en polsdruk berekenen volgens systolische en diastolische druk. Now the exact ratio between mean arterial pressure .This is a health tool that is designed to obtain the mean arterial pressure (MAP) which describes an average blood pressure during a cardiac cycle based on: 1) Systolic blood pressure (SBP) – consistent with the force that pushes blood through the arteries when the heart beats/contracts.Pulmonary hypertension is a type of high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart.With zero arterial pressure, there would be no flow through any organ and, at the other extreme with high arterial pressure, there is an excessive workload on the heart and potential injury of arterial vessels.The GETs are used to monitor arterial blood pressure from N=7 individuals for 300+ minutes each. Although for monitoring purposes, vascular resistance is a calculated parameter derived from pressure and flow values, in circulation biomechanics, flow and pressure are, vice .Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is often estimated from cuff systolic (S) and diastolic (D) blood pressure (BP) using a fixed arterial form factor (FF, usually 0. Pooling of blood in the legs and feet is common. Blood pressure is remarkably easy to alter and can be affected by many activities. Variations in arterial pressure during positive-pressure ventilation have been used as a measure of fluid responsiveness.Interpretation of Arterial Pressure Index. Normal values are considered between 90 and 120 mmHg. die de organen perfunderen.The scale of the pressure meter ranges from 0 to 300 mmHg. Modern cardiac monitors, sometimes referred to as pulmonary artery (PA) pressure monitoring devices, such as . METHOD OF INSERTION AND/OR USE. MAP is influenced by cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance, each of which is influenced by several variables. For example, if your diastolic pressure is 87 and your systolic pressure if 120, you’d begin by multiplying 87 by 2 . The best way to treat them is to prevent . 48 inches of non-compressible rigid-walled, fluid filled tubing.Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is a critical hemodynamic factor. cuff pressure at which the amplitudes start to increase to 25-50% of maximum = systolic. To calculate your MAP, two values are required. cuff should be near level of heart. Invasive arterial pressure monitoring is a standard prac-tice in critically ill patients [1] since it allows accurate and beat to beat assessment of mean arterial pressure (MAP), and also delivers valuable information about cardiac function, heart–lung interactions, the arterial system and valvular diseases [2].The arterial pressure waveform is the combination of various pressure changes in the vascular system like reflection, harmonic frequency production, propagation, and damping. Arterial BP acts as the driving force for blood flow through the tissues of the body. The Valsalva manoeuvre, a forced expiration against a closed or narrowed glottis, causes a complex sequence of pressure changes which are described in Section 14. There is a 5 mmHg arterial pressure drop from the heart to the head and foot due to resistance and 2 mmHg for the returning venous blood.Flow, Pressure, and Resistance in Blood Vessels Overview. The blood passes through the arteries in order of decreasing luminal diameter, starting in the largest artery .When systemic arterial blood pressure is measured, it is recorded as a ratio of two numbers (e. Arterial diseases can occur in any part of your body. Arterial line transducer set up. hartdebiet en de systeemweerstand weer.The use of cerebral autoregulation monitoring to identify patient-specific optimal mean arterial pressure (MAP OPT) has emerged as a technique to augment cerebral oxygen delivery in post-cardiac arrest patients.Invasive arterial pressure monitoring is a standard practice in critically ill patients [] since it allows accurate and beat to beat assessment of mean arterial pressure (MAP), and also delivers valuable information about cardiac function, heart–lung interactions, the arterial system and valvular diseases []. XX/YY is where XX represents the systolic, and YY the diastolic.The arterial baroreceptor reflex is the single most important mechanism providing short-term regulation of arterial pressure. Mean arterial pressure = (diastolic pressure + systolic pressure) / 2.What is Pulmonary Artery Pressure Monitoring? A Swan Ganz™ catheter (also known as a PA catheter) has been used for more than 30 years to monitor heart and lung function but is not designed for permanent monitoring of heart failure.9, there is a chance of arterial injury.The arterial pressure is 100 at the level of the heart and the venous pressure is 2 mmHg. It is directly linked to the cardiac output.
The absence of proper regulation of MAP can have important pathophysiological consequences.Aufrufe: 84,1Tsd.For more accurate calculation of mean arterial pressure, the brachial artery pressure curve can also be recorded by means of a tonometer. Low MAP can cause inadequate blood flow to organs, syncope, and shock.Arterial pressure (ΔP) = Cardiac output (Q) x Peripheral resistance (R).This MAP calculator (Mean Arterial Pressure calculator) finds the average arterial blood pressure during a single cardiac cycle. The investigators then purged the system of any air bubble with a dedicated inflated flush system set at 300 mmHg.
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) Calculator
The fundamental waveform is produced by blood flow as it travels the arterial system, pressure from the expansion and recoil of the aorta, and the superimposed . If MAP is measured directly, a . Different technologies for invasive and noninvasive BP monitoring are available.Voor de neonaat is deze grenswaarde ongeveer 30 mmHg en voor de volwassene ongeveer 50 à 60 mmHg. The right side of the figure indicates the person in the upright posture.First, the arterial pressure transducer was leveled and zeroed to the intersection of the anterior axillary line and the fifth intercostal space.9, the patient is doubtful to have an arterial injury. The rate and character of the arterial pulse has been used for millennia for the diagnosis of a wide range of disorders.Central arterial pressure, arterial stiffness, and pulse pressure have independent predictive values for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. 원인②: 환자의 혈압이 떨어진 경우→ 혈관을 통한 혈액의 흐름이 감소됨. If the API is greater than 0. On the other hand, elevated MAP contributes to increased oxygen demand by the heart, ventricular remodeling, .Arterial diseases affect the arteries in your body, which send oxygen-rich blood from your heart and lungs to other parts of your body.
Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure
When the arteries become blocked, the supply of oxygen and nutrients is cut off, resulting in various problems. Peripheral artery disease is usually a sign of a buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries (atherosclerosis). Die Messung erfolgt über einen Pulmonaliskatheter / Swan-Ganz-Katheter, der in den Stamm der Arteria pulmonalis eingelegt wird. is normally between 65 and 110 mmHg.

Physiological Aspects of Arterial Blood Pressure
Pulse pressure and mean arterial pressure are calculated values based upon the systolic and diastolic pressures. In pregnancy blood pressure gradually falls and reaches a minimum at approximately 6 months, so in . The systolic pressure is the higher value (typically around 120 mm Hg) and reflects the arterial pressure resulting from the ejection of blood during . Normally,the mean arterial blood pressure falls within the range of 70–110mmHg,so 100 is normal.The mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) can be defined as an approximate of the time-weighted median blood pressure in large arteries during the cardiac cicle.
MAP Calculator (Mean Arterial Pressure)
Hier entspricht der MAD annähernd dem arithmetischen Mittel. The pressure meter has a rubber pump on it for inflating the cuff and a button for letting the air out. For blood to flow through a vascular bed there must be a pressure gradient between the arterial and venous ends of this bed. Then, divide the sum by 3 to get the mean arterial pressure.Mean arterial pressure = diastolic pressure + 1/3 (pulse pressure) The calculation of the mean arterial pressure for patients who have high heart rates is done through the arithmetic media, given the fact that there will be a change in the shape of the arterial pressure pulse.
- Asus Q Led Core Aktivieren _ Gaming-Mainboard ROG CROSSHAIR VII HERO
- Atlantik Young Leaders | Young Leaders‘ Voices
- Attack Of The B Team 21 : Attack Of The B Team Episode 1
- Aspekt Der Kontrolle , Der Wunsch nach Kontrolle kann auch zu weit gehen
- Audi A3 1.8 T Gebrauchtwagen – Audi A3 aus 1998 gebraucht kaufen
- Astronomie Modellen , Mein Sonnensystem
- Audi A2 Sicherungskasten Anleitung
- Asterix Und Obelix Filme Kostenlos
- Asterix Und Obelix Ganzer Film
- Asus Eb1501P Datenblatt , USB-AC58 AC1300
- Aspartame Erfahrungen – Aspartam
- Attractions Near Salzburg : The 12 best things to do in Salzburg
- Async Wait Until Finished _ Python async/await Tutorial
- Atomkraftwerk Ukraine _ Kernkraftwerk Tschernobyl
- Assassin’S Creed Origins | Assassin’s Creed Origins on Xbox One, PS4, PC