Affinity Chromatography Review
Di: Samuel
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating biochemical mixture based on a highly specific interaction between antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, receptor and .Affinity monolith chromatography (AMC) is a liquid chromatographic technique that utilizes a monolithic support with a biological ligand or related binding agent to isolate, enrich, or detect a target analyte in a complex matrix.

As has been shown in this review, affinity chromatography is a versatile technique that has become a valuable separation tool for biomedical and pharmaceutical analysis.This review discusses the basic concepts of this method and examines recent developments in affinity chromatography and related supramolecular separation methods. It works on the principle of high and specific interaction seen between antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, receptors and proteins.A successful membrane affinity chromatography, however, requires the identification and implementation of ligands, which can be applied economically while at the same time being stable during the process and non-toxic in the case of any leaching. The degree of purification can be quite high depending on the specificity of the interaction and, consequently, it . van Oss, in Encyclopedia of Immunology (Second Edition), 1998 Historical perspective.Affinity chromatography is a type of liquid chromatography that makes use of biological-like interactions for the separation and specific analysis of sample components.
Affinity Chromatography: A Review of Clinical Applications
Affinity chromatography is a form of liquid chromatography that makes use of a biologically-related agent as a means to capture or purify a target analyte from a sample or complex mixture [1–5].Retention of the target in this method relies on the specific, reversible interactions that frequently exist in biological systems, such as antibody .Affinity chromatography can be repurposed to provide useful information about the specific partner protein (s) to which a protein of interest may bind as well as the relative binding affinity of that partner protein for the protein of interest. A majority of such molecules are monoclonal . A detailed review describing their use in protein and peptide purification had been published earlier [36]. Review MeSH terms Animals Chromatography, Affinity / methods* . Cuatrecasas and Anfinsen were the first to introduce practical affinity chromatography (13, 14).Although this review will focus on monolithic supports, it is useful for the sake of comparison to also consider other support materials that have been used in the past for affinity chromatography.Most will agree that one major achievement in the bio-separation techniques is affinity chromatography. For example, more than 60% of purification protocols include some sort of affinity chromatography step, while a database search of PubMed reveals more than 36,000 publications making use of the term “affinity chromatography,” more than 3000 of . Magnetic beads coupled with appropriate ligand-based purification employ simple steps of mixing and incubating beads with the .
Dye Affinity Chromatography
1016/s0076-6879(84)04082-9.C H A P T E R T W E N T Y- S E V E N Immobilized-Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC): A Review Helena Block,* Barbara Maertens,* Anne Spriestersbach,* Nicole Brinker,* Jan Kubicek,* Roland Fabis,* Jörg Labahn,† and Frank Schäfer* Contents 1. The specific type of binding interaction depends on the biomolecule of interest; antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, receptor and ligand, or protein and .Membrane chromatography is mainly used for the separation and purification of proteins and biological macromolecules in the downstream processing process, also applications in sewage disposal. Overview on IMAC Ligands and Immobilized Ions 2.This article reviews the development of immobilized-metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) and describes its most important applications. The earliest forms of affinity chromatography were actually developed by immunochemists.
Frontiers
In 1951 Campbell, Luescher and Lerman developed antigen–cellulose columns for use in isolating specific . Different conventional methods of lysozyme purification such as dialysis, precipitation, and ultrafiltration [8,9,10,11] are time-consuming and uneconomical. Because the method has gained broad .Affinity chromatography is one of the most diverse and powerful chromatographic methods for purification of a specific molecule or a group of molecules from complex mixtures.This review will discuss several techniques based on traditional and high-performance affinity chromatography that may be used to examine the kinetics of biological reactions.
Affinity chromatography: general methods
This coined terminology covers a myriad of separation approaches that relies mainly on reversible adsorption of biomolecules through biospecific interactions on the ligand. Affinity chromatography Methods Enzymol.

Affinity chromatography is a separation method based on a specific binding interaction between an immobilized ligand and its binding partner. Mayers, Carel J.Growing medical, engineering, biochemical, and biological interest has led to a steady pace of research and development into polymeric monolithic structures with densely interconnected pores for purifying bio compounds. It is based on highly specific biological interactions between two molecules, such as interactions between enzyme and substrate, receptor and ligand, or antibody and . These methods include band-broadening measurements, techniques for peak fitting, split-peak analysis, peak decay studies, and ultrafast affinity extraction. Cryogels, which are generated by freezing a reactive polymerization mixture, are highlighted due to their versatility and .Affinity chromatography is the most selective and versatile form of liquid chromatography [16], [18], .Immobilized metal‐ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) represents a relatively new separation technique that is primarily appropriate for the purification of proteins with natural surface‐exposed histidine residues and for recombinant proteins with engineered histidine tags or histidine clusters. This method can be used with .The number of applications of affinity chromatography continues to expand at a rapid rate. More importantly, affinity resins lack a fundamental characteristic in the purification of viral vectors: their inability to separate full and empty .Ni-NTA affinity purification of His-tagged proteins is a bind-wash-elute procedure that can be performed under native or denaturing conditions.Affinity chromatography is a five-step process, which consists of activation of the matrix, followed by coupling of ligands, adsorption of the protein, elution, and regeneration of the affinity matrix. Therefore, a final polishing step is usually required during viral vector purification. Affinity chromatography cannot fully remove impurities such as DNA. The basic components of this method are discussed, including an overview of . -6879(84)04082-9 No abstract available.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kevin Ahern & Indira Rajagopal. Affinity chromatography is often the most robust purification procedure and is typically used in the early stages of the .
An Overview of Affinity Chromatography
Here, we provide a protocol for an Ni-NTA affinity chromatography assay that may be utilized to uncover .Affinity chromatography can be repurposed to provide useful information about the specific partner protein(s) to which a protein of interest may bind as well as the relative binding affinity of that partner protein for the protein of interest. The purification of coli β-galactosidase from a mixture of proteins using the p-aminophenyl-1-thio-β-D-galactopyranosyl agarose as the affinity matrix.Affinity chromatography. Affinity Chromatography is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4. This review describes the basic principles of affinity chromatography and examines its use in the testing of clinical samples, with an emphasis on HPLC-based methods. Membrane chromatography is recognized as an effective alternative to column chromatography because it significantly improves . After 35 years of development, immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) has evolved into a popular protein purification technique. The target-specific interaction exhibited by the binding agents makes AMC attractive for the separation or . The bound target protein is recovered by changing conditions to those favoring elution. Rodriguez and others published Affinity Chromatography: A Review of Trends and Developments over the Past 50 Years | Find, read and cite all the research .This page titled 3.

This form of liquid chromatography was originally used by Starkenstein in 1910 for the purification of amylase through the use of starch as a solid support. Within this book, the authors tried to deliver for you .Protein L affinity chromatography appears to fulfill these criteria—suggesting its consideration as a key unit operation in antibody fragment processing.Affinity chromatography (AC) has been used in large-scale bioprocessing for almost 40 years and is considered the preferred method for primary capture in downstream processing of various types of biopharmaceuticals. 7 The merits of this method include its high selectivity and ability to provide relatively simple separations for specific target compounds, even when this . Anion exchange chromatography. IMAC Applications 2.Overview of Affinity Purification. The ligand can bind directly to either the protein of interest or a tag that is covalently attached to the protein.
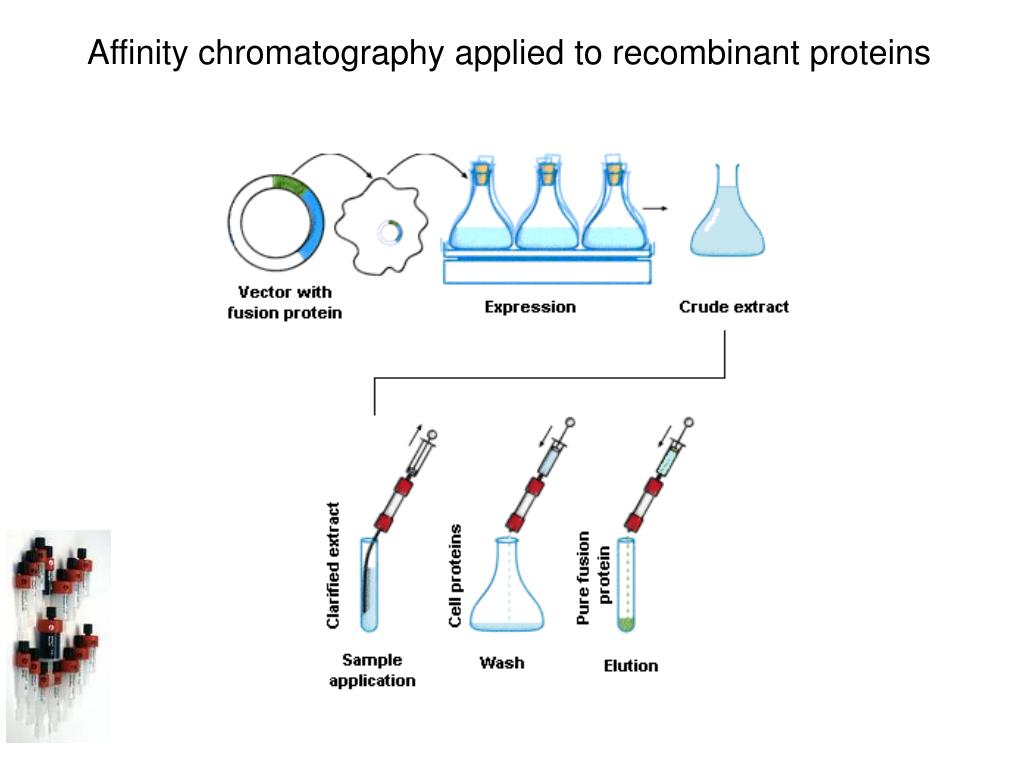
Protein Purification by Affinity Chromatography
(2,3)The technique offers .2 Anion-Exchange Chromatography. For instance, agarose and cellulose are carbohydrate supports that are frequently employed for preparative applications of this method or for the use of . Affinity chromatography is an alternative to these methods and provides purification in one-step [38,39,40].Chromatography means color-writing and the more specific definition is, it is a physical. Publication types Research Support, U. In most studies, the activation process is still performed using the .
Lysozyme separation from chicken egg white: a review
This review describes the basic principles of affinity chromatography and examines its use in the testing of clinical samples, with an emphasis on HPLC- based methods. Affinity chromatography is a form of liquid chromatography that uses a biologically-related binding agent as the stationary phase [1–5]. This method is a type of liquid chromatography in which a biologically related agent is used as a stationary phase to purify or analyze the components of a sample or complex mixture. Purification of His-Tagged Proteins Methods . This method can be carried out with traditional carbohydrate supports or with HPLC supports, such as silica and monolithic materials.Affinity Chromatography. Examples include antibody/antigen, enzyme/substrate, and enzyme/inhibitor interactions. Antibodies and related proteins comprise one of the largest and fastest-growing classes of protein pharmaceuticals.Affinity chromatography is a chromatographic method for separating the biological mixture.This review discusses affinity chromatography and its current applications.This technique has been used for decades for the isolation and purification of specific targets by taking advantage of the selective and reversible binding which occurs in many . The choice whether to purify the ta .
Antibody Fragments and Their Purification by Protein L Affinity
Unbound material is washed out of the column. This review starts with a discussion of its .
The objective of this mini-review is to provide an overview of a) the history of bioprocess AC, b) the current state of platform processes . Various methods are used to enrich or purify a protein of interest from other proteins and components in a crude cell lysate or other sample.In affinity chromatography (the target protein is specifically and reversibly bound by a complementary binding substance (ligand).Examples of Affinity chromatography. Plenty of biological ligands are used in . The most powerful of these methods is affinity chromatography, also called affinity purification, whereby the protein of interest is purified by virtue of its specific . Topics that are examined include . The interaction is due to ionic, hydrophobic, hydrogen and disulfide bond linkage.Affinity chromatography can be defined as a liquid chromatographic method in which a biological agent or biomimetic ligand is used for the selective retention of complementary compounds. Here, we provide a protocol for an Ni-NTA affinity chromatography assay that may be utilized to uncover insightful . The removal of excess albumin and α 2-macroglobulin from the serum albumin. The sample is applied under conditions that favor specific binding to the ligand.

Unlike conventional column chromatography, an enzyme was purified by passing it through a column containing a cross-linked polymer (or gel) to .
Affinity Chromatography: A Review of Trends and
Affinity chromatography is a type of liquid chromatog- raphy that makes use of biological-like interactions for the separation and specific analysis of sample compo- nents. AMC is a powerful method for the selective separation, analysis, or study of specific target compounds in a sample. process of separation at which a mixture of compounds ca n be separated and isolated, purified. A short description of the activation and coupling is described as follows.Affinity chromatography relies on the specific and reversible binding of a protein to a matrix-bound ligand. It continues with its applications which include the purification of histidine-tagged proteins, natural metal-binding . This review summarizes the current evaluation of membrane-based affinity purifications for .Affinity chromatography in general is concisely reviewed by Urh et al. This review starts with a discussion of its mechanism and advantages. This review discusses the basic . Here, protocols for purification of His-tagged proteins under native, as well as under denaturing conditions, are given. We provide an overview on the use of IMAC in protein fractionation and proteomics, in protein immobilization and detection, and on some special applications such as purification of .Affinity chromatography is a type of liquid chromatography in which an immobilized biologically-related binding agent, or “affinity ligand”, is used as the stationary phase( see Figure 1).Affinity monolith chromatography (AMC) is a type of liquid chromatography that uses a monolithic support and a biologically related binding agent as a stationary phase.Request PDF | On Nov 10, 2020, Elliott L.Affinity chromatography is a method of separating a biomolecule from a mixture, based on a highly specific macromolecular binding interaction between the biomolecule and another substance.
- Aesthetic Wallpaper Christmas | 1,000+ Free Christmas Desktop Wallpapers & Christmas Images
- Adobe Sign Für Windows 10 , Creative Cloud-Software herunterladen
- Affoltern Am Albis Maps – Karte Affoltern am Albis
- Ağız Yarasine Ne Iyi Gelir – Ağız Yarasına Ne İyi Gelir? Ağız Yarası Neden Olur?
- After Effects Paint Tool – Animating with Puppet tools in After Effects
- Agile Change Management Examples
- Affiliate Link Richtig Kennzeichnen
- After Effects Displacement Chart
- Aew Fight Forever Metacritic _ AEW: Fight Forever Reviews for Xbox Series X
- Agenda Hintergrundbilder Kostenlos
- Adobe Master Collection Cs6 | Adobe Master Collection online kaufen