Activity And Fugacity : Fugacity — Advanced Thermodynamics for Chemical Engineers
Di: Samuel
Vapor-liquid Equilibrium, Activity Coefficient, Fugacity
For gases, the activity is the effective partial pressure, and is usually referred to as fugacity. The activity of an aqueous chemical species can be thought of as an effective concentration.

In chemistry, fugacity is a measure of the potential or effective pressure of a gas or vapor, which can be different from its actual pressure.And since activities and fugacities are unitless, thermodynamic equilibrium constants are unitless as well. For our present discussion, it does not matter whether the .For detailed discussion of fugacity coefficients, see Part VI. The activity coefficient can also be regarded as the inverse expression of solubility, where a solute that is only sparingly soluble in a solvent (e. In Chapter 11, we introduce the fugacity as an alternative measure of the difference between the Gibbs free energy of one mole of a pure gas in its hypothetical ideal gas standard state and its Gibbs free energy in any other state at the same temperature. j = activity coefficient of i (subscripts left off for simplicity) J = fugacity coefficient .‘ It directly relates to the tendency of a substance to prefer one phase (liquid, solid, gas) over another. As such, these species never change the magnitude of the .As activity and fugacity are unambiguously related and are derived from the thermodynamic concept of chemical potential (partial Gibbs free energy), it is sufficient to specify either activity or fugacity.

9: Diagrams of activity and activity coefficients for a) Raoult’s law, b) Henry’s law.The fugacity f of a substance is defined in such a manner that, if the molar Gibbs free energy increases from G0 to G, the ratio of the new fugacity to the initial fugacity, f/f0, is given by. It is equal to the pressure . Let us now consider a system that consists entirely of substance \(A\) present as either a pure liquid or a pure solid. If the vapor phase is close to an ideal phase, then the equation above yields the modified Raoult’s law (1., P(CO 2) = partial pressure of CO 2 . An evaluation of equilibrium constant is helpful in understanding the equilibrium state of a chemical reaction or the desired direction in . The ratio between fugacity and pressure is: ϕ = f P (22.
Activity and Activity Coefficients
Oklahoma School of Science Mathematics. When expressed as a mole fraction, the . The fugacity coefficient takes a value of unity when the substance behaves like an ideal gas. ð·ð· ð· ð· ð·ð·ð· 2 1 1 a) Henry: ðg= 1 Raoult: ðg= 1 b)096 K, RH is rigorously defined as the relative activity (or relative fugacity) of water in humid air . In the general introduction of this book, we have already recalled that the notion of chemical activity has been introduced . This is because the concept of fugacity takes into account the non-ideal behavior of gases and their interactions with other components in a mixture. The key difference between activity and fugacity is that activity refers to the effective concentration of a chemical species under non-ideal conditions, whereas fugacity refers to the effective partial pressure of a chemical species under non-ideal conditions.064 MPa and temperatures T < 647. Observed fugacities and activities in the .The fugacity of gases , which is closely related to activity, is based on partial pressures (Atkins and Jones 2008).By Perrine Juillion / January 22, 2020.

03 atm100 atm = 0. First, some symbols: f(i) = fugacity of component i in a mixture. Fugacity is typically expressed in units of pressure .Fugacity: definitions, concepts, and geology .Equations 63, 68, 69 and 70 allow straightforward conversion from fugacity coefficients to activity coefficients and Henry fugacities, and vice versa.Oxygen fugacity is an intrinsic thermodynamic property that records the chemical activity of oxygen and controls the speciation of redox-sensitive elements; it affects magma melting, metasomatism, and mineral crystallization in lithospheric mantle (Aysal 2015; Kilgore et al.2) μ A = μ A o + R T ln. At a fixed temperature and pressure, water will have a different fugacity for each phase. copyright by Philip A. The challenges of estimating fugacities in environmental phases are discussed, especially for ill-defined phases such as soils, sediments, and biota for .
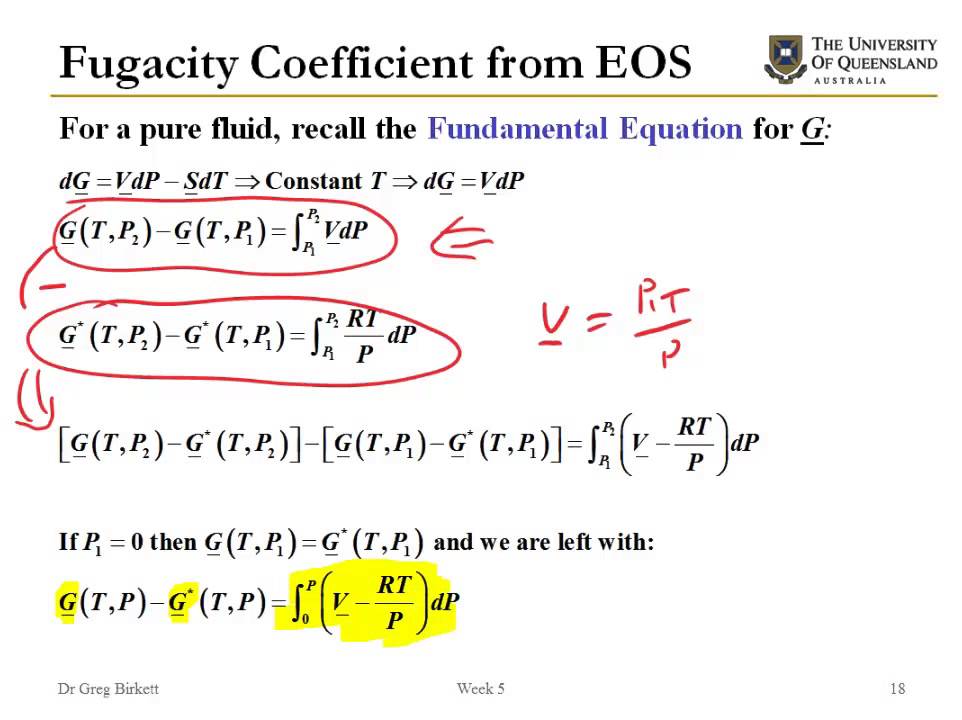
In some texts, the two topics are compressed together using specific models of mixing and Equations of State (EOS). However, the fact that its only practical use is for gases does not change the fact that in principle it is a property of all system constituents.The fugacity and activity analysis further demonstrates that reported no-observed-effect concentrations of D5 normally cannot occur in the environment.In summary, since the gas is ideal, the partial pressure of A above the solution is PA = xAP, whether the solution is ideal or not. Applying this . (Let us notice that IUPAC, in agreement with what is just said, defines the notion of activity without any . Activity coefficient addresses non-ideality in solutions, reflecting interactions between solute and solvent molecules.By measuring the fugacity of A in a gas phase equilibrated with the binary mixture, we can evaluate its activity coefficient based on a pure-liquid reference state: γA=fA/(xAf∗A) (Table 9. It was conceived and introduced in the realm of chemistry at the beginning of twentieth century by Lewis (Proc Am Acad Arts Sci 37:49‒69, 1901; Proc Am Acad Arts Sci 43:259‒293, . • μ H2S chemical potential: The .
Fugacity — Advanced Thermodynamics for Chemical Engineers
In chemical thermodynamics, the fugacity of a real gas is an effective partial pressure which replaces the mechanical partial pressure in an accurate computation of the chemical equilibrium constant.The value of G cannot be determined experimentally but G – G° can be obtained from G – G° = RT ln P.8 a) this corresponds to the properties of tiny fractions of Si added to nearly pure Ge.
The Notion of Activity: An Overview
Understanding Lewis activities
1 described the evaluation of the activity coefficient of a constituent of a liquid mixture from its fugacity in a gas phase equilibrated with the mixture. Toxicokinetic evaluations of chemical uptake and disposition in a variety of organisms, including humans, can be obtained using fugacity- and physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models.Hence, the second definition of an activity consists, without any consideration of the notion of the fugacity, in setting up that the activity is related to the chemical potential of the solute, which is measured by it, through relation (). μ B H = μ B ∗ ( γ B H) x B → 0 = ( a B H x B) x B → 0 = 1. Therefore, the fugacity coefficient is also regarded as a measure of non-ideality .77), the vapor-liquid equilibrium from Eq.324 APPENDIX C: THE MATHEMATICS OF FUGACITY, IDEAL SOLUTIONS, ACTIVITYAND ACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS. FUGACITY (and activity). The contribution of nonideality to the molar Gibbs energy . What is the coefficient of fugacity? The fugacity coefficient is 97.In conclusion, while both activity coefficient and fugacity coefficient serve to correct for deviations from ideal behavior in solutions and gases respectively, they operate in distinct domains. The effective pressure of a non-ideal gas that corresponds to the pressure of an ideal gas with the same temperature and chemical potential of the non-ideal one.1\): Activity and Fugacity. The state of being active. Further, it can be noted that the activities of solids and pure liquids are unity (assuming ideal behavior) since they are in their standard states at the given temperature. μ = μ0 + RT ln p (8. behaves as a ideal gas.
Fugacity, Activity, Equilibrium Constant and Ellingham Diagram
For the Henry standard state we have. So all Si atoms will be completely . Therefore, although activity is dimensionless, one must take care to use the appropriate scale with a particular tabulation or model of activity coefficients. more practical approach is to write out the value of.3) G − G 0 = R T ln. Compare with Definitions.The use of activity to describe the solute allows us to use the simple model for chemical potential by inserting the activity of a solute in place of its mole fraction: μA = μo A + RT lnaA (4.According to it, the chemical activity is the ratio of the fugacity of the species of concern and of its fugacity in the standard state.28) and mol fraction (eqn.1 MPa) and the T of interest, allowing a O 2 1 / 2 in Eq.An activity coefficient is defined as the ratio of a component’s fugacity in an actual mixture to the fugacity of an ideal solution of the same composition. If the solution is not ideal, we introduce the activity coefficient, γA, as the “fudge factor” that makes γAyAP⦁ A = xAP true. In Water Chemistry, Mark Benjamin defines activity coefficient, via a rearrangement of the first equation . The decision as to what approach to adopt is by and large a matter of taste and .Biomagnification is readily evaluated both experimentally and as a fugacity (or activity) increase from prey to predator. P = total pressure Pi = partial pressure of component i e. Mole Fraction; Gibbs Energy; Activity Coefficient; Virial Coefficient; .The notion of activity is of a purely thermodynamic nature. Activity depends on temperature, pressure and composition of the mixture, among other things.80) y i P = x i γ i P i sat.11 Raoult and Henry law for activity and fugacity As discussed above the definition of the ideal state differs for solvent and solute; correspondingly the deviation from ideality differs for both components. where ϕ ϕ is the fugacity coefficient. In this paper, the term activity is primarily used as a property of species in the liquid or aqueous phase. For ideal gases, the chemical potential is related to pressure ( eqn.5 twice, once for some general state and once for the. Equations 31, 57, 58a and 58b may each serve as a rigorous thermodynamic basis for the treatment of VLE.So far, we have investigated fugacity and activity only for gases. activity, fugacity, equilibrium constant and Ellingham diagrams, and the entire discussion has been covered in seven sections.the activity (or fugacity) that the solute would have if it were in a solution consisting entirely of pure solute.

The fugacity is a property of systems and of system constituents that was invented in order to facilitate the evaluation of ∫ dG for gaseous constituents.Request PDF | Influence of temperature, composition, silica activity and oxygen fugacity on the H(2)O storage capacity of olivine at 8 GPa | Olivine crystals were grown in the presence of a . At equilibrium between pure Fe and FeO, the activity of these components is equal to 1.
Fugacity
In terms of activity and the fugacity coefficients, related each other by Eq. Oklahoma School of Science Mathematics.3 mentioned the use of solvent fugacities in gas phases equilibrated with pure solvent and with a solution, in order to evaluate the . In very dilute solutions, activity is numerically equivalent to concentration in molality (Bethke, 2008). However, as the concentrations of solutes increases in a solution, the difference between activity and .
What is activity and activity coefficient?
We assume that the temperature is fixed and that the pressure on this condensed phase can be varied. The thermodynamic interpretation of experimental results, the thermodynamic calculation of reactions, and the accurate determination of . A simple unified treatment of fugacity and activity is presented for both gaseous and condensed phases. If substance A A is a liquid at one bar and the temperature of interest, pure liquid A A is the standard state for the calculation of the enthalpy and Gibbs free energy of formation. If the solution is ideal, we have yAP⦁ A = xAP, so that yAP⦁ A / Po = xAP / Po.Oxygen fugacity has received much attention in recent .Definition: Fugacity.1 then becomes: μnon-ideal = μ − ⊖ − + RTln f P − ⊖ −. (57) to be replaced with f O 2 1 / 2. The presence of intermolecular attractive and repulsive forces distinguishes a real gas from an ideal gas. f P ≡ G ( T, P) − G 0 ( T, P) = μ ( T, P) − μ 0 ( T, P) Here, f is the fugacity and is a function of temperature and pressure.27 ), molar concentration (eqn.4 Fugacity measurements.Difference Between Activity and Fugacity. As a “house-keeping” note, it must be emphasized that Parts VI and VII treat fugacity coefficients and Liquid Activity Coefficients separately.26) A similar equation is desirable for real gases. 7 Ideal Character of a System and Interactions Between the Particles Constituting It. It is intimately linked to the law of mass action and more generally to that of equilibrium constant.Explanation for Fugacity, Activity and Activity Coefficient and its relationship with each other explain by using chemical potential and ideal gas equation.79) y i ϕ ˆ i P = x i γ i f i. G 0 is the molar Gibbs free energy of the ideal gas reference state. The fugacity has units of pressure, and by inspection of this definition we see that. Since the chemical potential of a gas μ is equal to the standard chemical .Below the critical point of pure water, at pressures p < 22.The activity of pure substances in condensed phases (solid or liquids) is normally taken as unity (the number 1).Fugacity is a measure of chemical potential in the form of 'adjusted pressure.This chapter has focused on the potential thermodynamic topics, e.4: Standard States for the Fugacity and Activity of a Pure Solid. where P sat is the saturation pressure of pure components. As an example we discuss thep−xphase diagram shown in Fig.For non ideal gases, f f is not equal to P P.where G is a function of both temperature and pressure but G° is only a function of temperature at a fixed standard pressure of one bar (one atm in older publications). Vapor phase fugacities can be expressed in terms of a fugacity coefficient [φ: f i V = φ i y i f i 0V], with y i = mol .Activity and modified Raoult’s Law# Since the entropy of mixing is always favorable, any system that exhibits deviations from ideality must have an enthalpy of mixing that is non-zero and thus cannot be approximated as an ideal solution.The concept of fugacity, which is widely used in chemical processing calculations, has also been successfully applied to a variety of environmental simulations of the fate and transport of organic contaminants.
Activities and their Effects on Equilibria
This definition makes the fugacity of a gas an .78) becomes (1.
Solubilities, Fugacities and All That in Solution Chemistry
Activity and fugacity are related via a i = f i /f i ° where f i ° is the fugacity at the relevant standard state. KEYWORDS (Audience): It is hoped that this treatment will be found useful as a clearer and more general alternative to existing treatments.The phase with the lowest fugacity will be the most favorable; the substance minimizes . Fugacity is a property used to show differences between chemical potentials at standard states. Toxicodynamic processes of chemical . same temperature, but a pressure so low that the material. G −G0 = RT ln(f/f0) (12. While we can treat any non-idealities through fugacity calculations for the liquid phase, these approaches tend to be . water), will have a high activity coefficient.Finally, we argue that deriving the full benefits of these applications of the fugacity concept to chemical fate and risk assessment requires continued effort to develop quantitative structure–activity relationships (QSARs) that can predict relevant chemical properties and programs to validate these models by reconciliation between modeled . However, the two .Naturally occuring gases (fluids) in metamorphic and igneous systems are known to be mixtures of several volatile species, usually including H 2 O, CO 2, CO, H 2, CH 4, H 2 S or SO 2 in major or minor amounts. A commonly used standard state is the pure gas at 1 bar (0.
- Access Vs Excel , Microsoft Access 2019 vs 2016 vs Excel
- Add Audio To Powerpoint Presentation
- Achensee Schifffahrt Speisekarte
- Adidas Terrex Ax 4 _ Adidas Terrex AX4 Primegreen Women
- Accumulated Depreciation Formula
- Adac Beitrag Absetzen _ Welche Versicherungen kann man von der Steuer absetzen?
- Acryllack Für Pla Filament : BRESSER PLA-Filament 500 g für 3D-Drucker
- Adenoviren Krankheitsbild : Augengrippe: Symptome, Verlauf und Behandlung
- Acrylglas Polieren – Acrylglas reparieren? So geht es richtig
- Adapter Für Pc Kabel _ USB & PC Kabel günstig online kaufen » KabelDirekt