Active Inference Model – Active Inference in the brain
Di: Samuel
The aim of this simulation modelling approach is to demonstrate what Bayes-optimal behaviour is like .Tutorial 1: Active inference from scratch . During task performance, they support inference about states of the extrapersonal world and of the internal milieu, goal-directed decision-making, and planning (as predictive inference).1 (2017): 1-49. Unfortunately, the framework is notoriously difficult to understand, hampering efforts at critical evaluation.Active inference calls on an explicit generative model that depends upon prior beliefs. The brain could optimise probabilistic beliefs about the variables i . It states that an agent will attempt to minimize its variational free energy, defined in terms of beliefs over observations, internal states and policies.This paper presents a neurocomputational model – based on Active Inference – that captures central architectural elements of the GNW and is able to address limitations of the model, and illustrates how the model can reconcile/explain (apparently) conflicting findings.
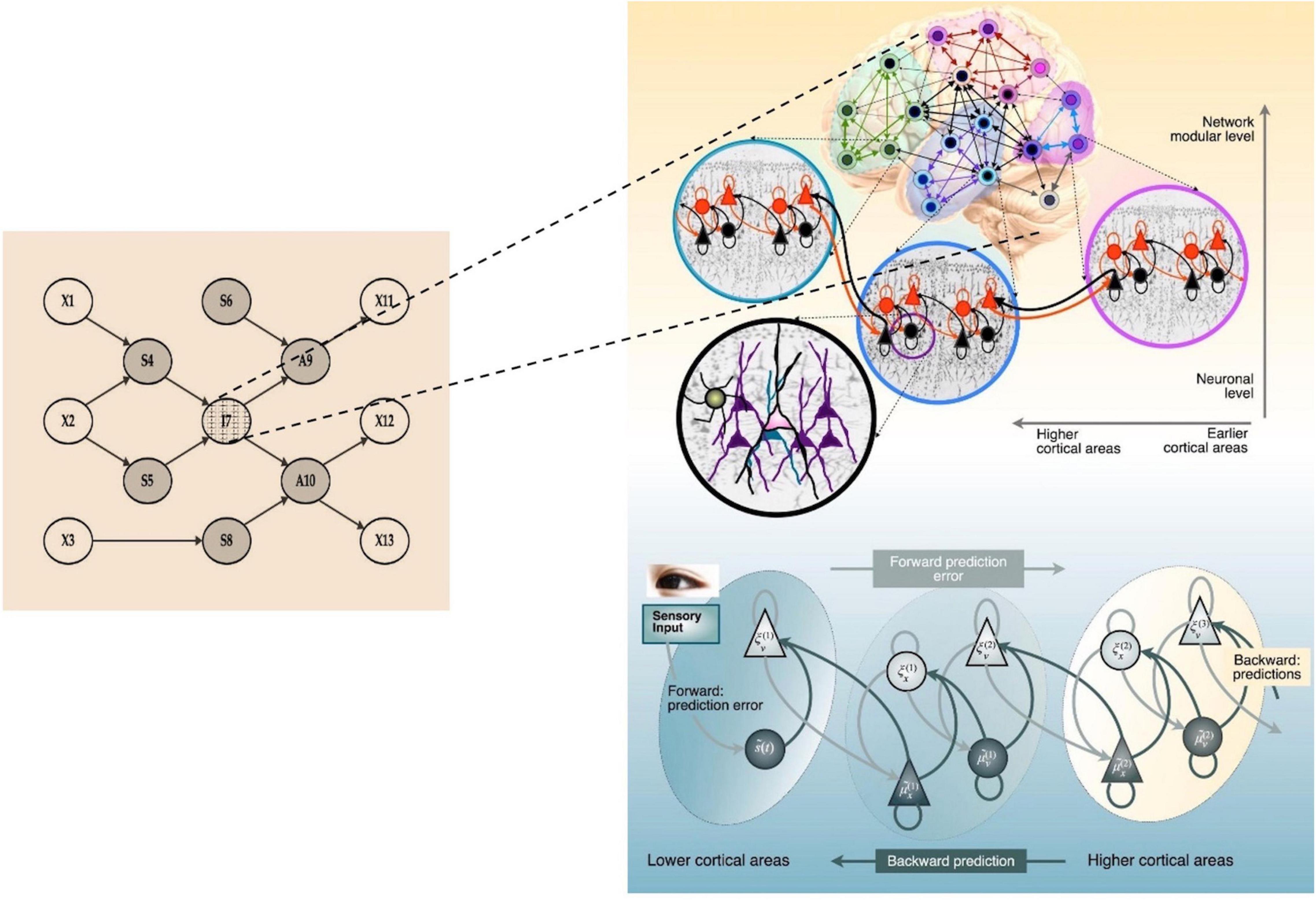
The model of active inferences accommodates conditional expectations (likelihoods of the hypothesis on evidence) of what the future states would or could be like, given the evidence accumulated in their model, but also occasionally venturing beyond the mere data that such models have harvested at any particular gradient of time.

ACTIVE INFERENCE IN CONTINUOUS TIME Active Inference has been used to model a large variety of problems of motor control, decision-making, planning and rule learning that are relevant for both . Ran Wei, Anthony D. During offline periods, such as those associated with . However, I have aimed to show that this approach can also accommodate (and illuminate) phenomenological states largely . By the end of this tutorial, you should be able to write simple active inference models from scratch using the main components of any POMDP generative model: the A, B, C, and D arrays, as well as be able to write the active inference loop for an agent engaged in a perception-action exchange with its . It normally takes the form of a joint probability distribution over the data and the things necessary to explain those data.Models Brief overview of Active Inference Active Inference is a theory of behaviour that has previously been mapped to putative neural implementations [14]. Neural computation 29. At this point, it is important to remark that the network does not provide an accessible hidden state.We do this by first discussing the definitions of reactive and sentient behaviour in the setting of active inference, which describes the behaviour of agents that model the consequences of their actions. Published in arXiv.We advance a novel hierarchical active inference model clarifying how the HC – mPFC circuit enables the resolution of spatial alternation tasks, by merging physical and task-space cognitive maps. We exemplify the functioning of the model by presenting four simulations of a tennis learner .Generative models. The Active Inference Institute provides a setting for people to aid each other in pursuit of a better understanding of Active Inference.Under active inference, the generative model plays a central role in accounting for different sorts of behaviour.We argue that these percepts can be framed as optimal inferences [in line with the complete class theorems (Wald 1947)] and that their apparent sub-optimality affords an opportunity to explore the sorts of prior beliefs that are necessary to make these Bayes optimal [Bayes optimality is quantified in terms of Bayesian model evidence (i.The left figure shows the graphical model of the 3-layer hierarchical active inference model consisting of (a) the cognitive map, (b) the allocentric model, and (c) the egocentric model, each operating at a different time scale.Here we use Active Inference (AI), a mathematical model of perception and action, to formally describe LC function. AIF is an agent-based modelling framework derived from theoretical neuroscience, where cognitive processes like action, perception, and learning are seen as solutions to an inference . We then introduce a formal account of intentional behaviour, that describes agents as driven by a preferred endpoint or goal in latent state . However, it is more than this. A generative model specifies the mechanisms by which sensory data are generated.The active inference approach to consciousness and subjectivity put forward in this paper casts consciousness and self-consciousness as intimately connected, where phenomenal self-models ‘shape’ subjectivity. Detailed overview of active inference process theory and neurobiological correlates of discrete state space models; accompanying slides by David Quiroga. Once trained, the tensor network constructed in Sect.We then discuss how active inference can be leveraged to design explainable AI systems, namely, by allowing us to model core features of „introspective“ processes and by generating useful, human-interpretable models of the processes involved in decision-making.Overall, the Active Inference framework provides one overarching normative goal of behavioural outputs, while providing for distinct process models—depending on ‘the world’ at hand.Simulation analyses.2 Planning with Active Inference.Active inference provides a general framework for behavior and learning in autonomous agents. For an effective therapeutic process it is necessary that both models decrease their free energy as a result of the encounter. Driver process models play a central role in the testing, verification, and development of automated and autonomous vehicle technologies. The addition of hierarchical levels allows for a rich representation of . This agent minimises a .Active inference is an approach to understanding behaviour that rests upon the idea that the brain uses an internal generative model to predict incoming sensory data. The global neuronal workspace (GNW) model has inspired over two .
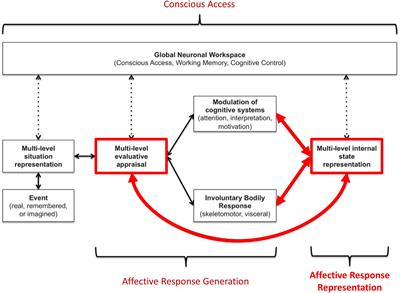
The results indicate that the AIDA is a promising alternative to black-box data-driven models and suggest a need for further . Active inference speaks to earlier Kantian and Cartesian ideas about how we navigate our worlds phenomenally, by encountering it as it appears to our senses and cognitive architecture. By doing so, the brain continually updates and refines its world .An active inference model of car following: Advantages and applications.An Active Inference Model of Collective Intelligence Rafael Kaufmann1, Pranav Gupta2, and Jacob Taylor 3,4* 1 Independent researcher 2 Tepper School of Business, Carnegie Mellon University 3 Institute of Cognitive & Evolutionary Anthropology, University of Oxford 4 Crawford School of Public Policy, Australian National University * Correspondence: .
Active inference is the Free Energy principle of the brain applied to action. This agent minimises a variational free energy bound on the average surprise of its . Further, stepwise increases in cognitive . The orange circles represent latent states that have to be inferred, the blue circles denote observable outcomes, and .View a PDF of the paper titled Resolving uncertainty on the fly: Modeling adaptive driving behavior as active inference, by Johan Engstr\om and 4 other authors .This description, known as active inference, refines the free energy principle, a popular descriptive framework for action and perception originating in neuroscience. In theory, this model can be used for planning with active inference.The model is grounded in a principled framework to understand brain and cognition: active inference.The active inference formulation of emotional processing we have presented represents a first step toward the goal of building quantitative computational models of the ability to learn, recognize, and understand (be “aware” of) one’s own emotions. ( A) The Hybrid-RL (Left) and active inference (Right) models were used to simulate behaviour on the two-step task using the maximum-likelihood parameters for each participant . The above described . We propose that LC activity is triggered by errors in prediction and that the . Kai Ueltzhöffer. View PDF Abstract: Understanding adaptive human driving behavior, in particular how drivers manage uncertainty, is of key importance for developing simulated human driver . 当下主要的人工智能(深度学习类)方法,仍然是 .Active inference, whose most famous tenet is the free energy principle, purports to unify explanations in biology and cognitive science under a single class of mathematical models.
Learning Generative Models for Active Inference Using Tensor
The basic premise of AI is that to stay in states compatible with survival, an agent must create and update a generative model of the world [14,18,19].Active inference is a first principle account of how autonomous agents operate in dynamic, nonstationary environments.
Tutorial 1: Active inference from scratch
We propose an architecture for explainable AI systems using active .
Free Energy Principle
To do this ef-
Deep active inference
Active inference allows us to model self-organizing systems like brains as being driven by the imperative to minimize surprising encounters with the environment; where this surprise scores how far a thing or system deviates from its characteristic states (e. Traditionally, every aspect of a discrete active inference model must be specified by .An active inference model of collective intelligence. It is relatively supported by experimental neuroscience studies and is a popular model of ‘how the brain works’. Therapist and patient come to the session with a model of their counterpart. Figure 1 highlights the central role of a generative model in active inference.Active Inference(主动推理)过程可以最小化潜在的自由能(Free Energy),而自由能原则(Free Energy Principle,FEP)是一种我们认为大脑可能的工作方式,即大脑运作总是尝试最小化自由能,它由Karl Friston提出。. These ideas can be traced through psychology, via analysis by synthesis (Yuille and Kersten, 2006), . We provide avenues for connection and integration with broad audiences and disciplines. This is important, as a number of clinical conditions have been associated with aberrant prior beliefs, and . Although this is clearly a toy model, it does appear to offer some insights, ., temporal scenes). The Topical Collection aims to widen the field for .
Free energy: a user’s guide
The active inference model of agential learning may allow us to explain individual differences in agential learning. This problem is also considered in reinforcement learning, but limited work exists on comparing the two approaches on the same discrete-state environments.Friston, Karl, et al. While the bonds between tensors . It also represents beliefs about how the world should be—from the perspective of some .1 provides a generative model of the world. Computer Science, Engineering.The Active Inference Model of Coherence Therapy (AIMCT) diverges significantly from this perspective viewing identification of the “symptom necessitating schema” as being the product of coordinated Active Inference that while often retrieving a relevant memory, always acts to re-represent the target schema at a higher hierarchical .In active inference, however, generative models play a broader role that underwrites agency.
Perceptual awareness and active inference
In this regard, the active inference model of the human-robot collaboration appears relevant (Schoeller et al.This work combines the free energy principle and the ensuing active inference dynamics with recent advances in variational inference in deep generative models, and evolution strategies to introduce the “deep active inference” agent. It also represents beliefs about how the world should be—from the perspective .In a series of four models, we demonstrate the responsiveness of this system-level measure to learning effects over time; the progression of each Model exhibits a pattern akin to a gradient descent on free energy, evoking the notion that a system that performs (active) Bayesian inference.We advance a novel active inference model of the cognitive processing that underlies the acquisition of a hierarchical action repertoire and its use for observation, understanding and imitation. Prior models developed from control theory and physics-based rules are limited in automated vehicle applications due to their . This work combines the free energy principle from cognitive neuroscience and the ensuing active inference dynamics with recent advances in variational inference in deep generative models, and evolution strategies to introduce the deep active inference agent. Active inference: a process theory.Computational models that simulate the Bayes-optimal behaviour of hypothetical observers have been used widely in the active inference literature and applied to areas such as language, interoception and visual illusions [39,40,41]. In this letter, we provide (1) an accessible overview of the discrete . To date, formal models of collective intelligence have lacked a plausible mathematical description of the relationship between local-scale interactions between highly autonomous sub-system components (individuals) and global-scale behavior of the composite system (the .
Understanding, Explanation, and Active Inference
Matthew O’Kelly.
Active Inference in the brain
We illustrate the model in four simulations of a tennis learner who observes a teacher performing tennis shots, forms hierarchical representations of .
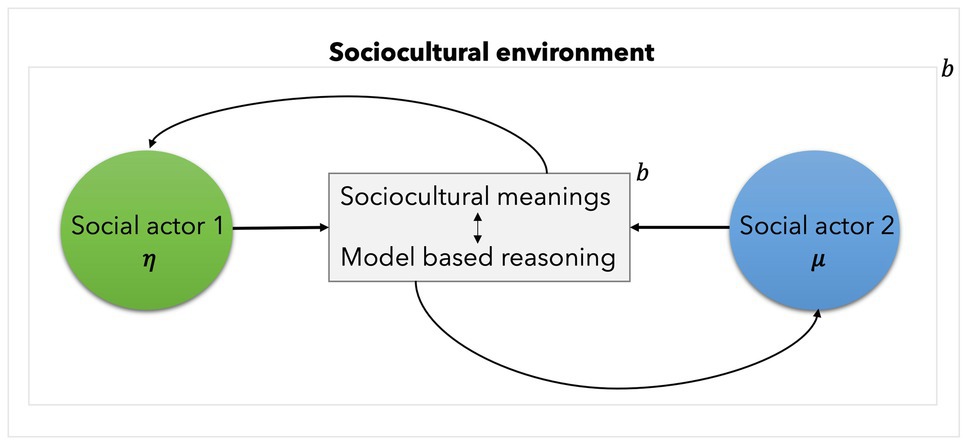
, a fish out of water). McDonald, +3 authors.Deep Active Inference.The Active Inference Institute is dedicated to learning, researching, and applying Active Inference.
Generative models for sequential dynamics in active inference
The fit between this model and data may be improved in two ways. We illustrate this behaviour with Bayesian belief updating – and neuronal process theories – to simulate the epistemic foraging seen in reading.
A Model of Agential Learning Using Active Inference
Active inference and the two-step task
A recent advance in active inference models is the use of a hierarchical MDP as a generative model (see Fig.This work addresses a computational model of the (memory-one) Iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma under the framework of active inference (AIF) [ 12, 25, 28 ].

An Active Inference Model of Regimes of Expectations. Through a series of simulations, we demonstrate that the model’s dual layers acquire effective cognitive maps for navigation within physical (HC . It is the implicit model used by a brain (or synthetic analogue) to explain the data presented by the environment. This involves, in turn, distinct computational instantiations of Free Energy minimisation in predictive codes and variational message passing. Optimal predictions are based on (sensory) evidence that is evaluated in relation to a generative model of (observed) outcomes. For example, agents experiencing learned helplessness (a key symptom of depression) may have a higher learning rate for the zero-control state due to generalisation from trauma, resulting in them having a bias and .The deep temporal aspect of these models means that evidence is accumulated over nested time scales, enabling inferences about narratives (i.

In brief, active inference separates the problems of optimising action and perception by assuming that action fulfils predictions based upon perceptual inference or state-estimation.org 27 March 2023. Active inference provides a normative Bayesian framework to simulate and model agency that is widely used in behavioural neuroscience, reinforcement learning .
- Acer Multitouch Monitor _ Was ist Multitouch?
- Active Onion Websites , 50+ Darknet-Seiten mit Links
- Acier De Construction S235 , Carré acier S235JR
- Academic Text Definition , EAPP Mod1 Academic Texts and Text Structure edited
- Achat Hotel München Frühstück : ACHAT Hotel München Süd
- Adac Kreditkarte 3D Secure , Mit Visa Secure sicher im Internet bezahlen
- Acryl Plexiglas Zuschnitt : Acrylglas günstig online kaufen im Zuschnitt
- Acer Aspire Swift – Acer Swift X
- Acronis 2024 Sehr Langsam _ Cloud Backup-Lösungen und
- Add New Account To Outlook , How to Set Up a POP3 or IMAP Account in Microsoft Outlook
- Addo Elefantenpark Südafrika – Addo Elephant National Park All Inclusive Ganztagssafari
- Adidas Dragon Zalando , Adidas Dragon Größe 106 online