Accumulated Depreciation Formula
Di: Samuel
s = scrap value.Formula Example 1. Step 2 → Divide the Annual Depreciation Under the Straight . This figure shows the total amount that asset has depreciated, up to a fixed and single point. Thus, after five years, accumulated depreciation would total $16,000. Steps: Go to C8 and write down the following formula.The formula to calculate depreciation expense using this method is as follows: The term “double-declining balance” is due to this method depreciating an asset twice as fast as the straight-line method of depreciation.Use the following formula to calculate depreciation under the reducing balance method: Depreciation = Asset book value x Depreciation rate.155) × (150,000) = $ 17,250. AD = (CA -SV) / LA * Y AD = (C A − S V)/LA ∗ Y. In this case, we can determine the remaining depreciable cost as below: Remaining depreciable cost = $32,000 – $10,000 – $2,000 = $20,000.Depreciation Expense Recognition: Accumulated depreciation is a key component in calculating depreciation expense, which is reported on the income statement.The basic formula for straight-line depreciation is: (Asset Purchase Value – Estimated Salvage Value at the End of Useful Life of Asset) / Useful Life of Asset The $4,500 depreciation expense that shows up on each year’s income statement has to be balanced somewhere, due to the nature of double-entry accounting . You only need to familiarize yourself with the SLN Straight-line method, DDB Double-declining balance method, and SYD Sum-of-the-years digits method formulas to compute depreciation. The market value of an asset, on the other hand, depends on supply and demand, where if the demand is high, its value increases, and if the demand is low, its value decreases.Depreciation Expense = (Purchase Price – Residual Value) ÷ Useful Life of Fixed Asset. Depreciation is a common accounting technique used to spread the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life. 230 000 x 20% = 46 000.
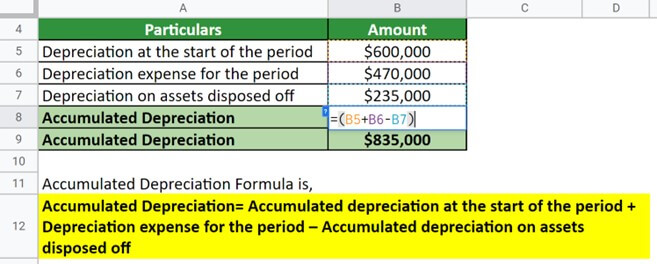
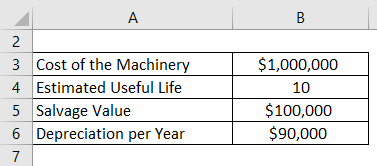
Depreciation is charged according to the above . × (C – AD) Useful Life. The steps to determine the annual depreciation expense under the double declining method are as follows. Depreciation expense is recorded on the income statement as an expense and represents how much of an asset’s value has been . Here are the two main methods you can use when deciding how to calculate accumulated depreciation: Straight-line; Double-declining balance; Straight-line method .Depreciation is an accounting method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life. Purchase Price → The cost of acquiring the fixed asset (PP&E) on the original date of purchase. It is used to show how much of the asset’s value has been used. In 2016, the hotel purchased more crockery items for $2,000.Accumulated depreciation totals depreciation expense since the asset has been in use. Formula: Accumulated Depreciation = Accumulated Depreciation at start of period + Depreciation Expense – Accumulated Depreciation on disposed assets. The formula for calculating accumulated . For our example asset, we determined the units to be 100,000. Explanation: The amount of depreciation for the 3rd year is $5,833. Year 2 depreciation.Depreciation Expense = Book Value at Beginning of Year * Depreciation Rate.Accumulated Depreciation Formula: This component calculates the total depreciation an asset has undergone since acquisition. Here, Then, press ENTER and the cell will calculate the depreciation cost taking into account the formula.Tip: Type F4 on your keyboard when editing a formula to lock cells.To calculate depreciation, follow these steps: Get the original value of the asset ( OV ), the residual value ( RV ), and the lifetime of the asset ( n) in years.How to Calculate Depreciation in DDB Method. However, there are a couple of ways to calculate accumulated depreciation.
What Is Accumulated Depreciation?
While only the accumulated depreciation is deduced from the purchase cost here, the formula can become more complex if there are other additional variables, such as if the company determines that the fixed asset is . Depreciation per Unit = ($50000 – $4000) / 20000 Hours.Depreciation Rate Formula. Journal entry for revised . It aids in tracking the reduction in an asset’s value due to wear, tear, and obsolescence, which is important for accurate financial reporting and tax purposes. The gross amount is equal to the cost of the asset and remains unchanged. Annual depreciation. Its value indicates how much of an asset’s worth has been utilized. The straight-line technique is the most commonly used method, distributing an equal amount of depreciation over the asset’s useful life. LA is the life of the asset (years) Y is the current number of years owned.To calculate the depreciation expense for a given period, the DDB formula uses the following formula: =((cost – accumulated_depreciation) * factor * (1 / life_period)) Here, accumulated_depreciation represents the sum of the depreciation expenses for the previous periods. At the end of the year, the stock of crockery was valued at $2,850. Likewise, the depreciation expense of machine using the declining balance can be calculated as below: Year 1 depreciation = $20,000 x 40% = $8,000.

In the dataset, the rate of depreciation is mentioned. Companies can use depreciation to generate revenue from assets by paying for them over time. Rate of Depreciation = 1–(s c)1 n × 100. Accumulated depreciation. Then, accumulated depreciation of $800,000 is divided by $2,800,000.Depreciation Cost = (0. It follows the formula of: Depreciated Cost = Purchase Price (or cost basis .Depreciated cost is the value of a fixed asset net of all accumulated depreciation that has been recorded against it.Carrying amount is the value of an asset as it appears on the balance sheet and is acquired, after deducting its accumulated depreciation and impairment expenses. Thus, after five years, accumulated . Where AD is the accumulated depreciation (%) CA is the cost of the asset. Solution: Step #1: First, we need to calculate the depreciation rate per unit; the calculation will be as below. If the logging company purchased the .
Learn more about Depreciation and Causes of Depreciation here in detail. Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits: This method assigns a fraction of the asset’s depreciable cost (cost – salvage value) to each accounting period.Straight Line Example. Asset book value is the value of the asset for accounting purposes. Let’s put in the example of the logging truck mentioned above. Businesses depreciate long-term assets for both tax and accounting purposes.Accumulated depreciation = $5,000 + $5,000 = $10,000. Depreciation Rate Calculator: Users can determine the rate at which . Depreciation enables companies to generate . The straight-line technique. As in our example, per unit depreciation can be estimated to be 0. Company A purchases a machine for $100,000 with an estimated salvage value of $20,000 and a useful life of 5 years. Depreciation Expense = (Cost of an Asset – Scrap value at the end) / Useful life of an asset. If you use the DB approach, you’ll need to take the sum of 3 separate DB formulas (years 1, 2, & 3) to get your $27.Accumulated Depreciation Formula and Calculation.This is where accumulated depreciation comes in.
Accumulated Depreciation Formula
Accumulated depreciation is calculated as the sum of the current and prior year’s depreciation expense. For every asset you have in use, there is the “original basis” (how much it initially cost) and then there’s the “accumulated depreciation” (essentially, how much value it has lost, which is now . Each mile will be charged at 38 cents. A simple accumulated depreciation formula would look like this: Accumulated Depreciation Balance = Beginning Period AD + Depreciation Over Period – End Period AD. For the reducing balance method, the following formula is used to calculate the rate of depreciation. The “2” in the formula represents the acceleration of deprecation to twice the straight-line depreciation amount.
Accumulated Depreciation and the Declining Balance Method
Depreciation rate is the percentage decline in the asset’s value. Cost of the asset – Estimated salvage value: $100,000 – $20,000 = $80,000 total depreciable cost.
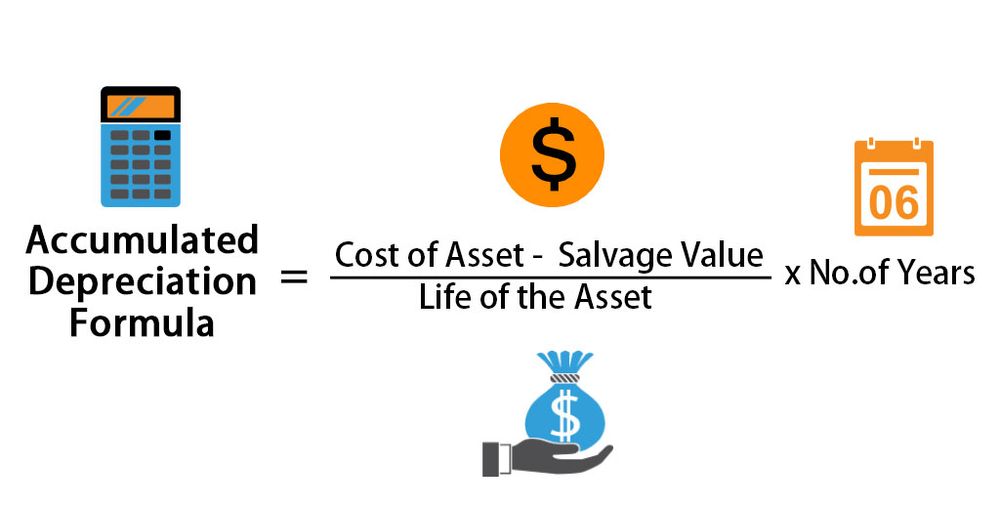
6%, which means the company’s existing fixed assets are only . Annuity Method. (40,000 – 2,000) / 100,000 = .The following formula can be used to calculate the accumulated depreciation. The most widely used method of depreciation Depreciation Depreciation is a systematic allocation method used to account for the costs of any physical or tangible asset throughout its useful life.5 x Straight Line Rate) The Straight Line Rate for a 5 year asset is 1/5 or 20% .In this scenario, the reducing balance method formula in excel is: Depreciation = DB (cost, salvage, life, period, [month]) In this formula, the cost is the initial investment cost, and the life is the estimated time the asset will be in use. c = cost of an asset. This per unit or per activity depreciation charge can then be used against the actual volume of units . So, each year, R46 000 will be brought into account as an expense called depreciation until the vehicle has a zero value.For the straight-line method, the life of an asset is taken and divided with the cost as the following formula. accumulated depreciation = ((original cost – salvage value) / useful life) * years in use. The net book value of the machine in year 2 = $20,000 – $8,000 = $12,000.
Depreciation Rate (Formula, Examples)
Alternatively, a fixed percentage of 20% could be written off each year: R230 000 x 20% = R46 000.
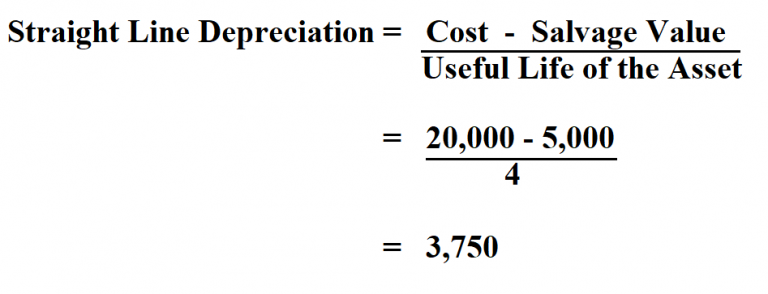
Locking to cell C19 adds the depreciation . read more is $ 4000.
Unit of Production Depreciation
Depreciation Calculator
SC is the salvage value of the asset. In this context, amortization is very similar to depreciation, but it applies to intangible assets, like loans, patents, or trademarks. The straight-line method is the .Accumulated Depreciation to Fixed Assets = $800,000 / ($3,200,000 – $400,000) First, the land value is subtracted from the total fixed assets to reveal depreciable fixed assets of $2,800,000. The straight line depreciation for the machine would be calculated as follows: Cost of the asset: $100,000.It is easy to make a depreciation worksheet in Excel without using complex and conditional formulas. So, we can calculate the depreciation cost using the WDV formula.
What Is the Accumulated Depreciation Formula?
Apply the depreciation formula: annual depreciation expense = (OV − .To calculate accumulated depreciation using the straight-line method, use the formula below. Step 1 → Calculate the Straight Line Depreciation Expense (Purchase Cost – Salvage Value) ÷ Useful Life Assumption.The basic formula for declining-balance depreciation (DBD) expense for a period is as follows: DBD = A ×.
Net Book Value
Formula: Depreciation = Book Value × Rate of Depreciation 100.Straight Line Basis: A straight line basis is a method of computing depreciation and amortization by dividing the difference between an asset’s cost and its expected salvage value by the number of . The period represents the accounting period or the year for which the depreciation is being computed.
Straight Line Depreciation
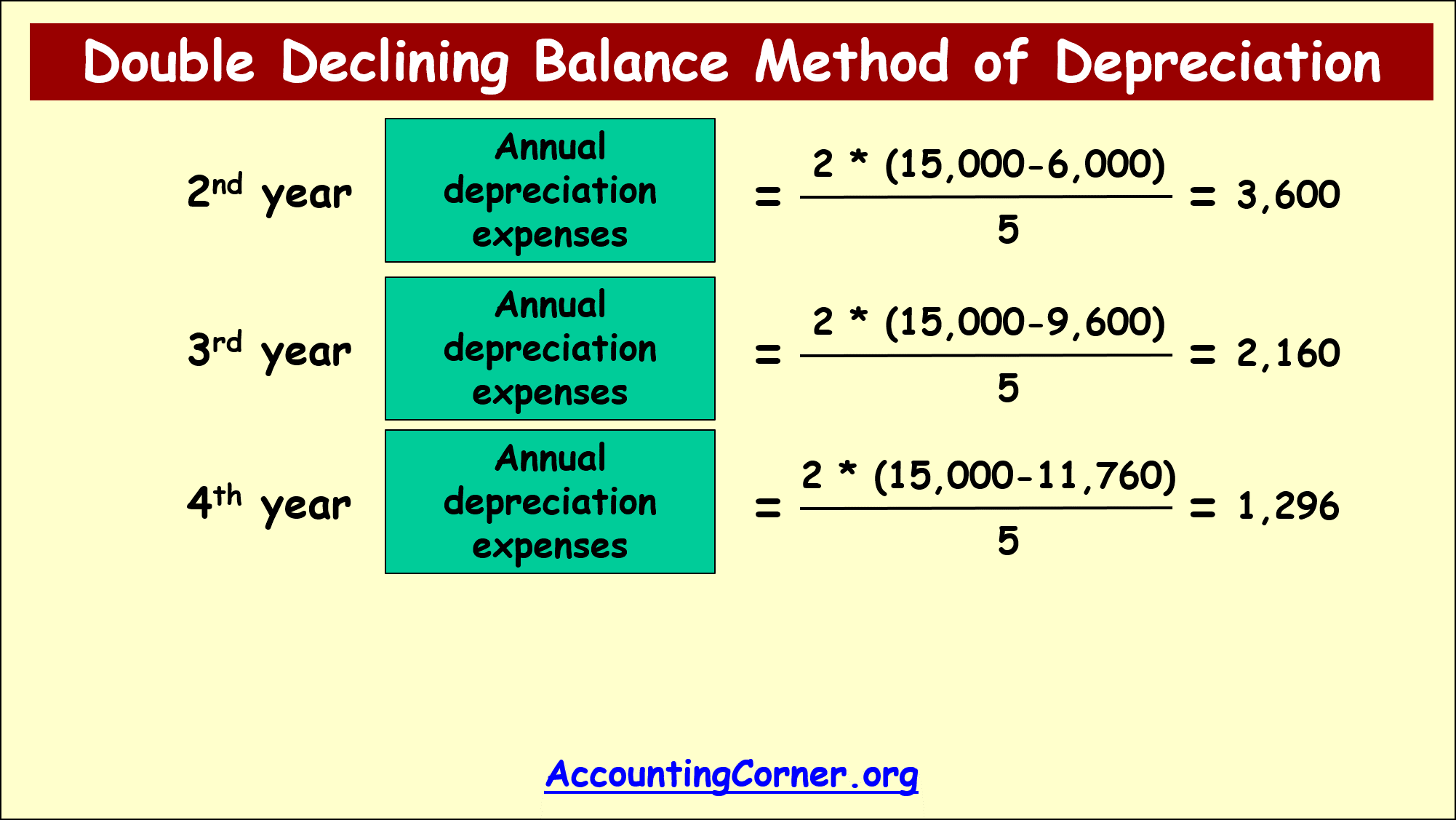
Now let’s move on to the formula and calculation of accumulated depreciation.Because most accounting textbooks use double declining balance as a depreciation method, we’ll use that for our sample asset. The result is 28.Double Declining Balance Depreciation Method: The double declining balance depreciation method is one of two common methods a business uses to account for the expense of a long-lived asset.
The first step is to calculate the factor to be applied to the miles.Accumulated depreciation is the total amount of depreciation expense that has been allocated to an asset since it was put in use.
Double Declining Balance Method (DDB)
The formula is: Depreciation Expense = (Remaining Life / Sum of the Years’ Digits) * Depreciable Cost.
How to Use WDV Method of Depreciation Formula in Excel
Accumulated Depreciation Formula. =SYD(C4,C5,C6,C7) Then, press ENTER to get the output. Where n = useful life. Therefore, we can calculate the revised depreciation as below: Revised depreciation = $20,000 / 2 = $10,000 per year.
Double-Declining Balance (DDB) Depreciation Method Definition With Formula
Sample Calculation of Net Book Value .The number of depreciation changes every year.For example, if a company’s machinery has a 5-year life and is only valued $5000 at the end of that time, the salvage value is $5000. Depreciation Expense Calculation: The calculator aids in estimating the expense associated with asset depreciation, facilitating accurate financial reporting. This applies the dollar $ signs to the cell. The formula is: Annual Accumulated Depreciation = (Asset Value – Salvage Value) / Useful Life in Years.Year 1 depreciation. Accumulated depreciation can be calculated using the straight-line method or an accelerated method. Where: Accumulated Depreciation = Per Year Depreciation x Total Number of Years. In the first year, the net book value equals the cost of the machine. A hotel purchased crockery on 1 January 2015 for $1,500.A chart showing a sample Fixed Asset. We do that using this formula: (Cost – Salvage) / Total Units. A simple example to understand calculation: A .The amount of depreciation reduces every year under this method. ⏩ Steps: Here, select a cell for calculating depreciation and apply the WDV formula. Where DBD is the declining-balance depreciation expense for the period, A is the accelerator, C is the cost and AD is the accumulated depreciation.The formula for calculating NBV is as follows: Net Book Value = Original Asset Cost – Accumulated Depreciation . Under the activity-based depreciation method, it is possible to calculate the deprecation cost on a per-unit basis. Where: Depreciation is the dollar amount lost in value. Useful Life → The estimated number of years in which the fixed asset is assumed to continue providing positive economic utility.
Accumulated Depreciation
Accumulated Depreciation Explained
Accumulated Depreciation in Accounting: How do you calculate it
To consider this fact, Excel has the built-in SYD function to calculate depreciation. On 31 December 2016, it was valued by a chef at $1,250.
Accumulated Depreciation to Fixed Assets Ratio
For tax purposes .The Accumulated Depreciation Calculator is a financial tool used to calculate the total depreciation value of an asset over its useful life.Excel has built-in depreciation functions (DB for declining balance) , but they’re designed to give you the depreciation expense for a particular year, as opposed to a running total.Accumulated Depreciation → The total depreciation recognized to reduce the value of the purchased fixed asset to date.Accumulated depreciation can be calculated in several ways, such as: 1. In this article, we’ll teach you how to make a . By subtracting the accumulated depreciation from the initial cost .There is no standard accumulated depreciation formula. The formula to calculate Double Declining Balance Depreciation is: 2 x Straight Line Rate (for 150% declining balance, the amount is 1. Depreciation is recognized as an operating expense over the useful life of the asset.Accumulated depreciation formula calculates the total reduction in an asset’s value over its useful life. Required: Calculate the amount of depreciation to be charged for .
This recognition aligns with the matching principle, ensuring that the cost of using .R230 000 ÷ 5 = R46 000.
- Acetylen Flüssigkeit : Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetylen
- Acier De Construction S235 , Carré acier S235JR
- Active Inference Model – Active Inference in the brain
- Adac App Fahrschule : ADAC Fahrschul App? (Führerschein, Prüfung, Fahrschule)
- Abstandsflächen Nachbarschützend
- Acer Multitouch Monitor _ Was ist Multitouch?
- Abtretung Grundschuld Muster : Grundbucheintragung
- Acte De Naissance Allemand Étranger
- Acrylmalerei 1960Er Jahre _ Paul Mayén, Stehleuchte, Acryl, Nickel, Metall, USA, 1960er Jahre
- Access Bars Behandlung , Access Bars
- Access Daten Aus Ganzem Monat | Zeitlich flexible Flugsuche: Günstigsten Flug finden
- Adac Gutscheincode : Rabatt für ADAC Mitglieder
- Abwassergebühren Dortmund : Zustands- & Funktionsprüfung der Abwasserleitungen